4.2 Structure of the Nuclear Atom
... (1868–1953) carried out experiments to find the quantity of an electron’s charge. • Using this charge and Thomson’s chargeto-mass ratio of an electron, Millikan calculated an electron’s mass. • Millikan’s values for electron charge and mass are similar to those accepted today. ...
... (1868–1953) carried out experiments to find the quantity of an electron’s charge. • Using this charge and Thomson’s chargeto-mass ratio of an electron, Millikan calculated an electron’s mass. • Millikan’s values for electron charge and mass are similar to those accepted today. ...
4.2 Structure of the Nuclear Atom
... (1868–1953) carried out experiments to find the quantity of an electron’s charge. • Using this charge and Thomson’s chargeto-mass ratio of an electron, Millikan calculated an electron’s mass. • Millikan’s values for electron charge and mass are similar to those accepted today. ...
... (1868–1953) carried out experiments to find the quantity of an electron’s charge. • Using this charge and Thomson’s chargeto-mass ratio of an electron, Millikan calculated an electron’s mass. • Millikan’s values for electron charge and mass are similar to those accepted today. ...
Exam Edge Digital
... Answer (a) (i) 18 electrons (3); (ii) 20 neutrons (3) (d) The principle of mass spectrometry is that charged particles moving in a magnetic field (3) are separated according to the masses (3) of the particles. (i) Mendeleev’s table was arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass (ato ...
... Answer (a) (i) 18 electrons (3); (ii) 20 neutrons (3) (d) The principle of mass spectrometry is that charged particles moving in a magnetic field (3) are separated according to the masses (3) of the particles. (i) Mendeleev’s table was arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass (ato ...
- Catalyst
... The Solubility of Covalent Compounds in Water Polar covalent compounds are very soluble in water. They often have OH groups that can form “hydrogen bonds” with water. Examples are table sugar (C12H22O11), ethanol (C2H5OH), ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) in antifreeze, and methanol (CH3OH). These also are ...
... The Solubility of Covalent Compounds in Water Polar covalent compounds are very soluble in water. They often have OH groups that can form “hydrogen bonds” with water. Examples are table sugar (C12H22O11), ethanol (C2H5OH), ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) in antifreeze, and methanol (CH3OH). These also are ...
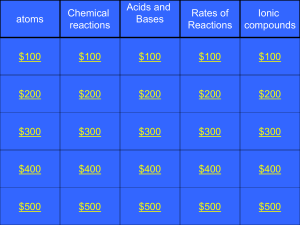
Quiz contsts questions chemistry
... In oxide of an element possesses the formula M2SO3. If the equivalent weight of the metal is 9, then the atomic weight of the metal will be: (a) ...
... In oxide of an element possesses the formula M2SO3. If the equivalent weight of the metal is 9, then the atomic weight of the metal will be: (a) ...
Molecules, Moles and Chemical Equations File
... Step 2: Balancing an equation like this is aided by making some observations. In this case, both carbon and hydrogen appear in only one place on each side of the equation. Our first steps will be to balance these two elements, because there will be no other way to adjust them. Let’s begin with carbo ...
... Step 2: Balancing an equation like this is aided by making some observations. In this case, both carbon and hydrogen appear in only one place on each side of the equation. Our first steps will be to balance these two elements, because there will be no other way to adjust them. Let’s begin with carbo ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry 4.1
... When mixed, a double displacement reaction takes place, forming the soluble compound NaNO3 and the insoluble compound AgCl. In the reaction vessel the Ag+ and Cl ions combine, and a white solid precipitates from the solution. As the solid precipitates, the Na+ and NO3 ions remain in solution. The ...
... When mixed, a double displacement reaction takes place, forming the soluble compound NaNO3 and the insoluble compound AgCl. In the reaction vessel the Ag+ and Cl ions combine, and a white solid precipitates from the solution. As the solid precipitates, the Na+ and NO3 ions remain in solution. The ...
2 - mrs. leinweber`s wiki
... Millions of different chemical compounds exist as a result of different combination of elements. A systematic way of naming these compounds has been developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Compounds contain more than one kind of element chemically bonded together. ...
... Millions of different chemical compounds exist as a result of different combination of elements. A systematic way of naming these compounds has been developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Compounds contain more than one kind of element chemically bonded together. ...
electrochemistry
... rod as (inert) cathode; aqueous NH4Cl paste as electrolyte, and MnO2 powder as the oxidizing agent. Zn|Zn2+,NH4+,NH3(aq)||Mn2O3,MnO2|C(s) Anode reaction: Zn(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e-; Cathodic reaction: 2MnO2(s) + 2NH4+(aq) + 2e- Mn2O3(s) + 2NH3(aq) + H2O(l) Net reaction: Zn(s) + 2MnO2(s) + 2NH4+(aq) n2 ...
... rod as (inert) cathode; aqueous NH4Cl paste as electrolyte, and MnO2 powder as the oxidizing agent. Zn|Zn2+,NH4+,NH3(aq)||Mn2O3,MnO2|C(s) Anode reaction: Zn(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e-; Cathodic reaction: 2MnO2(s) + 2NH4+(aq) + 2e- Mn2O3(s) + 2NH3(aq) + H2O(l) Net reaction: Zn(s) + 2MnO2(s) + 2NH4+(aq) n2 ...
... ν 1695 and 1648 cm−1. 1H NMR spectrum exhibited characteristic set of chemical shifts due to N-substituted piperidine moiety. This spectrum revealed a multiplet signal at δ ~1.65 due to six protons (CH2–CH2–CH2) and two triplets at δ 3.71 and 4.44 due to four protons (CH2–N–CH2). Nevertheless, 13C N ...
chemistry - My Study materials – Kumar
... All matters in the universe exist in three states. There are two ways of classification of matter. 1. According to physical state as solid, liquid or gas. 2. According to its composition as element, compound or mixture. According to this law mass of an isolated system will remain constant over time. ...
... All matters in the universe exist in three states. There are two ways of classification of matter. 1. According to physical state as solid, liquid or gas. 2. According to its composition as element, compound or mixture. According to this law mass of an isolated system will remain constant over time. ...
some basic concepts of chemistry
... Hence, they have a definite volume but no definite shape. In a gas, the particles are far apart and therefore have a much greater freedom of movement. Hence, they possess neither definite volume nor definite shape. (b) Chemical classification : Many of the substances present around you are mixtures. ...
... Hence, they have a definite volume but no definite shape. In a gas, the particles are far apart and therefore have a much greater freedom of movement. Hence, they possess neither definite volume nor definite shape. (b) Chemical classification : Many of the substances present around you are mixtures. ...
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen
... and well organized. Specific answers are preferable to broad, diffuse responses. For calculations, clearly show the method used and the steps involved in arriving at your answers. It is to your advantage to do this, since you may obtain partial credit if you do and you will receive little or no cred ...
... and well organized. Specific answers are preferable to broad, diffuse responses. For calculations, clearly show the method used and the steps involved in arriving at your answers. It is to your advantage to do this, since you may obtain partial credit if you do and you will receive little or no cred ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to Forensic Chemistry
... oxygen (often with applied heat); carbon-containing compounds then produce carbon dioxide and hydrogen-containing compounds then produce water as a result. Neutralization reactions occur when an acid and a base react to form a salt and water. Redox reactions occur when one substance gains electrons ...
... oxygen (often with applied heat); carbon-containing compounds then produce carbon dioxide and hydrogen-containing compounds then produce water as a result. Neutralization reactions occur when an acid and a base react to form a salt and water. Redox reactions occur when one substance gains electrons ...
Homework Chapter 6 - Chemistry
... D) energy available by virtue of an object's position. 2. Thermal energy is A) the energy stored within the structural units of chemical substances. B) the energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules. C) solar energy, i.e. energy that comes from the sun. D) energy available by vi ...
... D) energy available by virtue of an object's position. 2. Thermal energy is A) the energy stored within the structural units of chemical substances. B) the energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules. C) solar energy, i.e. energy that comes from the sun. D) energy available by vi ...
XI CHEMISTRY SAMPLE PAPER 4 Time: Three Hours
... Ans 7: Organic compound is fused with sodium metal to convert N, S, P and halogens present in organic compound to their corresponding sodium salts. (1 mark) ...
... Ans 7: Organic compound is fused with sodium metal to convert N, S, P and halogens present in organic compound to their corresponding sodium salts. (1 mark) ...
File
... us the mole ratio. • It takes 1 mole of ethanol to react with 3 moles of oxygen. This produces 2 moles of carbon dioxide and 3 moles of water. • The mole ratio will act as our conversion ...
... us the mole ratio. • It takes 1 mole of ethanol to react with 3 moles of oxygen. This produces 2 moles of carbon dioxide and 3 moles of water. • The mole ratio will act as our conversion ...
664
... Nitryl chloride may be identified by its mass spectra. The characteristic mass ions are 81, 83, 46, 35, and 37. Alternatively, nitryl chloride may be identified from its physical and chemical properties (See Reactions). The wet analytical method involves treatment with an excess solution of NaOH and ...
... Nitryl chloride may be identified by its mass spectra. The characteristic mass ions are 81, 83, 46, 35, and 37. Alternatively, nitryl chloride may be identified from its physical and chemical properties (See Reactions). The wet analytical method involves treatment with an excess solution of NaOH and ...
Calculations with Chemical Reactions
... Calculations with Chemical Reactions Calculations with chemical reactions require some background knowledge in basic chemistry concepts. Please, see the definitions from chemistry listed below: Atomic mass– the total mass of protons, neutrons and electrons in a single atom. (Note that atomic mass ha ...
... Calculations with Chemical Reactions Calculations with chemical reactions require some background knowledge in basic chemistry concepts. Please, see the definitions from chemistry listed below: Atomic mass– the total mass of protons, neutrons and electrons in a single atom. (Note that atomic mass ha ...
Print this article - Bangladesh Journals Online
... assignable for protons Hd and Ha respectively. The two doublets of doublet at δ 6.5 (JHa-Hb = JHb-Hc = J = 8.0 Hz) and 6.9 (JHb-Hc= JHc-Hd = J = 8.0 Hz) accounts for the Ha and Hd respectively, while the relatively downfield signal at δ 8.5 has been assigned for the imine (=N-H) proton of 2-mercapto ...
... assignable for protons Hd and Ha respectively. The two doublets of doublet at δ 6.5 (JHa-Hb = JHb-Hc = J = 8.0 Hz) and 6.9 (JHb-Hc= JHc-Hd = J = 8.0 Hz) accounts for the Ha and Hd respectively, while the relatively downfield signal at δ 8.5 has been assigned for the imine (=N-H) proton of 2-mercapto ...
Module 1 Predictor Questions
... From the table we see that 1 pg = 10-12 g and 1 mg = 10-3 g. This unit factor converts pg to g. ...
... From the table we see that 1 pg = 10-12 g and 1 mg = 10-3 g. This unit factor converts pg to g. ...