Atomic Structure Note Packet
... _____________ = SI unit for amount of substance A mole simply represents a______________________, much in the same way that a dozen represents a set of twelve. Ex: Just as you can have a dozen cans of soda or a dozen donuts, you can have a mole of stars or a mole of water molecules. So a dozen eggs ...
... _____________ = SI unit for amount of substance A mole simply represents a______________________, much in the same way that a dozen represents a set of twelve. Ex: Just as you can have a dozen cans of soda or a dozen donuts, you can have a mole of stars or a mole of water molecules. So a dozen eggs ...
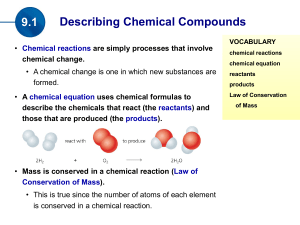
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... which states that molecules must collide in order to react. • Collisions must also be effective, which means that they must have sufficient energy for a reaction to occur. ...
... which states that molecules must collide in order to react. • Collisions must also be effective, which means that they must have sufficient energy for a reaction to occur. ...
Chapter 20 – The Representative Elements
... 3 Zn(s) + 8 HNO3(6 M) 3 Zn(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NO(g) + 4 H2O(l); 4 Zn(s) + 10 HNO3(3 M) 4 Zn(NO3)2(aq) + N2O(g) + 5 H2O(l); Note that, the higher the concentration of the nitric acid used in the reaction, the less the change in the oxidation state of nitrogen. This seems reasonable because in concentr ...
... 3 Zn(s) + 8 HNO3(6 M) 3 Zn(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NO(g) + 4 H2O(l); 4 Zn(s) + 10 HNO3(3 M) 4 Zn(NO3)2(aq) + N2O(g) + 5 H2O(l); Note that, the higher the concentration of the nitric acid used in the reaction, the less the change in the oxidation state of nitrogen. This seems reasonable because in concentr ...
Chap 9 Redox Review Q`s
... A current is passed through molten sodium chloride. Identify the substance formed at each electrode and write an equation to represent the formation of each substance. Determine the mole ratio in which the substances are formed. ...
... A current is passed through molten sodium chloride. Identify the substance formed at each electrode and write an equation to represent the formation of each substance. Determine the mole ratio in which the substances are formed. ...
GROUP 13 ELEMENTS -THE BORON FAMILY -
... Gallium, Ga Gallium has the chemical symbol Ga and atomic number 31. It has the electron configuration [Ar]2s2 2p1 and +3 oxidation state. The melting point is 29.8º C and therefore melts by increasing room temperature by a little. Gallium is important because it forms gallium arsenide (GaAs), whic ...
... Gallium, Ga Gallium has the chemical symbol Ga and atomic number 31. It has the electron configuration [Ar]2s2 2p1 and +3 oxidation state. The melting point is 29.8º C and therefore melts by increasing room temperature by a little. Gallium is important because it forms gallium arsenide (GaAs), whic ...
Lecture 1: RDCH 710 Introduction
... Neutron irradiation of U * Consecutive neutron capture on 235U * 238U(n,2n)237U237Np + b* Alpha decay of 241Am Used at target for 238Pu production by neutron irradiation Reaction with 23 MeV and 30 MeV electrons to produce 236Pu Critical mass is 73 kg 2500 kg in environment from fallout 2 ...
... Neutron irradiation of U * Consecutive neutron capture on 235U * 238U(n,2n)237U237Np + b* Alpha decay of 241Am Used at target for 238Pu production by neutron irradiation Reaction with 23 MeV and 30 MeV electrons to produce 236Pu Critical mass is 73 kg 2500 kg in environment from fallout 2 ...
Chapter 30 - The Chemical Basis of Animal Life
... into simpler units. An element is designated by either a one- or two-letter abbreviation of its Arabic, English, German, or Latin name. For example, O is the symbol for the element oxygen, H stands for hydrogen, and Na is the symbol for sodium (from the Latin, natrium). Currently, scientists recogni ...
... into simpler units. An element is designated by either a one- or two-letter abbreviation of its Arabic, English, German, or Latin name. For example, O is the symbol for the element oxygen, H stands for hydrogen, and Na is the symbol for sodium (from the Latin, natrium). Currently, scientists recogni ...
Matter
... In a system of two or more phases, each phase is a visibly different part which has different properties The variation in properties may be : - different physical properties in each phase - different chemical properties - different physical and chemical properties ...
... In a system of two or more phases, each phase is a visibly different part which has different properties The variation in properties may be : - different physical properties in each phase - different chemical properties - different physical and chemical properties ...
Section 1 The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... • The law of definite proportions states that a compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions, regardless of how the compound is made or how much of the compound is formed. • Because the law of definite proportions holds true for all chemical substances in all reactions, mole ra ...
... • The law of definite proportions states that a compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions, regardless of how the compound is made or how much of the compound is formed. • Because the law of definite proportions holds true for all chemical substances in all reactions, mole ra ...
Chemistry - Schoodoodle
... 3. All atoms of a given element are distinct from all atoms of any other element. The mass, size, and chemical properties of the atoms of one element are different from the mass, size, and chemical properties of the atoms of any other element. 4. Chemical compounds form when atoms combine in whole-n ...
... 3. All atoms of a given element are distinct from all atoms of any other element. The mass, size, and chemical properties of the atoms of one element are different from the mass, size, and chemical properties of the atoms of any other element. 4. Chemical compounds form when atoms combine in whole-n ...
Part I - American Chemical Society
... (C) Metallic K is formed at one electrode and O2 and H+ are formed at the other. (D) Metallic K is produced at one electrode and elemental F2 is produced at the other. 42. A CuSO4 solution is electrolyzed for 20. minutes with a current of 2.0 ampere. What is the maximum mass of copper that could be ...
... (C) Metallic K is formed at one electrode and O2 and H+ are formed at the other. (D) Metallic K is produced at one electrode and elemental F2 is produced at the other. 42. A CuSO4 solution is electrolyzed for 20. minutes with a current of 2.0 ampere. What is the maximum mass of copper that could be ...
Chem152
... is the empirical formula of the product? A) VO B) V2O3 C) V2O5 D) V3O2 E) V5O2 48. Fructose is a sugar found in fruit and honey. Calculate the empirical formula for fructose given its percent composition: 40.00% C, 6.72% H, and 53.29% O. A) CHO B) CH2O C) CHO2 D) C3H6O3 E) C6HO8 49. What is the mole ...
... is the empirical formula of the product? A) VO B) V2O3 C) V2O5 D) V3O2 E) V5O2 48. Fructose is a sugar found in fruit and honey. Calculate the empirical formula for fructose given its percent composition: 40.00% C, 6.72% H, and 53.29% O. A) CHO B) CH2O C) CHO2 D) C3H6O3 E) C6HO8 49. What is the mole ...
Chapter1011
... • Write the MO diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and sketch the bonding and antibonding MO’s. [note: H 1s energy = -13 eV, Cl 3s energy = -25 eV, Cl 3p energy = -14 ...
... • Write the MO diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and sketch the bonding and antibonding MO’s. [note: H 1s energy = -13 eV, Cl 3s energy = -25 eV, Cl 3p energy = -14 ...
File
... convergence of energy levels. The higher the energy the smaller the difference in energy between successive energy levels. This means the lines in a spectrum will converge The limit of this convergence indicates the energy required to completely remove the electron from the atom. For example in the ...
... convergence of energy levels. The higher the energy the smaller the difference in energy between successive energy levels. This means the lines in a spectrum will converge The limit of this convergence indicates the energy required to completely remove the electron from the atom. For example in the ...
VCAA Study Design - Chemistry Education Association
... • (Chemical sciences) The atomic structure and properties of elements are used to organise them in the Periodic Table • (Chemical sciences) Different types of chemical reactions are used to produce a range of products and can occur at different rates • (Earth sciences) Global systems, including the ...
... • (Chemical sciences) The atomic structure and properties of elements are used to organise them in the Periodic Table • (Chemical sciences) Different types of chemical reactions are used to produce a range of products and can occur at different rates • (Earth sciences) Global systems, including the ...
Isotopes of Hydrogen
... SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 1 Explain what isotopes are. Isotopes are atoms of the same elements that have different masses. The isotopes of a particular element all have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 2 Define atomic number and mass numbe ...
... SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 1 Explain what isotopes are. Isotopes are atoms of the same elements that have different masses. The isotopes of a particular element all have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 2 Define atomic number and mass numbe ...
AP Semestar Exam REVIEW
... a. takes a proton from an Arrhenius acid. b. is reduced in a chemical reaction. c. gains electrons in a chemical reaction. d. loses electrons in a chemical reaction. e. gives a proton to an Arrhenius base. ____ 26. Assign oxidation numbers to each atom in calcium perchlorate, Ca(ClO4)2. a. Ca = 0; C ...
... a. takes a proton from an Arrhenius acid. b. is reduced in a chemical reaction. c. gains electrons in a chemical reaction. d. loses electrons in a chemical reaction. e. gives a proton to an Arrhenius base. ____ 26. Assign oxidation numbers to each atom in calcium perchlorate, Ca(ClO4)2. a. Ca = 0; C ...
Thermodynamics
... 6. What is internal energy? 7. How is enthalpy related to internal energy? 8. What is an exothermic reaction? Give an example. 9. What is an endothermic reaction? Give an example. 10. Define a thermochemical equation. 11. Write the thermochemical equation for the combustion of carbon. 12. The value ...
... 6. What is internal energy? 7. How is enthalpy related to internal energy? 8. What is an exothermic reaction? Give an example. 9. What is an endothermic reaction? Give an example. 10. Define a thermochemical equation. 11. Write the thermochemical equation for the combustion of carbon. 12. The value ...
The Building Block of matter What is an atom?
... • Atom has two parts. At the center, there is ______1____charge due to____2_____ which have ____3______ charge. Intense mass at center is due to ____4_______ and _____5____ which are neutral. _____6__ and ___7______ have the same __8______. Negatively charged particles are called ___9_______ and t ...
... • Atom has two parts. At the center, there is ______1____charge due to____2_____ which have ____3______ charge. Intense mass at center is due to ____4_______ and _____5____ which are neutral. _____6__ and ___7______ have the same __8______. Negatively charged particles are called ___9_______ and t ...
2018 Specimen Paper 2 - Cambridge International Examinations
... The volume of hydrogen given off in the reaction is measured over time. The graph shows the results of two experiments, R and S. ...
... The volume of hydrogen given off in the reaction is measured over time. The graph shows the results of two experiments, R and S. ...
CHEM102 Chemistry II Spring 10-11 Mid
... 2) The balanced equation for the reaction occurring when iron(III) oxide, a solid, is reduced with pure carbon to produce carbon dioxide and molten iron is 2) C A) 2 FeO3 + 3 C (s) → 2 Fe (l) + 3 CO2 (g). B) 2 FeO + C (s) →? 2 Fe (l) + CO2 (g). C) 2 Fe2O3 + 3 C (s) → 4 Fe (l) + 3 CO2 (g). D) 4 Fe2O3 ...
... 2) The balanced equation for the reaction occurring when iron(III) oxide, a solid, is reduced with pure carbon to produce carbon dioxide and molten iron is 2) C A) 2 FeO3 + 3 C (s) → 2 Fe (l) + 3 CO2 (g). B) 2 FeO + C (s) →? 2 Fe (l) + CO2 (g). C) 2 Fe2O3 + 3 C (s) → 4 Fe (l) + 3 CO2 (g). D) 4 Fe2O3 ...
quantum - kurtniedenzu
... form: use the last noble gas to indicate filled shells. Find the last noble gas before the element under consideration. Start the electron configuration with the symbol for this noble gas element and just tack on the extra electrons: ...
... form: use the last noble gas to indicate filled shells. Find the last noble gas before the element under consideration. Start the electron configuration with the symbol for this noble gas element and just tack on the extra electrons: ...
atom
... • Negatively Charged Particles In 1909, Ernest Rutherford aimed a beam of small, positively charged particles at a thin sheet of gold foil. The next slide ...
... • Negatively Charged Particles In 1909, Ernest Rutherford aimed a beam of small, positively charged particles at a thin sheet of gold foil. The next slide ...
AS Chemistry - Crawshaw Academy
... be comfortable with the basic Chemistry from the GCSE course, most significantly: ‘Bonding and Structure’, ‘Periodicity’, ‘Chemical Formulae’, Chemistry Calculations’ and ‘Balancing Equations’. In order for you to settle into the course quickly it is essential that you do some background work on the ...
... be comfortable with the basic Chemistry from the GCSE course, most significantly: ‘Bonding and Structure’, ‘Periodicity’, ‘Chemical Formulae’, Chemistry Calculations’ and ‘Balancing Equations’. In order for you to settle into the course quickly it is essential that you do some background work on the ...