The Cubic Atomic Model
... that does make mechanical sense, we could start with just a proton and an electron. We could also make the assumption that the proton and electron have a definite size and possesses a non-zero radius. Objects we see in the world have a definite size, so it is not unreasonable to assume that protons ...
... that does make mechanical sense, we could start with just a proton and an electron. We could also make the assumption that the proton and electron have a definite size and possesses a non-zero radius. Objects we see in the world have a definite size, so it is not unreasonable to assume that protons ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS
... kg. Later experiments by Rutherford determined that at the center of an atom is a positively charged, compact, heavy nucleus. The charge on the atomic nucleus is +Ze (Z is the atomic number of the atom). The fundamental unit of positive charge in the nucleus is the proton. ♦ Chemical identity of an ...
... kg. Later experiments by Rutherford determined that at the center of an atom is a positively charged, compact, heavy nucleus. The charge on the atomic nucleus is +Ze (Z is the atomic number of the atom). The fundamental unit of positive charge in the nucleus is the proton. ♦ Chemical identity of an ...
Chemical Formulas and Composition Stoichiometry
... • Law of Definite Proportions – different pure samples of a compound always contain the same elements in the same proportion by mass – _______ of atoms can also affect the properties of compounds even if they have the same chemical formula. Demo: John Cullen’s demonstration ...
... • Law of Definite Proportions – different pure samples of a compound always contain the same elements in the same proportion by mass – _______ of atoms can also affect the properties of compounds even if they have the same chemical formula. Demo: John Cullen’s demonstration ...
Redox
... loses all of its valence electrons. When this occurs it goes from a neutral atom (0 charge) to a cation with a positive charge of: ...
... loses all of its valence electrons. When this occurs it goes from a neutral atom (0 charge) to a cation with a positive charge of: ...
Chapter 18: Chemical Thermodynamics
... Hf is the heat of _________________. Formation reactions have - _____________ product - produce a __________ mole of that product - use only ____________ as reactants in their standard states. Sign of H (__) Rxn is exothermic, gives off heat, heat is a product. (__) Rxn is endothermic, abso ...
... Hf is the heat of _________________. Formation reactions have - _____________ product - produce a __________ mole of that product - use only ____________ as reactants in their standard states. Sign of H (__) Rxn is exothermic, gives off heat, heat is a product. (__) Rxn is endothermic, abso ...
5073 Chemistry IGCSE ordinary level for 2016
... Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. This simple model could explain the millions of different materials around us. Differences between atoms give eleme ...
... Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. This simple model could explain the millions of different materials around us. Differences between atoms give eleme ...
How Good Is the Quantum Mechanical Explanation of the Periodic
... achieving a full-shell configuration, at atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 36, 54, and so forth. This is a separate question from the closing of the shells. For example, if the shells were to fill sequentially, Pauli’s scheme would predict that the second period should end with element number 28 or nickel, ...
... achieving a full-shell configuration, at atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 36, 54, and so forth. This is a separate question from the closing of the shells. For example, if the shells were to fill sequentially, Pauli’s scheme would predict that the second period should end with element number 28 or nickel, ...
Type of Bonding
... • only metals atoms are involved • e- are completely delocalized and mobile throughout entire material • non-directional • coulombic in origin, occurs between oppositely charged species • electron transfer from one atom to another • force between an ion and a dipole or two dipoles where the (+) char ...
... • only metals atoms are involved • e- are completely delocalized and mobile throughout entire material • non-directional • coulombic in origin, occurs between oppositely charged species • electron transfer from one atom to another • force between an ion and a dipole or two dipoles where the (+) char ...
The mole
... elements combined in a compound, with subscripts showing the smallest whole-number mole ratio of the different atoms in the compound. The following steps are used to determine the empirical formula: First convert the percentage composition to a mass composition. If a compound is 78% B and 22% H, w ...
... elements combined in a compound, with subscripts showing the smallest whole-number mole ratio of the different atoms in the compound. The following steps are used to determine the empirical formula: First convert the percentage composition to a mass composition. If a compound is 78% B and 22% H, w ...
Material presented
... • Obtain the total number of electrons in the atom from the atomic number • Every electron has a place to stay • Electrons in atoms occupy the lowest energy orbitals that are available – 1s first • Each principal energy level, n contains only n sublevels • Each sublevel is composed of orbitals • No ...
... • Obtain the total number of electrons in the atom from the atomic number • Every electron has a place to stay • Electrons in atoms occupy the lowest energy orbitals that are available – 1s first • Each principal energy level, n contains only n sublevels • Each sublevel is composed of orbitals • No ...
Complete ionic equation
... -When other atoms are by themselves they don’t have any subscripts, for example iron is just Fe ...
... -When other atoms are by themselves they don’t have any subscripts, for example iron is just Fe ...
LN_atoms_etc
... Matter consists of individual atoms. All atoms of a given chemical element are identical. Different chemical elements have differing atoms of different mass. Atoms are indestructible – they retain their identity in reactions. Compounds are formed from a combination of elements in small whole number ...
... Matter consists of individual atoms. All atoms of a given chemical element are identical. Different chemical elements have differing atoms of different mass. Atoms are indestructible – they retain their identity in reactions. Compounds are formed from a combination of elements in small whole number ...
Redox Reactions C12-1-10
... hence, an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent. This makes sense since as one reactant is losing electrons (being oxidized), the other is gaining electrons (being reduced) Oxidation numbers can be helpful in determining whether a reaction is redox or non-redox. When a change in oxidation number occu ...
... hence, an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent. This makes sense since as one reactant is losing electrons (being oxidized), the other is gaining electrons (being reduced) Oxidation numbers can be helpful in determining whether a reaction is redox or non-redox. When a change in oxidation number occu ...
Name: Northwest Vista College Chem 1311
... 42. (6 pts) During a titration the following data were obtained. A 10. mL portion of an unknown monoprotic acid solution was titrated with 1.0 M NaOH; 40. mL of the base were required to neutralize the sample. What is the molarity of the acid solution? Answer: This is stoichiometry of an acid base r ...
... 42. (6 pts) During a titration the following data were obtained. A 10. mL portion of an unknown monoprotic acid solution was titrated with 1.0 M NaOH; 40. mL of the base were required to neutralize the sample. What is the molarity of the acid solution? Answer: This is stoichiometry of an acid base r ...
Introductory Chemistry, 2nd Edition Nivaldo Tro - Tutor
... HX dissolves in water to form acids Tro's Introductory Chemistry, Chapter 4 ...
... HX dissolves in water to form acids Tro's Introductory Chemistry, Chapter 4 ...
Test-tube Reactions - University of Manitoba
... hence, an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent. This makes sense since as one reactant is losing electrons (being oxidized), the other is gaining electrons (being reduced) Oxidation numbers can be helpful in determining whether a reaction is redox or non-redox. When a change in oxidation number occu ...
... hence, an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent. This makes sense since as one reactant is losing electrons (being oxidized), the other is gaining electrons (being reduced) Oxidation numbers can be helpful in determining whether a reaction is redox or non-redox. When a change in oxidation number occu ...
Basic chemistry - Ross University
... flow from the hot body to the cold, until both have the same temperature. This is an example for a general principle called the second law of thermodynamics: The direction of a reaction is the one where the entropy (disorder) of the universe is maximized, that is ∆S ≥ 0. Note: The second law of ther ...
... flow from the hot body to the cold, until both have the same temperature. This is an example for a general principle called the second law of thermodynamics: The direction of a reaction is the one where the entropy (disorder) of the universe is maximized, that is ∆S ≥ 0. Note: The second law of ther ...
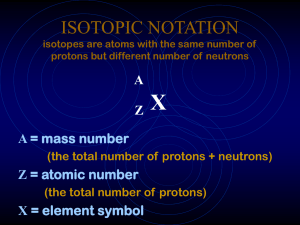
ISOTOPIC NOTATION isotopes are atoms with the same number
... • Generally the formula used is: % X + % Y + % Z… = atomic mass. An instrument called the mass spectrometer is generally used to determine the percentages and individual masses of each isotope. ...
... • Generally the formula used is: % X + % Y + % Z… = atomic mass. An instrument called the mass spectrometer is generally used to determine the percentages and individual masses of each isotope. ...
1 Q. If ΔrH is positive, what can you say about the reaction? 2 Q If
... 10 Q. In terms of reactants and products, what happens in a reaction which is in dynamic equilibrium? ...
... 10 Q. In terms of reactants and products, what happens in a reaction which is in dynamic equilibrium? ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... develop his model, Bohr used the concept of forces of attraction between positive and negative charges. This method allowed him to calculate the radius of the electron shells around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. Schrödinger, on the other hand, used the energy of electrons to calculate the shape of ...
... develop his model, Bohr used the concept of forces of attraction between positive and negative charges. This method allowed him to calculate the radius of the electron shells around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. Schrödinger, on the other hand, used the energy of electrons to calculate the shape of ...
Chapter 2 Elements and Compounds 2.1 The Structure of the Atom
... Elements in the same group in the periodic table have the same number of electrons in the highest energy level, called the valence electrons. Atoms with the same number of valence electrons have similar chemical properties. Similarities or trends in physical properties can also be related to the arr ...
... Elements in the same group in the periodic table have the same number of electrons in the highest energy level, called the valence electrons. Atoms with the same number of valence electrons have similar chemical properties. Similarities or trends in physical properties can also be related to the arr ...