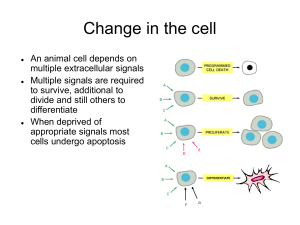
Types of signals and types of receptors and which occur in Thyroid
... Negative feedback loop: What is it and why is it important? ...
... Negative feedback loop: What is it and why is it important? ...
signal molecule
... (e.g. estrogen, vitamin D, thyroid hormone, retinoic acid) and bind to intracellular receptors The hormone-receptor complex has an exposed DNA binding site and can activate transcription directly (or, more typically as a homo- or hetero-dimer) This usually initiates a cascade of transcription events ...
... (e.g. estrogen, vitamin D, thyroid hormone, retinoic acid) and bind to intracellular receptors The hormone-receptor complex has an exposed DNA binding site and can activate transcription directly (or, more typically as a homo- or hetero-dimer) This usually initiates a cascade of transcription events ...
Robertson-1
... inactive receptor becomes a different complex once the inverse agonist binds. Therefore, there are now fewer inactive receptors present. 5. To compensate for the lack of inactive receptors, the active receptors change conformation to become inactive. This occurs in order to ...
... inactive receptor becomes a different complex once the inverse agonist binds. Therefore, there are now fewer inactive receptors present. 5. To compensate for the lack of inactive receptors, the active receptors change conformation to become inactive. This occurs in order to ...
Chapter 5 Chemical Messengers
... • Signal transduction is the process of producing a response afer a messenger binds to a receptor in the target • Receptor Properties o Specificity: One messenger may bind to many receptor types o One target may have many types of receptors o The number of receptors per cell varies and is dynamic • ...
... • Signal transduction is the process of producing a response afer a messenger binds to a receptor in the target • Receptor Properties o Specificity: One messenger may bind to many receptor types o One target may have many types of receptors o The number of receptors per cell varies and is dynamic • ...
ap® biology 2015 scoring guidelines
... Smell perception in mammals involves the interactions of airborne odorant molecules from the environment with receptor proteins on the olfactory neurons in the nasal cavity. The binding of odorant molecules to the receptor proteins triggers action potentials in the olfactory neurons and results in t ...
... Smell perception in mammals involves the interactions of airborne odorant molecules from the environment with receptor proteins on the olfactory neurons in the nasal cavity. The binding of odorant molecules to the receptor proteins triggers action potentials in the olfactory neurons and results in t ...
Cell Signaling - Erlenbeck`s Science Room
... Ligand binds to receptor which activates a relay molecule. This attracts an inactive protein kinase. To make it active, ATP must give a phosphate to the protein which activates it (changes shape). This bumps into another protein kinase.. Add a phosphate to activate it.. Sends message along until it ...
... Ligand binds to receptor which activates a relay molecule. This attracts an inactive protein kinase. To make it active, ATP must give a phosphate to the protein which activates it (changes shape). This bumps into another protein kinase.. Add a phosphate to activate it.. Sends message along until it ...
Neurotrophin Signaling
... death in numerous cells, including injured neurons, but promotes migration, growth and survival in other cells. In the next development (2008), NGF was found to exist in both unprocessed ('pro') and mature forms. On some cells the mature NGF preferentially activates TrkA, whereas proNGF only activat ...
... death in numerous cells, including injured neurons, but promotes migration, growth and survival in other cells. In the next development (2008), NGF was found to exist in both unprocessed ('pro') and mature forms. On some cells the mature NGF preferentially activates TrkA, whereas proNGF only activat ...
Brain and drugs
... longer → more inhibitory signals alcohol causes, that GABA binds more frequently → increases the inhibitory effect of GABA , more impulses ...
... longer → more inhibitory signals alcohol causes, that GABA binds more frequently → increases the inhibitory effect of GABA , more impulses ...
Types of synaptic transmission
... AMPA- amino methyl propionic acid –gated channels found in most excitatory synapses in brain.GluR1-GluR4 NMDA-N- methyl D aspartate-gated channels .they allow entry of ca++ and have slower kinetics because Mg++ blocks the NMDA receptors and when larger depolarization occur Mg++ detaches and opens ch ...
... AMPA- amino methyl propionic acid –gated channels found in most excitatory synapses in brain.GluR1-GluR4 NMDA-N- methyl D aspartate-gated channels .they allow entry of ca++ and have slower kinetics because Mg++ blocks the NMDA receptors and when larger depolarization occur Mg++ detaches and opens ch ...
邵吉民_Signaling_and_diseases
... Activates IR -subunit PTK activity -subunit phosphorylates Tyr residues on cytoplasmic domains as well as downstream substrates (IRS) ...
... Activates IR -subunit PTK activity -subunit phosphorylates Tyr residues on cytoplasmic domains as well as downstream substrates (IRS) ...
Arrestin - Psychiatry Training
... •Review aspects of chemical transmission and intracellular signalling in the brain •Role of neurotransmitter/signal transduction abnormalities in selected neurological/psychiatric disorders –Rational pharmacology for nervous system disorders –Prediction of side-effect profile ...
... •Review aspects of chemical transmission and intracellular signalling in the brain •Role of neurotransmitter/signal transduction abnormalities in selected neurological/psychiatric disorders –Rational pharmacology for nervous system disorders –Prediction of side-effect profile ...
Student notes
... o How G protein-coupled receptors, receptor tyrosine kinases, ligand-gated ion channels, and intracellular receptors receive cell signals and start transduction o How a cell signal is amplified by a phosphorylation cascade, via second messengers (such as cAMP or Ca 2+ ions) and protein kinases. o Ho ...
... o How G protein-coupled receptors, receptor tyrosine kinases, ligand-gated ion channels, and intracellular receptors receive cell signals and start transduction o How a cell signal is amplified by a phosphorylation cascade, via second messengers (such as cAMP or Ca 2+ ions) and protein kinases. o Ho ...
Endocrinology 2
... cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA). PKA is a tetramer, consisting of two regulatory subunits (R) and two catalytic subunits (C). In the absence of cAMP, R2C2 is inactive. The binding of cAMP to the R chains releases the C chains from the R2 complex, which are then catalytically active. Acti ...
... cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA). PKA is a tetramer, consisting of two regulatory subunits (R) and two catalytic subunits (C). In the absence of cAMP, R2C2 is inactive. The binding of cAMP to the R chains releases the C chains from the R2 complex, which are then catalytically active. Acti ...
Diabetes & The Endocannabinoid System: Prospects For
... – Yet again, also activates the PLCγ-PKC pathway, and IP3 mediated intracellular Ca2+ release, like the CB receptors – How then, can cannabinoids be beneficial? ...
... – Yet again, also activates the PLCγ-PKC pathway, and IP3 mediated intracellular Ca2+ release, like the CB receptors – How then, can cannabinoids be beneficial? ...
Slide ()
... Mechanism of thyroid hormone receptor action. The thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) form heterodimers that bind specifically to thyroid hormone response elements (TRE) in the promoter regions of target genes. In the absence of hormone, TR binds co-repressor (CoR) proteins t ...
... Mechanism of thyroid hormone receptor action. The thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) form heterodimers that bind specifically to thyroid hormone response elements (TRE) in the promoter regions of target genes. In the absence of hormone, TR binds co-repressor (CoR) proteins t ...
Cell signalling
... • receptors that activate G proteins which in turn act upon effector proteins, either ion channels or enzymes, in the plasma membrane. ...
... • receptors that activate G proteins which in turn act upon effector proteins, either ion channels or enzymes, in the plasma membrane. ...
JAK/STAT signalling • Binding of cytokines (small protein ligands) to
... latent transcription factors, always present in the cytoplasm, ready to be activated by JAK. ...
... latent transcription factors, always present in the cytoplasm, ready to be activated by JAK. ...
Anti-CCR4 antibody ab83250 Product datasheet 1 Image
... Use a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Predicted molecular weight: 41 kDa. Good results were obtained when blocked with 5% non-fat dry milk in 0.05% PBS-T. ...
... Use a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Predicted molecular weight: 41 kDa. Good results were obtained when blocked with 5% non-fat dry milk in 0.05% PBS-T. ...
Mechanisms by which chemical messengers control cells
... “consensus sequence” – a particular pattern of amino-acids recognised by the enzyme !!! ...
... “consensus sequence” – a particular pattern of amino-acids recognised by the enzyme !!! ...
Allosteric Function(s) of Proteins
... academia. Specifically, ideas from molecular dynamics have reshaped receptor theory from the rigid single-active state concepts prevalent historically into a modern view of dynamic protein ensembles of multiple receptor active states. Second, the technology of pharmacological assays has exploded to ...
... academia. Specifically, ideas from molecular dynamics have reshaped receptor theory from the rigid single-active state concepts prevalent historically into a modern view of dynamic protein ensembles of multiple receptor active states. Second, the technology of pharmacological assays has exploded to ...
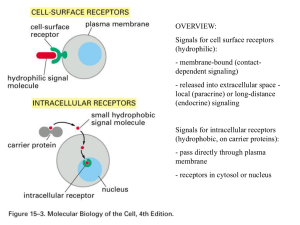
No Slide Title
... - membrane-bound (contactdependent signaling) - released into extracellular space local (paracrine) or long-distance (endocrine) signaling Signals for intracellular receptors (hydrophobic, on carrier proteins): - pass directly through plasma membrane - receptors in cytosol or nucleus ...
... - membrane-bound (contactdependent signaling) - released into extracellular space local (paracrine) or long-distance (endocrine) signaling Signals for intracellular receptors (hydrophobic, on carrier proteins): - pass directly through plasma membrane - receptors in cytosol or nucleus ...
Document
... binding to and transducing its signal to a trimeric G protein •G protein has 3 subunits: a, b and g. Ligand-bound receptor interacts with G protein, causing conformational change. Ga subunit exchanges GDP for GTP and dissociates from Gbg. Both a and b/g can be active signaling components. •GTP-bound ...
... binding to and transducing its signal to a trimeric G protein •G protein has 3 subunits: a, b and g. Ligand-bound receptor interacts with G protein, causing conformational change. Ga subunit exchanges GDP for GTP and dissociates from Gbg. Both a and b/g can be active signaling components. •GTP-bound ...