G protein-coupled receptor
... Receptor Types There are 3 subclasses of membrane receptors: 1. channel linked receptors – ion channel that opens in response to a ligand 2. enzymatic receptors – receptor is an enzyme that is activated by the ligand 3. G protein-coupled receptor – a Gprotein (bound to GTP) assists in transmitting ...
... Receptor Types There are 3 subclasses of membrane receptors: 1. channel linked receptors – ion channel that opens in response to a ligand 2. enzymatic receptors – receptor is an enzyme that is activated by the ligand 3. G protein-coupled receptor – a Gprotein (bound to GTP) assists in transmitting ...
No Slide Title
... (SMRT)-mSin3a-histone deacetylase-1 (HDAC-1) complex associates with the nuclear retinoic acid receptor (RAR)-retinoid X receptor (RXR) heterodimeric complex. The HDAC activity of the complex maintains the tight association between deacetylated histones and chromatin that results in repressed gene t ...
... (SMRT)-mSin3a-histone deacetylase-1 (HDAC-1) complex associates with the nuclear retinoic acid receptor (RAR)-retinoid X receptor (RXR) heterodimeric complex. The HDAC activity of the complex maintains the tight association between deacetylated histones and chromatin that results in repressed gene t ...
Concept 11.2 Reception: A signaling molecule binds to a receptor
... -Hormones like the steroid testosterone have the ability to bind to a receptor protein, activating it. The receptor protein then enters the nucleus and can turn on specific genes. -Special proteins called transcription factors are able to turn on specific genes, that it is able to turn on genes tha ...
... -Hormones like the steroid testosterone have the ability to bind to a receptor protein, activating it. The receptor protein then enters the nucleus and can turn on specific genes. -Special proteins called transcription factors are able to turn on specific genes, that it is able to turn on genes tha ...
slides#10 - DENTISTRY 2012
... Everywhere, intestinal mucosa, lungs, skin, mast cells, basophiles, CNS ( role as a neurotransmitter) Release: - Specific (Antigen-mediated) Ag-Ab → mast cell degranulation - Non-specific (non-antigen-mediated) Drugs (antibiotics, anticancerous agents, compound 48/80…etc), dyes, venoms, mechanical ...
... Everywhere, intestinal mucosa, lungs, skin, mast cells, basophiles, CNS ( role as a neurotransmitter) Release: - Specific (Antigen-mediated) Ag-Ab → mast cell degranulation - Non-specific (non-antigen-mediated) Drugs (antibiotics, anticancerous agents, compound 48/80…etc), dyes, venoms, mechanical ...
Untitled
... The basic pathway of signal transduction is: signal > reception > transduction > amplification > response. First, a cell surface receptor is activated by a ligand and the signal is transmitted into the cell by a second messenger. This is followed by signal amplification via a phosphorylation cascade ...
... The basic pathway of signal transduction is: signal > reception > transduction > amplification > response. First, a cell surface receptor is activated by a ligand and the signal is transmitted into the cell by a second messenger. This is followed by signal amplification via a phosphorylation cascade ...
CELL SIGNALLING
... Conformational change in G – protein, causing it to bind GTP. G protein (with GTP bound) migrates in membrane Binds to and activates adenyl cyclase enzyme (ATP cAMP) ...
... Conformational change in G – protein, causing it to bind GTP. G protein (with GTP bound) migrates in membrane Binds to and activates adenyl cyclase enzyme (ATP cAMP) ...
Endocrine System 1 - Napa Valley College
... - activation of G protein activates Phospholipase C enzyme in the cell membrane - phospholipase C cleaves a membrane phospholipid - forms 2 second messengers: diacylglycerol (DAG) inositol triphosphate (IP3) D. Stimulation of Hormone Secretion 1. neural - by neurons that synapse on endocrine cells 2 ...
... - activation of G protein activates Phospholipase C enzyme in the cell membrane - phospholipase C cleaves a membrane phospholipid - forms 2 second messengers: diacylglycerol (DAG) inositol triphosphate (IP3) D. Stimulation of Hormone Secretion 1. neural - by neurons that synapse on endocrine cells 2 ...
TYPES OF RECEPTORS
... 5. Gene transcribed into messenger RNA. 6. mRNA goes to the ribosomes 7. Translate mRNA into protein. ...
... 5. Gene transcribed into messenger RNA. 6. mRNA goes to the ribosomes 7. Translate mRNA into protein. ...
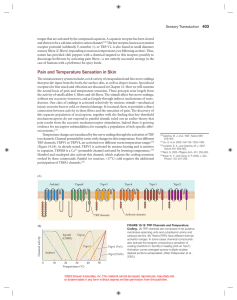
Pain and Temperature Sensation in Skin
... and sodium ions enter and depolarize the cell, causing action potential generation. Prolonged exposure of these endings to capsaicin eventually causes calcium accumulation and cell death. For this reason capsaicin is used as a long-term analgesic, presumably relieving chronic pain by killing C fiber ...
... and sodium ions enter and depolarize the cell, causing action potential generation. Prolonged exposure of these endings to capsaicin eventually causes calcium accumulation and cell death. For this reason capsaicin is used as a long-term analgesic, presumably relieving chronic pain by killing C fiber ...
Biology for Engineers: Cellular and Systems Neurophysiology
... • The functions of peptides are generally not well understood – They can have excitatory or inhibitory effects – They are best thought of as modulatory ...
... • The functions of peptides are generally not well understood – They can have excitatory or inhibitory effects – They are best thought of as modulatory ...
Slide ()
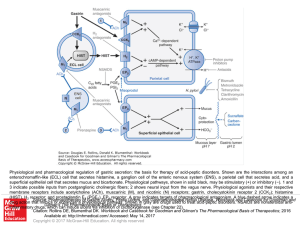
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
Introduction to Hormone Signalling Receptors and signals theme
... (electrical activity, hormone release) ...
... (electrical activity, hormone release) ...
Press release as pdf
... protein conformation changes. This, in turn, activates a signal chain inside the cell. As potential drug targets, receptor proteins are highly in demand for testing the efficacy of new pharmaceuticals. Of special interest are the G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) because a wide range of diseases c ...
... protein conformation changes. This, in turn, activates a signal chain inside the cell. As potential drug targets, receptor proteins are highly in demand for testing the efficacy of new pharmaceuticals. Of special interest are the G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) because a wide range of diseases c ...
2004 Biochemical and molecular biological aspects of glucose
... 2006 Koricanac G., Isenovic E., Stojanovic-Susulic V., Miskovic D., Zakula Z., RibaracStepic N. Time dependent effects of dexamethasone on serum insulin level and insulin receptors in rat liver and erythrocytes General Physiology and Biophysics, 25 (1), pp. 11-24. 2 Citiran u: Corticosterone has di ...
... 2006 Koricanac G., Isenovic E., Stojanovic-Susulic V., Miskovic D., Zakula Z., RibaracStepic N. Time dependent effects of dexamethasone on serum insulin level and insulin receptors in rat liver and erythrocytes General Physiology and Biophysics, 25 (1), pp. 11-24. 2 Citiran u: Corticosterone has di ...
Introduction to Neuropharmacology
... Receptor types and Selectivity • Drug Selectivity: selectivity of drug for effected receptor – Does drug bind to only α1 receptors or does it also bind to β1 and β2 receptors? ...
... Receptor types and Selectivity • Drug Selectivity: selectivity of drug for effected receptor – Does drug bind to only α1 receptors or does it also bind to β1 and β2 receptors? ...
Cell signalling - Bilkent University
... elaborate intercellular communication network that coordinates the growth, differentiation, and metabolism of the multitude of cells in diverse tissues and organs. • Errors in cellular information processing are responsible for diseases such as cancer, autoimmunity, and diabetes. By understanding ce ...
... elaborate intercellular communication network that coordinates the growth, differentiation, and metabolism of the multitude of cells in diverse tissues and organs. • Errors in cellular information processing are responsible for diseases such as cancer, autoimmunity, and diabetes. By understanding ce ...
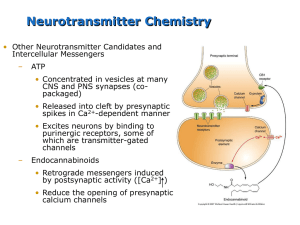
Chapter 06 - Neurotransmitter Systems
... Mode of operations • At resting, GDP is bound to the Ga. The whole complex floats around • When this complex bumps into the proper type of receptor that is bound to a transmitter molecule, GDP to GTP exchange occurs • Split of the complex into Ga and Gbg complex leads to the activation of effector p ...
... Mode of operations • At resting, GDP is bound to the Ga. The whole complex floats around • When this complex bumps into the proper type of receptor that is bound to a transmitter molecule, GDP to GTP exchange occurs • Split of the complex into Ga and Gbg complex leads to the activation of effector p ...
The Mechanism of Action for GerA Receptor
... Bacterial endospores are specific structures which develop from vegetative cells exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Thanks to those dormant forms bacteria can survive hard conditions, without a harm to their basic metabolic functions. Apart from high resistance to different environmental con ...
... Bacterial endospores are specific structures which develop from vegetative cells exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Thanks to those dormant forms bacteria can survive hard conditions, without a harm to their basic metabolic functions. Apart from high resistance to different environmental con ...
3-Mrp-Phe-Cha-Cha-Arg-Lys-Pro-Asn-Asp-Lys - Sigma
... mobilization and activation of protein kinase C (PKC). Other evidence indicates that PAR-1 is involved in the activation of the cascade of tyrosine kinase (Src family), PI3 kinase (PI3K), protein kinase B (Akt), and mitogenactivated protein kinase (MAPK). The PAR-2 receptor is expressed at high leve ...
... mobilization and activation of protein kinase C (PKC). Other evidence indicates that PAR-1 is involved in the activation of the cascade of tyrosine kinase (Src family), PI3 kinase (PI3K), protein kinase B (Akt), and mitogenactivated protein kinase (MAPK). The PAR-2 receptor is expressed at high leve ...
Growth Factor Receptor Signaling and Biology in Nervous System Development and Metabolic Regulation
... We plan to concentrate the main thrust of our future work on two programmes that complement and expand current areas of expertise. The first one focuses on the mechanisms of action and biological activities of the death receptor p75NTR (p75 neurotrophin receptor), and reflects our continued interest ...
... We plan to concentrate the main thrust of our future work on two programmes that complement and expand current areas of expertise. The first one focuses on the mechanisms of action and biological activities of the death receptor p75NTR (p75 neurotrophin receptor), and reflects our continued interest ...
Post-Doctoral Fellowship: Olfactory receptor
... Subject. Mammalian olfactory receptors belong to the G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) family. We have developed an original biosensor based on the attachment of GPCRs to an ion channel and referred to Ion Channel-Coupled Receptors (ICCRs) (Moreau et al. Nature Nanotechnology 2008). Motions of the ...
... Subject. Mammalian olfactory receptors belong to the G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) family. We have developed an original biosensor based on the attachment of GPCRs to an ion channel and referred to Ion Channel-Coupled Receptors (ICCRs) (Moreau et al. Nature Nanotechnology 2008). Motions of the ...