S4 Details of Bayesian Modelling.
... The major drawback of the classical analysis is the large number of tests to be performed due to the large number of possible combinations of SNPs and phenotypes and the uncertainty regarding the genetic model. In classical analysis, one has to define a certain model a priori and perform testing the ...
... The major drawback of the classical analysis is the large number of tests to be performed due to the large number of possible combinations of SNPs and phenotypes and the uncertainty regarding the genetic model. In classical analysis, one has to define a certain model a priori and perform testing the ...
An Integrated Genetic Analysis Package Using R
... or view the list within a web browser via help.start(). A PDF version of this file can be viewed with command vignette(”gap”,package=”gap”). You can cut and paste examples at end of each function’s documentation. Both genecounting and hap are able to handle SNPs and multiallelic markers, with the fo ...
... or view the list within a web browser via help.start(). A PDF version of this file can be viewed with command vignette(”gap”,package=”gap”). You can cut and paste examples at end of each function’s documentation. Both genecounting and hap are able to handle SNPs and multiallelic markers, with the fo ...
Slide 1
... – chromStart - The starting position of the feature in the chromosome or scaffold. The first base in a chromosome is numbered 0. – chromEnd - The ending position of the feature in the chromosome or scaffold. The chromEnd base is not included in the display of the feature. – name - Defines the name o ...
... – chromStart - The starting position of the feature in the chromosome or scaffold. The first base in a chromosome is numbered 0. – chromEnd - The ending position of the feature in the chromosome or scaffold. The chromEnd base is not included in the display of the feature. – name - Defines the name o ...
letter EJHG - HAL
... Given the disappointing results obtained by the Human Genetics community through systematic linkage screenings of the genome, Risch and Merinkangas argued that “the future of the genetics of complex diseases is likely to require large scale testing by association studies” 1. If linkage studies have ...
... Given the disappointing results obtained by the Human Genetics community through systematic linkage screenings of the genome, Risch and Merinkangas argued that “the future of the genetics of complex diseases is likely to require large scale testing by association studies” 1. If linkage studies have ...
PowerPoint
... Better estimate of variability or risk Chance of misclassification / measurement error • Large genetic effect size SNP risk allele with large odds ratio or explains a lot of trait variance This is unknown at beginning of study • Risk SNP is common This is unknown at beginning of study Calculate powe ...
... Better estimate of variability or risk Chance of misclassification / measurement error • Large genetic effect size SNP risk allele with large odds ratio or explains a lot of trait variance This is unknown at beginning of study • Risk SNP is common This is unknown at beginning of study Calculate powe ...
manuka short course
... An Introduction to Nutrigenetics & Nutrigenomics will define and illustrate (with practical examples) the difference between nutrigenetics, nutrigenomics and epigenetics. In this module we will also explore the concept of food responsiveness including examples illustrating how they can be used in cl ...
... An Introduction to Nutrigenetics & Nutrigenomics will define and illustrate (with practical examples) the difference between nutrigenetics, nutrigenomics and epigenetics. In this module we will also explore the concept of food responsiveness including examples illustrating how they can be used in cl ...
Jianfeng Xu, MD, DrPH: GWA - UCLA School of Public Health
... Sample size and false positives (Type I and II errors) Confirmation in independent study populations Increase the magnitude of effects of a specific gene ...
... Sample size and false positives (Type I and II errors) Confirmation in independent study populations Increase the magnitude of effects of a specific gene ...
Answering Reviewers - F6 Publishing Home
... candidate SNPs had to meet the following criteria: a minor allele frequency (MAF) > 0.2, the ΔS value > 0.25 and the target gene had to be previously reported as associated with GC.’ Furthermore, how about the associations between INSR rs1051690 SNP and clinical characteristics of GC? They should be ...
... candidate SNPs had to meet the following criteria: a minor allele frequency (MAF) > 0.2, the ΔS value > 0.25 and the target gene had to be previously reported as associated with GC.’ Furthermore, how about the associations between INSR rs1051690 SNP and clinical characteristics of GC? They should be ...
Ant genetics DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) Cells have two sources of
... Did the population expand or contract in the recent past? Do populations differ in past and present size? What are the genetic relationships of individuals? Which individuals have moved? (i.e. mark/recapture natural tags) Which individuals are clones? What is the average dispersal distance of offspr ...
... Did the population expand or contract in the recent past? Do populations differ in past and present size? What are the genetic relationships of individuals? Which individuals have moved? (i.e. mark/recapture natural tags) Which individuals are clones? What is the average dispersal distance of offspr ...
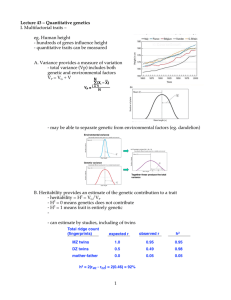
1 Lecture 43 â Quantitative genetics I. Multifactorial traits â eg
... - cross small “p” X large “l” - cross F1’s X large “l” - weight F2 fruit and genotype across genome “p/l” vs “l/l” - does weight differ? - For most genotypes, the answer is no but for a few it is yes (these are loci that contribute to the trait, in this case fruit size) - identified 28 loci responsi ...
... - cross small “p” X large “l” - cross F1’s X large “l” - weight F2 fruit and genotype across genome “p/l” vs “l/l” - does weight differ? - For most genotypes, the answer is no but for a few it is yes (these are loci that contribute to the trait, in this case fruit size) - identified 28 loci responsi ...
SNPs
... Before 1980, genetic maps were constructed by measuring recombination frequencies between genes giving measurable phenotypic traits This goes back at least to Sturtevandt and Morgan, if not to Mendel At that time, phenotypes were the only visible aspect of the genome ...
... Before 1980, genetic maps were constructed by measuring recombination frequencies between genes giving measurable phenotypic traits This goes back at least to Sturtevandt and Morgan, if not to Mendel At that time, phenotypes were the only visible aspect of the genome ...
understanding the role of pharmacotherapy and health disparities
... • Superficial physical characteristics commonly associated with racial groups: skin color, hair type and color, facial features, etc. • These characteristics have little or no relevance to drug response • Genetically determined differences in response to drugs exist among individuals and populations ...
... • Superficial physical characteristics commonly associated with racial groups: skin color, hair type and color, facial features, etc. • These characteristics have little or no relevance to drug response • Genetically determined differences in response to drugs exist among individuals and populations ...
Transmission-ratio distortion in the Framingham Heart Study | BMC
... could result in apparent linkage of the phenotype of ‘being alive’ to such a chromosomal regions. Further, this could result in false-positive linkage when ‘affected-only’ parametric or nonparametric linkage analysis is performed. Similarly, loci demonstrating TRD may be detectable in family-based a ...
... could result in apparent linkage of the phenotype of ‘being alive’ to such a chromosomal regions. Further, this could result in false-positive linkage when ‘affected-only’ parametric or nonparametric linkage analysis is performed. Similarly, loci demonstrating TRD may be detectable in family-based a ...
SNP - Asia University, Taiwan
... distribution of variation between individuals • Variation at DNA level = nucleotide insertions, deletions, and Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) or small nucleotide polymorphisms • SNP refers to any site where two or more different nucleotides are segregating in population. • Cluster of linked SN ...
... distribution of variation between individuals • Variation at DNA level = nucleotide insertions, deletions, and Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) or small nucleotide polymorphisms • SNP refers to any site where two or more different nucleotides are segregating in population. • Cluster of linked SN ...
Wilms tumor suppressor on the X Synonymous yet functional
... 241–252; 2007). The authors genotyped 58 SNPs across OCA2 in a collection of 3,839 adolescent twins, their siblings and their parents and identified eight haplotype blocks. Three SNPs in intron 1 that comprise one of these haplotypes showed the strongest association with blue eye color, with P value ...
... 241–252; 2007). The authors genotyped 58 SNPs across OCA2 in a collection of 3,839 adolescent twins, their siblings and their parents and identified eight haplotype blocks. Three SNPs in intron 1 that comprise one of these haplotypes showed the strongest association with blue eye color, with P value ...
The spectrum of human diseases
... Ancient disease loci are associated with haplotypes • Start with population genetically isolated for a long time such as Icelanders or Amish • Collect DNA samples from subgroup with disease • Also collect from equal number of people without disease • Genotype each individual in subgroups for haplot ...
... Ancient disease loci are associated with haplotypes • Start with population genetically isolated for a long time such as Icelanders or Amish • Collect DNA samples from subgroup with disease • Also collect from equal number of people without disease • Genotype each individual in subgroups for haplot ...
CSE280A Class Projects
... with probability ∝ 1 + s whereas other haplotypes are selected with probability ∝ 1. Each individual is mutated at m sites from its parent, where m is drawn from Poisson distribution with parameter µ. Assume that there is no recombination. 2. In the beginning, start with all haplotypes being all 0, ...
... with probability ∝ 1 + s whereas other haplotypes are selected with probability ∝ 1. Each individual is mutated at m sites from its parent, where m is drawn from Poisson distribution with parameter µ. Assume that there is no recombination. 2. In the beginning, start with all haplotypes being all 0, ...
Metabolomics meets Genomics
... Quality Control (QC) • Batch Effects: For GWAS, samples are processed together for genotyping in a batch. The size and composition of the sample batch depends on the type of the commercial array, for example, an Affymetrix array can genotype up to 96 samples, and an Illumina array can genotype up to ...
... Quality Control (QC) • Batch Effects: For GWAS, samples are processed together for genotyping in a batch. The size and composition of the sample batch depends on the type of the commercial array, for example, an Affymetrix array can genotype up to 96 samples, and an Illumina array can genotype up to ...
sv-lncs - acteon
... Trait Nucleotide (QTN). GWA studies promised to discover a large amount of QTN [1]. However, recent large studies mapped QTN that explained, at most, 11% of the phenotypic variance in human height despite it being a highly heritable trait (h2~0.8), testing >500K SNPs, sampling ~63,000 individuals an ...
... Trait Nucleotide (QTN). GWA studies promised to discover a large amount of QTN [1]. However, recent large studies mapped QTN that explained, at most, 11% of the phenotypic variance in human height despite it being a highly heritable trait (h2~0.8), testing >500K SNPs, sampling ~63,000 individuals an ...
TOHEuroVA - Computer Science
... Big data created by high-throughput and high-resolution experiment techniques Knowledge discovery of genetic factors associated with diseases is very important for early diagnosis and prevention of the diseases. ...
... Big data created by high-throughput and high-resolution experiment techniques Knowledge discovery of genetic factors associated with diseases is very important for early diagnosis and prevention of the diseases. ...
Blue Box PowerPoint Presentation Template
... chromosome whose inheritance can be followed • DNA segments near each other on a chromosome tend to be inherited together ...
... chromosome whose inheritance can be followed • DNA segments near each other on a chromosome tend to be inherited together ...
map distance
... All three affected offspring have inherited the B allele at locus 2 from their mother, whereas the three unaffected offspring have inherited the b allele. Thus, all six offspring are nonrecombinant for RP9 and marker locus 2. However, individuals II-1, II-3, and II-5 are recombinant for RP9 and mark ...
... All three affected offspring have inherited the B allele at locus 2 from their mother, whereas the three unaffected offspring have inherited the b allele. Thus, all six offspring are nonrecombinant for RP9 and marker locus 2. However, individuals II-1, II-3, and II-5 are recombinant for RP9 and mark ...
Tag SNP

A tag SNP is a representative single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in a region of the genome with high linkage disequilibrium that represents a group of SNPs called a haplotype. It is possible to identify genetic variation and association to phenotypes without genotyping every SNP in a chromosomal region. This reduces the expense and time of mapping genome areas associated with disease, since it eliminates the need to study every individual SNP. Tag SNPs are useful in whole-genome SNP association studies in which hundreds of thousands of SNPs across the entire genome are genotyped.