Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
... Answer: There is no word to receive the action of the verb shook and no direct object. Therefore shook is an intransitive verb in this sentence. ...
... Answer: There is no word to receive the action of the verb shook and no direct object. Therefore shook is an intransitive verb in this sentence. ...
Parts of Speech Table
... functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence. An individual word can function as more than one part of speech when used in different circumstances. Understanding parts of speech is essential for determining the correct definition of a word when using the ...
... functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence. An individual word can function as more than one part of speech when used in different circumstances. Understanding parts of speech is essential for determining the correct definition of a word when using the ...
Old English Grammar, Basically. GENERALIZATIONS Remember
... o 3) If you look up a noun and see that it’s feminine and ends in –e, it’s weak and declines like cyrice or sunne (p. 20) Mitchell and Rob say little about these nouns, because they’re so ...
... o 3) If you look up a noun and see that it’s feminine and ends in –e, it’s weak and declines like cyrice or sunne (p. 20) Mitchell and Rob say little about these nouns, because they’re so ...
Глоссарий курса
... 1. Article is a word used to modify a noun, which is a person, place, object, or idea. Articles in the English language are the definite article the and the indefinite articles a and an. 2. Noun is a word that functions as the name of some specific thing or set of things, such as living creatures, o ...
... 1. Article is a word used to modify a noun, which is a person, place, object, or idea. Articles in the English language are the definite article the and the indefinite articles a and an. 2. Noun is a word that functions as the name of some specific thing or set of things, such as living creatures, o ...
Checksheet - How to identify word class
... subordinate way. e.g. ‘because’, ‘however’, ‘if’, ‘so that’, ‘as though’ etc. Some conjunctions occur in pairs and link two parts of an utterance or sentence: ‘if...then’, ‘although...yet’, ‘both...and’, ‘either...or’ etc. ...
... subordinate way. e.g. ‘because’, ‘however’, ‘if’, ‘so that’, ‘as though’ etc. Some conjunctions occur in pairs and link two parts of an utterance or sentence: ‘if...then’, ‘although...yet’, ‘both...and’, ‘either...or’ etc. ...
Checksheet - How to identify word class
... subordinate way. e.g. ‘because’, ‘however’, ‘if’, ‘so that’, ‘as though’ etc. Some conjunctions occur in pairs and link two parts of an utterance or sentence: ‘if...then’, ‘although...yet’, ‘both...and’, ‘either...or’ etc. ...
... subordinate way. e.g. ‘because’, ‘however’, ‘if’, ‘so that’, ‘as though’ etc. Some conjunctions occur in pairs and link two parts of an utterance or sentence: ‘if...then’, ‘although...yet’, ‘both...and’, ‘either...or’ etc. ...
Lesson Plan #2 Lesson: Action Verb Lesson with Book, Game, and
... up with the sentences on their own. 3. They should not share their sentences with anyone. iii. Fold the note cards in half and put them in a bowl. Allow the students to take turns drawing a card from the bowl and act out the sentence. (Gardner’s: ...
... up with the sentences on their own. 3. They should not share their sentences with anyone. iii. Fold the note cards in half and put them in a bowl. Allow the students to take turns drawing a card from the bowl and act out the sentence. (Gardner’s: ...
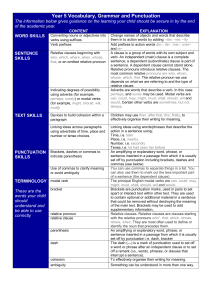
Year 5 Vocabulary Grammar and Punctuation
... A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, who ...
... A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, who ...
Grammatical Rules from Harbrace Handbook 3a Punctuating
... They do not understand the idea that __________________________. Only complete sentences make sense when placed in the frame sentence. If just part of a test sentence fits, you have probably located a comma splice or a fused sentence. Test sentence 1: Plasma is the fourth state of matter. Test: They ...
... They do not understand the idea that __________________________. Only complete sentences make sense when placed in the frame sentence. If just part of a test sentence fits, you have probably located a comma splice or a fused sentence. Test sentence 1: Plasma is the fourth state of matter. Test: They ...
Noun and Verb Twins Underline the word that is used once as a
... 2. All the student in that school wear uniforms. 3. Our watch don’t show the same time. 4. Why are all school bus painted yellow? 5. Seven protester were arrested after the riot. 6. We saw some bright flash of light coming from the woods. 7. Why must I pay four different tax on the same income? Verb ...
... 2. All the student in that school wear uniforms. 3. Our watch don’t show the same time. 4. Why are all school bus painted yellow? 5. Seven protester were arrested after the riot. 6. We saw some bright flash of light coming from the woods. 7. Why must I pay four different tax on the same income? Verb ...
Glossary of Grammar Terms: “Adjective” through “Conjunction”
... GENDER A grammatical category of words. In Spanish there are two genders: masculine and faminine. Here are a few examples: ...
... GENDER A grammatical category of words. In Spanish there are two genders: masculine and faminine. Here are a few examples: ...
Teacher Packet Level II: Week 1
... book. You do not have a book. d. Question: “to do”+ regular verb. Inverse of the negative sentence with auxiliary verb “to do.” Ex. Do you have a book? Does she have a pencil? ...
... book. You do not have a book. d. Question: “to do”+ regular verb. Inverse of the negative sentence with auxiliary verb “to do.” Ex. Do you have a book? Does she have a pencil? ...
Document
... i. Personal (tell if 1st, 2nd, 3rd person and if NOM, OBJ, or POSS) PRO ii. Interrogative (INT) iii. Possessive (POSS) iv. Demonstrative (DEM) v. Reflexive (REF) vi. Indefinite (IND) c. VERB – the action of the sentence i. Action (AV) ii. Linking (LV) iii. Helping (HV) can be 1, 2, or 3; used with e ...
... i. Personal (tell if 1st, 2nd, 3rd person and if NOM, OBJ, or POSS) PRO ii. Interrogative (INT) iii. Possessive (POSS) iv. Demonstrative (DEM) v. Reflexive (REF) vi. Indefinite (IND) c. VERB – the action of the sentence i. Action (AV) ii. Linking (LV) iii. Helping (HV) can be 1, 2, or 3; used with e ...
parts of the sentence review
... 1. the Complete Subject: includes the simple subject and all of the words that modify the simple subject 2. the Simple Subject: the noun or pronoun that answers the question Who? or What? is this sentence about? Example: ...
... 1. the Complete Subject: includes the simple subject and all of the words that modify the simple subject 2. the Simple Subject: the noun or pronoun that answers the question Who? or What? is this sentence about? Example: ...
Verbs
... this goo in our hair for twenty minutes. The audience attentively watched the latest production of Macbeth. Every spring, William moves all boxes and trunks from one side of the attic to the other. ...
... this goo in our hair for twenty minutes. The audience attentively watched the latest production of Macbeth. Every spring, William moves all boxes and trunks from one side of the attic to the other. ...
Negative verbs in other tenses
... The upshot of this is that, in all examples of Swahili verbs, on paper, either interpretation is possible (although I usually only give you one). Please do be aware of this. Note, however, that, when using the 2nd person, i.e. when talking about a person/people you are addressing directly, you are ...
... The upshot of this is that, in all examples of Swahili verbs, on paper, either interpretation is possible (although I usually only give you one). Please do be aware of this. Note, however, that, when using the 2nd person, i.e. when talking about a person/people you are addressing directly, you are ...
Chapter 2
... words, such as “not.” When we use be as a main verb, we simply put not after the form of be as in: 1. She is not a student. 2. They are not students. In case we don’t have an auxiliary verb or the verb is not “be” we introduce “do” and put the negative word after it. 1. He did not search the room ca ...
... words, such as “not.” When we use be as a main verb, we simply put not after the form of be as in: 1. She is not a student. 2. They are not students. In case we don’t have an auxiliary verb or the verb is not “be” we introduce “do” and put the negative word after it. 1. He did not search the room ca ...
Crash Course on Grammar, Common Usage and APA style
... when "I" or "ME" is linked to another pronoun, subject, or object using "and" or "or" Examples: Michael and I studied together. CORRECT "Michael" and "I" are the compound subjects of the sentence Michael and me studied together. INCORRECT "Me" cannot be used as a subject in a sentence. She told Mich ...
... when "I" or "ME" is linked to another pronoun, subject, or object using "and" or "or" Examples: Michael and I studied together. CORRECT "Michael" and "I" are the compound subjects of the sentence Michael and me studied together. INCORRECT "Me" cannot be used as a subject in a sentence. She told Mich ...
File
... A participial phrase consists of a participle plus any modifiers and complements of the participle. ...
... A participial phrase consists of a participle plus any modifiers and complements of the participle. ...
Verb
... a) Verbs are mainly of two kinds. b) They are – 1) Finite Verb & 2) Non- Finite Verb c) Finite Verb: A Finite Verb agrees or changes with the number & person of the subject. It also changes with the time or tense of the verb. A sentence is incomplete without a Finite verb. Examples: 1) I drew a pict ...
... a) Verbs are mainly of two kinds. b) They are – 1) Finite Verb & 2) Non- Finite Verb c) Finite Verb: A Finite Verb agrees or changes with the number & person of the subject. It also changes with the time or tense of the verb. A sentence is incomplete without a Finite verb. Examples: 1) I drew a pict ...
Subject Predicate
... a) Inflectional morphology: studies the way in which words vary in order to express grammatical contrasts in sentences, such as singular/past or past/present. These grammatical contrasts are called grammatical categories: ...
... a) Inflectional morphology: studies the way in which words vary in order to express grammatical contrasts in sentences, such as singular/past or past/present. These grammatical contrasts are called grammatical categories: ...
Using the Verb Gustar
... Gustar can be a confusing verb for English speakers learning Spanish. That's not because gustar, which often is used to translate English sentences using the verb "to like," is particularly unusual. To Spanish speakers it is just another verb. But it is used differently than the English verb it ofte ...
... Gustar can be a confusing verb for English speakers learning Spanish. That's not because gustar, which often is used to translate English sentences using the verb "to like," is particularly unusual. To Spanish speakers it is just another verb. But it is used differently than the English verb it ofte ...