Daily Grammar Practice - NOTES
... Reflexive – reflects back to self (myself, yourself, himself, herself, ourselves) Relative – starts dependent clauses (that, which, who, whom, whose, what) Interrogative – asks a question (Which? Whose? What? Whom? Who?) Demonstrative – demonstrates which one (this, that, these, those) Indefinite – ...
... Reflexive – reflects back to self (myself, yourself, himself, herself, ourselves) Relative – starts dependent clauses (that, which, who, whom, whose, what) Interrogative – asks a question (Which? Whose? What? Whom? Who?) Demonstrative – demonstrates which one (this, that, these, those) Indefinite – ...
Name:
... Appositive Phrase – An appositive is a noun or pronoun that is placed next to another noun or pronoun to identify or give additional information about it. An appositive phrase is an appositive plus any words that modify the appositive. (Joanne rode a hydrofoil across the English Channel, the body ...
... Appositive Phrase – An appositive is a noun or pronoun that is placed next to another noun or pronoun to identify or give additional information about it. An appositive phrase is an appositive plus any words that modify the appositive. (Joanne rode a hydrofoil across the English Channel, the body ...
powerpoint jeopardy - Mr. Phillips` Classroom
... following sentence: • “We quickly ran out of ice cream on the hot, scorching day, but that did not matter after all.” ...
... following sentence: • “We quickly ran out of ice cream on the hot, scorching day, but that did not matter after all.” ...
Eight Parts of Speech Pre-Test Name: Period: Directions: Use these
... Directions: Write True or False for the statements below. __________ 1. In order to have a prepositional phrase you need a preposition + any modifiers + an object (which is a noun or pronoun). __________ 2. Words such as, carpenter, cities, bricks, creativity, river, and running are all considered t ...
... Directions: Write True or False for the statements below. __________ 1. In order to have a prepositional phrase you need a preposition + any modifiers + an object (which is a noun or pronoun). __________ 2. Words such as, carpenter, cities, bricks, creativity, river, and running are all considered t ...
How to use verbals
... qualifiers of (adders of information to) nouns, verbs, adjectives, prepositions. To swim is good exercise. Here the infinitive “to swim” is acting as the subject of the verb “is”, like a noun would. You can also write, Australians love to swim. In this sentence the infinitive is acting like a noun a ...
... qualifiers of (adders of information to) nouns, verbs, adjectives, prepositions. To swim is good exercise. Here the infinitive “to swim” is acting as the subject of the verb “is”, like a noun would. You can also write, Australians love to swim. In this sentence the infinitive is acting like a noun a ...
Term Key Concept noun a word that names a person, place, thing
... Practice: Underline each pronoun. After the sentence, identify each pronoun as personal, reflexive, intensive, demonstrative, interrogative, relative, or indefinite. 1. This is Tito Puente himself at the ceremony to install his star on Hollywood’s Walk of Fame. 2. Many refer to him as the “King of L ...
... Practice: Underline each pronoun. After the sentence, identify each pronoun as personal, reflexive, intensive, demonstrative, interrogative, relative, or indefinite. 1. This is Tito Puente himself at the ceremony to install his star on Hollywood’s Walk of Fame. 2. Many refer to him as the “King of L ...
Action Verb Complements An ACTION VERB is a verb that shows
... The mayor appointed Ken treasurer. (OC as a noun) Our dog considers the sofa his. (OC as a pronoun) Some of my friends call me crazy. (OC as an adjective) The INDIRECT OBJECT answers the questions to what? for what? or to whom? for whom? after the action verb. An IO must be a noun or a pronoun. Exam ...
... The mayor appointed Ken treasurer. (OC as a noun) Our dog considers the sofa his. (OC as a pronoun) Some of my friends call me crazy. (OC as an adjective) The INDIRECT OBJECT answers the questions to what? for what? or to whom? for whom? after the action verb. An IO must be a noun or a pronoun. Exam ...
Parts of Speech Reference Sheet
... A prepositional phrase is formed by the preposition, its object, and any words that describe the object. The object of the preposition is the noun/pronoun in the prepositional phrase. Ex: Preposition Object of Preposition (On hot summer days,) that swimming pool is our favorite place. Practice: 1. ...
... A prepositional phrase is formed by the preposition, its object, and any words that describe the object. The object of the preposition is the noun/pronoun in the prepositional phrase. Ex: Preposition Object of Preposition (On hot summer days,) that swimming pool is our favorite place. Practice: 1. ...
101 Grammar intro
... 1. Latin is a dead language 2. Learning Latin gives a student 3. Elite Romans were bilingual in Latin and Greek 4. Roman boys studied literary and rhetorical texts ...
... 1. Latin is a dead language 2. Learning Latin gives a student 3. Elite Romans were bilingual in Latin and Greek 4. Roman boys studied literary and rhetorical texts ...
verb subject object passive nouns verbs nouns adverbs modify verb
... determiners and pronouns, which can refer back to earlier words conjunctions and adverbs, which can make relations between words clear ...
... determiners and pronouns, which can refer back to earlier words conjunctions and adverbs, which can make relations between words clear ...
Parts of a Sentence
... A conjunction is a part of the sentence that can join two separate sentences together without changing any of the words of the sentences. And, but, or, nor, for, so, and yet are the ...
... A conjunction is a part of the sentence that can join two separate sentences together without changing any of the words of the sentences. And, but, or, nor, for, so, and yet are the ...
More Pronouns - Henry County Schools
... • Verbal – a word the comes from a verb but used as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb – Like verbs, verbals can be described (modified) by adverbs and adverb phrases or have complements (words that complete the predicate). – Verbals with modifiers or a complement are called ...
... • Verbal – a word the comes from a verb but used as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb – Like verbs, verbals can be described (modified) by adverbs and adverb phrases or have complements (words that complete the predicate). – Verbals with modifiers or a complement are called ...
The Parts of Speech and Grammar Definitions
... 1. A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. a. Proper--name of a specific person, place, thing(George Washington) b. common--is not specific--dog, cat, girl, boy 2. Subject-is the part of a sentence which is doing something or about which something is said. (noun or pronoun) 3. A ...
... 1. A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. a. Proper--name of a specific person, place, thing(George Washington) b. common--is not specific--dog, cat, girl, boy 2. Subject-is the part of a sentence which is doing something or about which something is said. (noun or pronoun) 3. A ...
Parts of Speech
... An adverb is a word which usually describes a verb. It tells you how something is done. It may also tell you when or where something happened. Examples: slowly, intelligently, well, yesterday, tomorrow, here, everywhere ...
... An adverb is a word which usually describes a verb. It tells you how something is done. It may also tell you when or where something happened. Examples: slowly, intelligently, well, yesterday, tomorrow, here, everywhere ...
The Sentence
... The complete predicate is the verb and all its modifiers. Complete Predicate took us bowling yesterday ...
... The complete predicate is the verb and all its modifiers. Complete Predicate took us bowling yesterday ...
Freshman Grammar Program
... A proper noun is the name of a particular person, place, thing, or idea and is always capitalized. ...
... A proper noun is the name of a particular person, place, thing, or idea and is always capitalized. ...
Grammar Usage and Mechanics - South Brunswick School District
... The rose smells good. Numbers: Numbers zero through one hundred and any round numbers above that should be written out in words. All other numbers should be written as numerals. Ex: I have thirty-three dollars. She has 125 stamps. Participle: A word formed from a verb and used as an adjective or a n ...
... The rose smells good. Numbers: Numbers zero through one hundred and any round numbers above that should be written out in words. All other numbers should be written as numerals. Ex: I have thirty-three dollars. She has 125 stamps. Participle: A word formed from a verb and used as an adjective or a n ...
Week 2a
... It seems that in a fragment response, you need to have a determiner if you’re going to use a count noun. An adjective won’t do, hence adjectives can’t be the same as determiners. ...
... It seems that in a fragment response, you need to have a determiner if you’re going to use a count noun. An adjective won’t do, hence adjectives can’t be the same as determiners. ...
Parts of Speech Flip Chart Notes
... place............................store……...Wal-Mart thing...........................cereal………Cheerios ...
... place............................store……...Wal-Mart thing...........................cereal………Cheerios ...
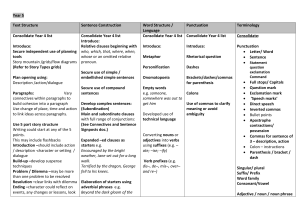
Year 5 Text Structure Sentence Construction Word Structure
... Develop complex sentences: build cohesion into a paragraph Use change of place, time and action (Subordination) Main and subordinate clauses to link ideas across paragraphs. with full range of conjunctions: (See Connectives and Sentence Use 5 part story structure Signposts doc.) Writing could start ...
... Develop complex sentences: build cohesion into a paragraph Use change of place, time and action (Subordination) Main and subordinate clauses to link ideas across paragraphs. with full range of conjunctions: (See Connectives and Sentence Use 5 part story structure Signposts doc.) Writing could start ...
Universidad Virtual English
... • There are three articles in English: a, an and the. • They always go before a noun. • A/an refers to countable singular nouns. They refer to any person, place or thing. • I want a porter to help me carry my luggage. • (It can be any of the porters working at the station) • They wanted to have a ni ...
... • There are three articles in English: a, an and the. • They always go before a noun. • A/an refers to countable singular nouns. They refer to any person, place or thing. • I want a porter to help me carry my luggage. • (It can be any of the porters working at the station) • They wanted to have a ni ...
Verbal Phrases Notes
... Notes based on handouts from The Writing Lab and The OWL at Purdue. Please visit http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/owlprint/627 for more details or examples. ...
... Notes based on handouts from The Writing Lab and The OWL at Purdue. Please visit http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/owlprint/627 for more details or examples. ...