The Periodic Table - Brookwood High School
... Widely accepted because it was able to predict the existence and properties of undiscovered elements Problem: elements were being placed in groups of elements with differing properties ...
... Widely accepted because it was able to predict the existence and properties of undiscovered elements Problem: elements were being placed in groups of elements with differing properties ...
Study Material - Tiwariacademy.net
... Mendeleev's periodic law :– The properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic mass. Mendeleev's periodic table based on the chemical properties of elements. Contain eight vertical columns called groups and seven horizontal rows called periods form Mendeleev’s peridic table. Achiev ...
... Mendeleev's periodic law :– The properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic mass. Mendeleev's periodic table based on the chemical properties of elements. Contain eight vertical columns called groups and seven horizontal rows called periods form Mendeleev’s peridic table. Achiev ...
Periodic Table Trends
... The greater the ‘shielding’ effect, the more readily the atom will lose its valence electrons to form an ion, i.e. ionise. The larger the atom, the more readily it ionises and the more reactive it is. The reactivity of the metals in Group II therefore, increases as one moves down the group as does ...
... The greater the ‘shielding’ effect, the more readily the atom will lose its valence electrons to form an ion, i.e. ionise. The larger the atom, the more readily it ionises and the more reactive it is. The reactivity of the metals in Group II therefore, increases as one moves down the group as does ...
The Periodic Table
... Periods = Horizontal rows #’d 1-7 Each period contains more and more elements ...
... Periods = Horizontal rows #’d 1-7 Each period contains more and more elements ...
Chapter 11
... Definition of Ionization Energy (IE) • Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion. The first or initial ionization energy or Ei of an atom or molecule is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of isolated gaseous atoms or ion ...
... Definition of Ionization Energy (IE) • Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion. The first or initial ionization energy or Ei of an atom or molecule is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of isolated gaseous atoms or ion ...
Unit One Periodicity of Elements and their Properties
... 6-Scientists cannot discover a new element between sulphur (16S) and chlorine (17CI). 7- In periods, by increasing the atomic number, the atomic size decreases. 8 .By increasing the atomic number within groups, the atomic size increases. ...
... 6-Scientists cannot discover a new element between sulphur (16S) and chlorine (17CI). 7- In periods, by increasing the atomic number, the atomic size decreases. 8 .By increasing the atomic number within groups, the atomic size increases. ...
Chapter 6 notes
... Elements in these groups are often referred to as __________________ elements because they display a wide range of physical and chemical properties. Transition Elements Copper, silver, gold, and _____________ are transition metals. The inner transition metals are characterized by f block. ...
... Elements in these groups are often referred to as __________________ elements because they display a wide range of physical and chemical properties. Transition Elements Copper, silver, gold, and _____________ are transition metals. The inner transition metals are characterized by f block. ...
notes - unit 3 - periodic table_student_2014
... blue when dissolved in water) This concept is ________ on the __________________!!! Tend to be _________________ almost every transition metal can _________________________________ depending on what other elements or polyatomic ions are present Have multiple oxidation states _________ reac ...
... blue when dissolved in water) This concept is ________ on the __________________!!! Tend to be _________________ almost every transition metal can _________________________________ depending on what other elements or polyatomic ions are present Have multiple oxidation states _________ reac ...
PreAP Chemistry
... Main Idea: Elements are organized into different _______________ in the periodic table according to their _______________ _______________. Organizing Elements by Electron Configuration • Recall electrons in the highest principal energy level are called _______________ electrons. • All ______________ ...
... Main Idea: Elements are organized into different _______________ in the periodic table according to their _______________ _______________. Organizing Elements by Electron Configuration • Recall electrons in the highest principal energy level are called _______________ electrons. • All ______________ ...
clean-color-coded-periodic-table_ochoa-edit
... Directions: Be sure to follow all instructions carefully and completely! Use your textbook (the back cover and pp. 177-181 will be very useful!) and any other resources to help you complete the periodic table. 1. Draw a RED diagonal line through the elements that exist as a gas at room temperature. ...
... Directions: Be sure to follow all instructions carefully and completely! Use your textbook (the back cover and pp. 177-181 will be very useful!) and any other resources to help you complete the periodic table. 1. Draw a RED diagonal line through the elements that exist as a gas at room temperature. ...
Chapter 7.1 Notes
... • One way scientists organized elements in the past was by their atomic mass. • To do this, they had to get the mass of a large chunk of the element and calculate the mass of a single atom. • Because there are isotopes of atoms.. (atoms with a different number of neutrons in the nucleus) the atomic ...
... • One way scientists organized elements in the past was by their atomic mass. • To do this, they had to get the mass of a large chunk of the element and calculate the mass of a single atom. • Because there are isotopes of atoms.. (atoms with a different number of neutrons in the nucleus) the atomic ...
AKS Review
... Groups(families)- vertical column on periodic table. Elements in the same family have similar properties because they have the same valence electron configuration Periodic law- “Properties of elements are a Periodic Function of the atomic number.” When elements are arranged by increasing atomic numb ...
... Groups(families)- vertical column on periodic table. Elements in the same family have similar properties because they have the same valence electron configuration Periodic law- “Properties of elements are a Periodic Function of the atomic number.” When elements are arranged by increasing atomic numb ...
Unit 5 – The Periodic Table
... • By 1700, only 14 elements had been isolated • Scientific discovery led to a higher rate of element discovery (20 in the 1700s) • A logical organization of elements was needed for all the new elements ...
... • By 1700, only 14 elements had been isolated • Scientific discovery led to a higher rate of element discovery (20 in the 1700s) • A logical organization of elements was needed for all the new elements ...
AP Chemistry – Chapter 7 Reading Guide: Periodic Table of the
... 10. Describe the general and physical and chemical behavior of the alkali metals, and alkali earth metals, and explain how their chemistry relates to their position on the periodic table. ...
... 10. Describe the general and physical and chemical behavior of the alkali metals, and alkali earth metals, and explain how their chemistry relates to their position on the periodic table. ...
Unit 3 - The Periodic Table
... Found in the ___________ of the periodic table (the D block) Form ___________________ in solution (ex: Cu is bright blue when dissolved in water) This concept is ALWAYS on the REGENTS EXAM!!! Tend to be _____________________ will lose electrons or gain them depending on what other ________ ...
... Found in the ___________ of the periodic table (the D block) Form ___________________ in solution (ex: Cu is bright blue when dissolved in water) This concept is ALWAYS on the REGENTS EXAM!!! Tend to be _____________________ will lose electrons or gain them depending on what other ________ ...
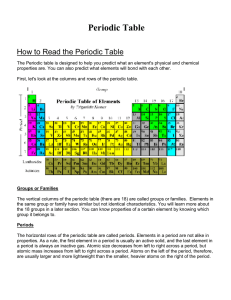
How to Read the Periodic Table
... like to form compounds with each other. These compounds are called ionic compounds. When two or more nonmetals bond with each other, they form a covalent compound. Metalloids Elements on both sides of the zigzag line have properties of both metals and nonmetals. These elements are called metalloids. ...
... like to form compounds with each other. These compounds are called ionic compounds. When two or more nonmetals bond with each other, they form a covalent compound. Metalloids Elements on both sides of the zigzag line have properties of both metals and nonmetals. These elements are called metalloids. ...
20151023082664
... o what patterns did he noticeo what was his final arrangement of the periodic tableo what was missing in his tableo how did he predict undiscovered elements o was he the first to make a periodic tableo what does the placement of the elements reveal links betweeno how were his predictionsSection 2 ...
... o what patterns did he noticeo what was his final arrangement of the periodic tableo what was missing in his tableo how did he predict undiscovered elements o was he the first to make a periodic tableo what does the placement of the elements reveal links betweeno how were his predictionsSection 2 ...
The Periodic Table/Trends Chapter 5
... The Metalloids or Semimetals have some characteristics of both ...
... The Metalloids or Semimetals have some characteristics of both ...
Periodic Table Notes
... TEKS 8.5C interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements TEKS 8.5B identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity ...
... TEKS 8.5C interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements TEKS 8.5B identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE The Periodic Table lists all known
... All the elements on the left side of the red line are metals. All the elements on the right side are nonmetals. However, the boxes with white circles on them represent metalloids, which have a combination of metallic and non-metallic properties. For example, Silicon is in Group 4. It looks quite shi ...
... All the elements on the left side of the red line are metals. All the elements on the right side are nonmetals. However, the boxes with white circles on them represent metalloids, which have a combination of metallic and non-metallic properties. For example, Silicon is in Group 4. It looks quite shi ...
Section 2: Exploring the Periodic Table
... 〉 What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons? 〉 If an atom gains or loses electrons, it no longer has an equal number of electrons and protons. Because the charges do not cancel completely, the atom has a net electric charge. ...
... 〉 What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons? 〉 If an atom gains or loses electrons, it no longer has an equal number of electrons and protons. Because the charges do not cancel completely, the atom has a net electric charge. ...
Full Chapter - CPO Science
... use the atomic mass unit (amu). The atomic mass of any element is the average mass (in amu) of an atom of each element. ...
... use the atomic mass unit (amu). The atomic mass of any element is the average mass (in amu) of an atom of each element. ...
Periodic Table - Marian High School
... use the atomic mass unit (amu). The atomic mass of any element is the average mass (in amu) of an atom of each element. ...
... use the atomic mass unit (amu). The atomic mass of any element is the average mass (in amu) of an atom of each element. ...
period trends notes - Pleasantville High School
... Rare Earth Elements The thirty rare earth elements are composed of the lanthanide and actinide series. One element of the lanthanide series and most of the elements in the actinide series are called trans-uranium, which means synthetic or man-made. Mendeleev In 1869, Dmitri Ivanovitch Mendelé ...
... Rare Earth Elements The thirty rare earth elements are composed of the lanthanide and actinide series. One element of the lanthanide series and most of the elements in the actinide series are called trans-uranium, which means synthetic or man-made. Mendeleev In 1869, Dmitri Ivanovitch Mendelé ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.