chapter5
... • Atomic radii decrease within a row going from left to right on the periodic table. – This last fact seems contrary to intuition. – How does nature make the elements smaller even though the electron number is increasing? ...
... • Atomic radii decrease within a row going from left to right on the periodic table. – This last fact seems contrary to intuition. – How does nature make the elements smaller even though the electron number is increasing? ...
Chapter 7 - HCC Learning Web
... • Look at electron configurations to determine whether electron affinity is positive or negative. • The extra electron in Ar needs to be placed in the 4s orbital which is significantly higher in energy than the 3p orbital. • The added electron in Cl is placed in the 3p orbital to form the stable 3p6 ...
... • Look at electron configurations to determine whether electron affinity is positive or negative. • The extra electron in Ar needs to be placed in the 4s orbital which is significantly higher in energy than the 3p orbital. • The added electron in Cl is placed in the 3p orbital to form the stable 3p6 ...
CHAPTER 6
... • Atomic radii decrease within a row going from left to right on the periodic table. – This last fact seems contrary to intuition. – How does nature make the elements smaller even though the electron number is increasing? ...
... • Atomic radii decrease within a row going from left to right on the periodic table. – This last fact seems contrary to intuition. – How does nature make the elements smaller even though the electron number is increasing? ...
Periodic table
... Therefore, considering the second period it has been found that, Lithium (Li) has the largest atomic size while Fluorine (F) has the smallest. Neon has its outermost shell completely filled (inert gas) i.e. it has structural stability of its outermost shell consisting of an octet of electrons. Why i ...
... Therefore, considering the second period it has been found that, Lithium (Li) has the largest atomic size while Fluorine (F) has the smallest. Neon has its outermost shell completely filled (inert gas) i.e. it has structural stability of its outermost shell consisting of an octet of electrons. Why i ...
Chapter 7. Periodic Properties of the Elements.
... simultaneously attracted to the nucleus, and repelled by the other electrons. Generally, the valence electrons are screened from the nucleus by the core electrons (~S, where S is the screening constant = number of core electrons). The effective nuclear charge is the approximate charge experienced by ...
... simultaneously attracted to the nucleus, and repelled by the other electrons. Generally, the valence electrons are screened from the nucleus by the core electrons (~S, where S is the screening constant = number of core electrons). The effective nuclear charge is the approximate charge experienced by ...
2. Classification of Elements and periodicity in properties
... ¾ They form complexes or co-ordinate covalent compounds. ¾ They readily form alloys like brass, bronze, german silver etc. INNER TRANSITION ELEMENTS: ¾ The f-block elements are called inner transition elements as they bring about transition among transition metals. ¾ The differentiating electron ent ...
... ¾ They form complexes or co-ordinate covalent compounds. ¾ They readily form alloys like brass, bronze, german silver etc. INNER TRANSITION ELEMENTS: ¾ The f-block elements are called inner transition elements as they bring about transition among transition metals. ¾ The differentiating electron ent ...
Chapter 6 the Periodic Table
... Periods • The boxes are arranged in order of increasing atomic number in a series of rows called periods. • Beginning with hydrogen in period 1, there are 7 periods. ...
... Periods • The boxes are arranged in order of increasing atomic number in a series of rows called periods. • Beginning with hydrogen in period 1, there are 7 periods. ...
The d-and f-Block Elements
... Due to the similar sizes of the lanthanides, it is difficult to separate them but due to lanthanide contraction their properties slightly vary (such as ability to form complexes). The variation in the properties is utilized to separate them. 2. Basic Strength of Hydroxide : Due to the lanthanide con ...
... Due to the similar sizes of the lanthanides, it is difficult to separate them but due to lanthanide contraction their properties slightly vary (such as ability to form complexes). The variation in the properties is utilized to separate them. 2. Basic Strength of Hydroxide : Due to the lanthanide con ...
Periodic Table Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource Unit Andrew D. Hulbert
... The transition metals constitute Groups 3 through 12 and are sometimes called the d-block elements because of their position in the periodic table. ...
... The transition metals constitute Groups 3 through 12 and are sometimes called the d-block elements because of their position in the periodic table. ...
The Periodic Table - Journigan-wiki
... If 1 mm= 1pm, how long would you cut a straw to represent fluorine’s atomic radius? If 1 mm= 1pm, how long would you cut a straw to represent germanium’s atomic radius? If 10 cm= 1 pauling, how long would you cut a straw to represent silver’s electronegativity? If 10 cm= 1 pauling, how long would yo ...
... If 1 mm= 1pm, how long would you cut a straw to represent fluorine’s atomic radius? If 1 mm= 1pm, how long would you cut a straw to represent germanium’s atomic radius? If 10 cm= 1 pauling, how long would you cut a straw to represent silver’s electronegativity? If 10 cm= 1 pauling, how long would yo ...
PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS
... · An ionic compound is composed of cations and anions arranged in a crystalline structure. CATIONS are positive ions formed by removal of ANIONS are negative ions formed by gaining electrons from metallic atoms. of electrons by nonmetallic atoms. ...
... · An ionic compound is composed of cations and anions arranged in a crystalline structure. CATIONS are positive ions formed by removal of ANIONS are negative ions formed by gaining electrons from metallic atoms. of electrons by nonmetallic atoms. ...
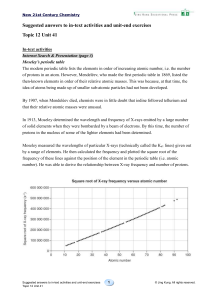
Ex. 41 Answer
... Thus, compared with O, the effective nuclear charge felt by the outermost shell electrons of F is greater. The electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus. So, the atomic radius of F is smaller than that of O. O and S belong to the same group. An atom of S has 1 more occupied electron shell than an a ...
... Thus, compared with O, the effective nuclear charge felt by the outermost shell electrons of F is greater. The electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus. So, the atomic radius of F is smaller than that of O. O and S belong to the same group. An atom of S has 1 more occupied electron shell than an a ...
Chapt 6: Arrangement of the Elements
... • In 1829, the German chemist J. W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physical properties. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • In 1829, the German chemist J. W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physical properties. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
The Upper Limit of the Periodic Table of Elements Points out to the
... table consisting of cells (each single cell manifests a single element). The cells are joined into periods along the horizontal axis (each row represents a single period), while the cells are joined into groups along the vertical axis (each column represents a single group). The resulting system is ...
... table consisting of cells (each single cell manifests a single element). The cells are joined into periods along the horizontal axis (each row represents a single period), while the cells are joined into groups along the vertical axis (each column represents a single group). The resulting system is ...
The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5) – Part 2
... 3. Group trend – ionization energy increases as you move up a group (or decreases as you move down a group). In general, as you do down a group the ionization energy decreases because the size of the atom is increasing and the outermost electrons are further from the nucleus. 1. Which atom has the h ...
... 3. Group trend – ionization energy increases as you move up a group (or decreases as you move down a group). In general, as you do down a group the ionization energy decreases because the size of the atom is increasing and the outermost electrons are further from the nucleus. 1. Which atom has the h ...
8th Grade Chap 4 Study Guide Answer Section
... b. can be hammered or rolled into flat sheets d. can transfer heat or electricity to another and other shapes. material. 22. The two most common alkaline earth metals are a. iron and silver. c. copper and zinc. b. calcium and magnesium. d. sodium and potassium. 23. Which of the following statements ...
... b. can be hammered or rolled into flat sheets d. can transfer heat or electricity to another and other shapes. material. 22. The two most common alkaline earth metals are a. iron and silver. c. copper and zinc. b. calcium and magnesium. d. sodium and potassium. 23. Which of the following statements ...
Periodic Properties of Elements
... Metals with more than one oxidation states exhibit more metallic behavior in their lower oxidation states - they acts as a reducing agent; An element with more than one oxidation state is a strong oxidizing agent when in its highest oxidation state. Trends Across the Periodic Among The Second Pe ...
... Metals with more than one oxidation states exhibit more metallic behavior in their lower oxidation states - they acts as a reducing agent; An element with more than one oxidation state is a strong oxidizing agent when in its highest oxidation state. Trends Across the Periodic Among The Second Pe ...
The Modern Periodic Table
... The transition elements are divided into transition metals and inner transition metals. The two sets of inner transition metals are called the lanthanide series and actinide series and are located at the bottom of the periodic table. ...
... The transition elements are divided into transition metals and inner transition metals. The two sets of inner transition metals are called the lanthanide series and actinide series and are located at the bottom of the periodic table. ...
UNIT-3 Classification of elements and periodicity
... 3. What observation made by Moseley showed that atomic number and not atomic mass is more fundamental property of an element? 4. With respect to long form of periodic table what are groups and periods? 5. How many groups and periods are present in the long form of periodic table? 6. How many element ...
... 3. What observation made by Moseley showed that atomic number and not atomic mass is more fundamental property of an element? 4. With respect to long form of periodic table what are groups and periods? 5. How many groups and periods are present in the long form of periodic table? 6. How many element ...
Periodic Table - Red Deer Public
... elements of his day. He observed that when classified according to atomic mass, similar properties appeared to repeat for about every eighth element His Attempt to correlate the properties of elements with musical scales subjected him to ridicule. In the end his work was acknowledged and he was vind ...
... elements of his day. He observed that when classified according to atomic mass, similar properties appeared to repeat for about every eighth element His Attempt to correlate the properties of elements with musical scales subjected him to ridicule. In the end his work was acknowledged and he was vind ...
File
... Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807.9.1) Can I use the Periodic Table to determine the properties of an element? (SPI0807.9.9) ...
... Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807.9.1) Can I use the Periodic Table to determine the properties of an element? (SPI0807.9.9) ...
chemistry - Illini West High School
... • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
... • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
Patterns in The Periodic Table
... absent student's appearance and temperament. In this way, we can predict the properties of any element simply by its assigned location in the periodic table. That is the power of the periodic table for the elements. ...
... absent student's appearance and temperament. In this way, we can predict the properties of any element simply by its assigned location in the periodic table. That is the power of the periodic table for the elements. ...
Intro To The Periodic Table
... How Was The Periodic Table Created? • Throughout history elements were discovered at different times but they were not put in any order to classify them. ...
... How Was The Periodic Table Created? • Throughout history elements were discovered at different times but they were not put in any order to classify them. ...
Periodic Table Trends Notes s4
... Cations more electrons Smaller than the corresponding atom Negatively charged ions formed ...
... Cations more electrons Smaller than the corresponding atom Negatively charged ions formed ...