Science - Rainhill High School
... the outer shell of electrons of the atoms • predict properties from given trends down the group. Describe the structure and bonding of metals in group 1 of the periodic table; the elements in Group 1 of the periodic table, known as the alkali metals: Students should be able to: • explain how propert ...
... the outer shell of electrons of the atoms • predict properties from given trends down the group. Describe the structure and bonding of metals in group 1 of the periodic table; the elements in Group 1 of the periodic table, known as the alkali metals: Students should be able to: • explain how propert ...
Document
... the behaviour of matter during chemical reactions. As you can see in Figure 3.1, the model of the atom that resulted from this theory was very simple. The second conceptual tool was Dmitri Mendeleev’s periodic table, which listed the known elements in order of increasing atomic mass. The resulting o ...
... the behaviour of matter during chemical reactions. As you can see in Figure 3.1, the model of the atom that resulted from this theory was very simple. The second conceptual tool was Dmitri Mendeleev’s periodic table, which listed the known elements in order of increasing atomic mass. The resulting o ...
Patterns in the periodic Table
... a higher first ionisation energy a higher mass number more occupied electron energy levels a larger nuclear charge ...
... a higher first ionisation energy a higher mass number more occupied electron energy levels a larger nuclear charge ...
Chapter 2 - UBC Physics
... alkali metals first (combining power of one), alkaline earths (two), etc. However, it was difficult to classify metals such as copper and mercury which had multiple combining powers, sometimes one and other times two. While trying to sort out this dilemma, Mendeleev noticed patterns in the propertie ...
... alkali metals first (combining power of one), alkaline earths (two), etc. However, it was difficult to classify metals such as copper and mercury which had multiple combining powers, sometimes one and other times two. While trying to sort out this dilemma, Mendeleev noticed patterns in the propertie ...
Chapter 7. Periodic Properties of the Elements
... • trends within row or column form patterns help make predictions of chemical properties and reactivity • Mendeleev and Meyer arranged elements in order of increasing atomic weight • certain elements were missing from this scheme • example, 1871 Mendeleev noted As belonged underneath P and not Si, t ...
... • trends within row or column form patterns help make predictions of chemical properties and reactivity • Mendeleev and Meyer arranged elements in order of increasing atomic weight • certain elements were missing from this scheme • example, 1871 Mendeleev noted As belonged underneath P and not Si, t ...
Organization of the Periodic Table
... • An isotope is an atom that has the same number of protons as other atoms of the same element do but that has a different number of neutrons. • Example: Hydrogen has three isotopes, shown ...
... • An isotope is an atom that has the same number of protons as other atoms of the same element do but that has a different number of neutrons. • Example: Hydrogen has three isotopes, shown ...
Inorganic and Physical Chemistry - university of nairobi staff profiles
... A mixture is a combination of two or more substances in which the substances retain their distinct identities. It is formed by physically mixing substances and but not by chemical combination. ...
... A mixture is a combination of two or more substances in which the substances retain their distinct identities. It is formed by physically mixing substances and but not by chemical combination. ...
Chapter 8
... y What is the periodic trend for ionization energy? y What is the difference between 1st and successive ionization energies? y ...
... y What is the periodic trend for ionization energy? y What is the difference between 1st and successive ionization energies? y ...
Solutions Tutorial 8
... General Principles of Chemistry – CHEM110 Tutorial 8 – 9th and 11th April 2014 Inorganic Chemistry Atomic Radii ...
... General Principles of Chemistry – CHEM110 Tutorial 8 – 9th and 11th April 2014 Inorganic Chemistry Atomic Radii ...
Chemistry A- Periodic Table Packet
... Example: All group 1 elements have one electron in the outer shells and all group 2 elements have two electrons in their outer shells. Periods (horizontal, “back and forth”) – same number of electron shells around nucleus Example: The elements in the first period all have one shell, the elements in ...
... Example: All group 1 elements have one electron in the outer shells and all group 2 elements have two electrons in their outer shells. Periods (horizontal, “back and forth”) – same number of electron shells around nucleus Example: The elements in the first period all have one shell, the elements in ...
General Principles of Chemistry – CHEM110 Tutorial 8 – 9 and 11
... General Principles of Chemistry – CHEM110 Tutorial 8 – 9th and 11th April 2014 Inorganic Chemistry Atomic Radii ...
... General Principles of Chemistry – CHEM110 Tutorial 8 – 9th and 11th April 2014 Inorganic Chemistry Atomic Radii ...
Bonding 1 - Deans Community High School
... negative electron will decrease and consequently the ionisation energy will decrease. This explains the fall in ionisation energy as we descend a group. As the nuclear charge increases, its attraction for the outermost electron/s increases and consequently ionisation energy increases. This explains ...
... negative electron will decrease and consequently the ionisation energy will decrease. This explains the fall in ionisation energy as we descend a group. As the nuclear charge increases, its attraction for the outermost electron/s increases and consequently ionisation energy increases. This explains ...
The Periodic Table
... The Periodic Table: Periods The periodic table provides information about the locations of electrons in an atomic of an element based on the period in which the element appears. There are seven periods in the periodic table. The two rows at the bottom of the table are actually parts of Period ...
... The Periodic Table: Periods The periodic table provides information about the locations of electrons in an atomic of an element based on the period in which the element appears. There are seven periods in the periodic table. The two rows at the bottom of the table are actually parts of Period ...
The Periodic Table
... Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po Fr Ra Ac Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg increase in reactivity 19 of 39 ...
... Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po Fr Ra Ac Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg increase in reactivity 19 of 39 ...
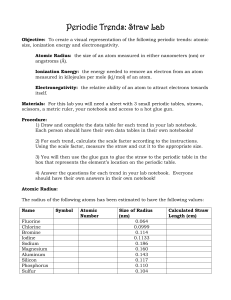
Periodic Trends: Straw Lab
... 1) In a sentence, describe the relationship between atomic number and the size of the atom’s radius going down a group on the periodic table. 2) Why does this relationship make sense in relation to what you know about elements on the periodic table? 3) In a sentence, describe the relationship betwee ...
... 1) In a sentence, describe the relationship between atomic number and the size of the atom’s radius going down a group on the periodic table. 2) Why does this relationship make sense in relation to what you know about elements on the periodic table? 3) In a sentence, describe the relationship betwee ...
xi_chem_ch3_classification of elements
... 21. Fourth and fifth period contains 18 elements 22. Sixth period contains 32 elements 23. In the modern periodic table, 14 elements of both sixth and seventh periods i.e. lanthanoids and actinoids respectively are placed separately at the bottom of the periodic table. 24. Elements with atomic numbe ...
... 21. Fourth and fifth period contains 18 elements 22. Sixth period contains 32 elements 23. In the modern periodic table, 14 elements of both sixth and seventh periods i.e. lanthanoids and actinoids respectively are placed separately at the bottom of the periodic table. 24. Elements with atomic numbe ...
Chapter 5
... • The trend to smaller atoms across a period is caused by the increasing positive charge of the nucleus, which attracts electrons toward the nucleus. • Atoms tend to be larger the farther down in a group they are found. • The trend to larger atoms down a group is caused by the increasing size of the ...
... • The trend to smaller atoms across a period is caused by the increasing positive charge of the nucleus, which attracts electrons toward the nucleus. • Atoms tend to be larger the farther down in a group they are found. • The trend to larger atoms down a group is caused by the increasing size of the ...
atomic radii
... • therefore, the alkali metals will lose electrons very easily (only one to lose) and have low IE, and....... • the noble gases (with 8 valence e-) will hold onto those electrons for dear life, and have very high IE. • this explains why the alkali metals are very reactive with most substances, and ...
... • therefore, the alkali metals will lose electrons very easily (only one to lose) and have low IE, and....... • the noble gases (with 8 valence e-) will hold onto those electrons for dear life, and have very high IE. • this explains why the alkali metals are very reactive with most substances, and ...
atomic radii
... • therefore, the alkali metals will lose electrons very easily (only one to lose) and have low IE, and....... • the noble gases (with 8 valence e-) will hold onto those electrons for dear life, and have very high IE. • this explains why the alkali metals are very reactive with most substances, and ...
... • therefore, the alkali metals will lose electrons very easily (only one to lose) and have low IE, and....... • the noble gases (with 8 valence e-) will hold onto those electrons for dear life, and have very high IE. • this explains why the alkali metals are very reactive with most substances, and ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... http://chemistry.about.com/od/elementgroups/a/lanthanides.htm On the other hand, the actinide series are of importance because of their radioactivity. All isotopes of these elements are denser, have higher melting and boiling points than the alkaline earth metals, but similar to the lanthanide serie ...
... http://chemistry.about.com/od/elementgroups/a/lanthanides.htm On the other hand, the actinide series are of importance because of their radioactivity. All isotopes of these elements are denser, have higher melting and boiling points than the alkaline earth metals, but similar to the lanthanide serie ...
Jan 26, 2015 - cloudfront.net
... • Leave planner out for grading today • Periodic Table coloring – Make your category key and color in table ...
... • Leave planner out for grading today • Periodic Table coloring – Make your category key and color in table ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... Linus Pauling, an American chemist (and winner of two Nobel prizes!) came up with the concept of electronegativity in 1932 to help explain the nature of chemical bonds. Since fluorine is the most electronegative element (has the greatest attraction for the bonding electrons) he assigned it a value a ...
... Linus Pauling, an American chemist (and winner of two Nobel prizes!) came up with the concept of electronegativity in 1932 to help explain the nature of chemical bonds. Since fluorine is the most electronegative element (has the greatest attraction for the bonding electrons) he assigned it a value a ...
The Periodic Table
... Elements in Group 6 only need two more electrons to fill their outer level. Elements in Group 7 only need one more electron to fill their outer level. ...
... Elements in Group 6 only need two more electrons to fill their outer level. Elements in Group 7 only need one more electron to fill their outer level. ...