Catalyst
... Catalyst 1. Open up the Bohr’s Model educanon video for today’s class. Complete the questions associated with the video. 2. Put your laptop at 45 degrees and place your eyes on me so I know when you’re finished. ...
... Catalyst 1. Open up the Bohr’s Model educanon video for today’s class. Complete the questions associated with the video. 2. Put your laptop at 45 degrees and place your eyes on me so I know when you’re finished. ...
Chapter_6_Notes_Periodic
... This collection of gaseous elements was referred to as the INERT GASES because they showed no chemical reactivity. They are also known as NOBLE GASES to convey the nonreactivity nature of these gases. Similarly, copper, silver and gold are referred to as Noble metals because of their resistance to c ...
... This collection of gaseous elements was referred to as the INERT GASES because they showed no chemical reactivity. They are also known as NOBLE GASES to convey the nonreactivity nature of these gases. Similarly, copper, silver and gold are referred to as Noble metals because of their resistance to c ...
tro2_ppt_lecture_02 - Louisiana Tech University
... • The nucleus has essentially the entire mass of the atom. – The electrons weigh so little they give practically no mass to the atom. • The nucleus is positively charged. – The amount of positive charge balances the negative charge of the ...
... • The nucleus has essentially the entire mass of the atom. – The electrons weigh so little they give practically no mass to the atom. • The nucleus is positively charged. – The amount of positive charge balances the negative charge of the ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
... • The nucleus has essentially the entire mass of the atom. – The electrons weigh so little they give practically no mass to the atom. • The nucleus is positively charged. – The amount of positive charge balances the negative charge of the ...
... • The nucleus has essentially the entire mass of the atom. – The electrons weigh so little they give practically no mass to the atom. • The nucleus is positively charged. – The amount of positive charge balances the negative charge of the ...
Chapter 3
... "law of octaves", about 55 elements: pattern of reactivity follows after 8 elements. However, no one had found a clear "order" in their properties until Mendeleev, Dmitri (18341907) arranged 63 then known elements in the order of increasing atomic mass in a periodic table and showed some chemical pr ...
... "law of octaves", about 55 elements: pattern of reactivity follows after 8 elements. However, no one had found a clear "order" in their properties until Mendeleev, Dmitri (18341907) arranged 63 then known elements in the order of increasing atomic mass in a periodic table and showed some chemical pr ...
File
... Include: periods, families (groups). Be able to: Identify periods vs. families on a periodic table of element and identify similarities within family members and period members. This includes the number of valence electrons, if the element is a metal, non-metal or metalloid, the number of shells the ...
... Include: periods, families (groups). Be able to: Identify periods vs. families on a periodic table of element and identify similarities within family members and period members. This includes the number of valence electrons, if the element is a metal, non-metal or metalloid, the number of shells the ...
Ch. 5 - Periodic Law
... In general, ionization energies of the main-group elements increases across a period. The increase is caused by increasing nuclear charge. A higher charge more strongly attracts electrons in the same energy level. Among the main-group elements, ionization energies generally decreases down the groups ...
... In general, ionization energies of the main-group elements increases across a period. The increase is caused by increasing nuclear charge. A higher charge more strongly attracts electrons in the same energy level. Among the main-group elements, ionization energies generally decreases down the groups ...
Honors Chemistry
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
Primeasia University
... properties of the elements (i.e. similar elements) are repeated after definite regular intervals or period. ...
... properties of the elements (i.e. similar elements) are repeated after definite regular intervals or period. ...
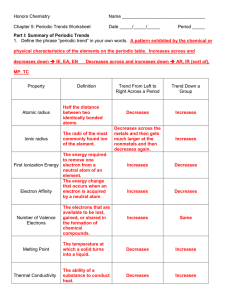
AP CHEMISTRY Periodic Trends Worksheet
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
Chapter 6: The Periodic Table
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
The Modern Periodic Table
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
Introduction: Elements on the periodic table are arranged
... Introduction: Elements on the periodic table are arranged in such a way that they exhibit patterns in their properties. In this activity, you will graph their properties and analyze their patterns. You will determine the trends for the following properties: atomic radius, electronegativity, and ioni ...
... Introduction: Elements on the periodic table are arranged in such a way that they exhibit patterns in their properties. In this activity, you will graph their properties and analyze their patterns. You will determine the trends for the following properties: atomic radius, electronegativity, and ioni ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends
... The properties of the elements exhibit trends and these trends can be predicted with the help of the periodic table. They can also be explained and understood by analyzing the electron configurations of the elements. This is because, elements tend to gain or lose valence electrons to achieve the sta ...
... The properties of the elements exhibit trends and these trends can be predicted with the help of the periodic table. They can also be explained and understood by analyzing the electron configurations of the elements. This is because, elements tend to gain or lose valence electrons to achieve the sta ...
Lorna Merklinger
... periodic properties? Learning Goal: 1. Students will be able to utilize the periodic table and understand how it is organized. Objectives: 1. Describe the atomic structure of an element using the periodic table. 2. Identify patterns on the periodic table. 3. Demonstrate knowledge of how elements com ...
... periodic properties? Learning Goal: 1. Students will be able to utilize the periodic table and understand how it is organized. Objectives: 1. Describe the atomic structure of an element using the periodic table. 2. Identify patterns on the periodic table. 3. Demonstrate knowledge of how elements com ...
Honors Chemistry
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
Table of Contents Chapter 5 Objectives Chapter 5 Mendeleev and
... has a positive or negative charge. • Sodium (Na), for example, easily loses an electron to form Na+. • Any process that results in the formation of an ion is referred to as ionization. • The energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom of an element is the ionization ...
... has a positive or negative charge. • Sodium (Na), for example, easily loses an electron to form Na+. • Any process that results in the formation of an ion is referred to as ionization. • The energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom of an element is the ionization ...
The atom: Ionisation energy and the periodic table
... separate names to identify them. The characteristics of each group are mostly determined by the electron con guration of the atoms of the element. • Group 1: These elements are known as the ...
... separate names to identify them. The characteristics of each group are mostly determined by the electron con guration of the atoms of the element. • Group 1: These elements are known as the ...
Answer
... arranged the elements in periods and groups in order of their increasing atomic weight. He placed the elements with similar properties in the same group. However, he did not stick to this arrangement for long. He found out that if the elements were arranged strictly in order of their increasing atom ...
... arranged the elements in periods and groups in order of their increasing atomic weight. He placed the elements with similar properties in the same group. However, he did not stick to this arrangement for long. He found out that if the elements were arranged strictly in order of their increasing atom ...
Section 2 Electron Configuration and the Periodic
... • A positive ion is known as a cation. • The formation of a cation by the loss of one or more electrons always leads to a decrease in atomic radius. • The electron cloud becomes smaller. • The remaining electrons are drawn closer to the nucleus by its ...
... • A positive ion is known as a cation. • The formation of a cation by the loss of one or more electrons always leads to a decrease in atomic radius. • The electron cloud becomes smaller. • The remaining electrons are drawn closer to the nucleus by its ...
File
... -------------1. The ion is positively charged and its radius is smaller than the radius of the atom. 2. The ion is positively charged and its radius 5. is larger than the radius of the atom. Which two characteristics are associated with 3. The ion is negatively charged and its radius metals? is smal ...
... -------------1. The ion is positively charged and its radius is smaller than the radius of the atom. 2. The ion is positively charged and its radius 5. is larger than the radius of the atom. Which two characteristics are associated with 3. The ion is negatively charged and its radius metals? is smal ...
The Periodic Table Test Review (3a-3b)
... 16. Identify the representative elements from the list given below. Na, Ca, Sc, Co, Ni, Si, N, Se, Cl, Ge 17. Why is argon placed before potassium in the modern periodic table? 18. Why do elements in the same group have similar properties? 19. Why is the size of a sodium ion (Na+) less than that of ...
... 16. Identify the representative elements from the list given below. Na, Ca, Sc, Co, Ni, Si, N, Se, Cl, Ge 17. Why is argon placed before potassium in the modern periodic table? 18. Why do elements in the same group have similar properties? 19. Why is the size of a sodium ion (Na+) less than that of ...
CHAPTER 8 PERIODIC RELATIONSHIPS AMONG THE ELEMENTS
... electrons are removed from the highest occupied n shell. In the formation of an anion from the neutral atom of a representative element, one or more electrons are added to the highest partially filled n shell. Representative elements typically gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable noble gas ele ...
... electrons are removed from the highest occupied n shell. In the formation of an anion from the neutral atom of a representative element, one or more electrons are added to the highest partially filled n shell. Representative elements typically gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable noble gas ele ...
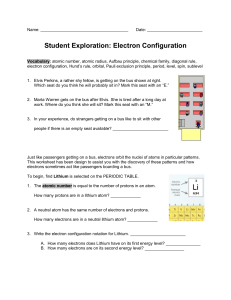
Student Exploration: Electron Configuration
... 9. Apply: Atoms are most stable when their outermost level is full. If their outermost level is not full, atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons until the level fills up. While doing this, atoms react and form chemical bonds with other atoms. Based on this, what can you infer about the reactiv ...
... 9. Apply: Atoms are most stable when their outermost level is full. If their outermost level is not full, atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons until the level fills up. While doing this, atoms react and form chemical bonds with other atoms. Based on this, what can you infer about the reactiv ...