The History of the Modern Periodic Table
... decided a better arrangement was possible and made a copy of that, which had similar elements grouped in vertical columns, unlike his first table, which grouped them horizontally. These historic documents still exist. That Mendeleev realized that he had discovered, rather than designed, the periodic ...
... decided a better arrangement was possible and made a copy of that, which had similar elements grouped in vertical columns, unlike his first table, which grouped them horizontally. These historic documents still exist. That Mendeleev realized that he had discovered, rather than designed, the periodic ...
Learning Targets
... 1. State the location and charges of each subatomic particle within the atom 2. Use the periodic table to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom 3. Define atomic number as it relates to subatomic particles 4. Define atomic mass as it relates to subatomic particles. 5. Dr ...
... 1. State the location and charges of each subatomic particle within the atom 2. Use the periodic table to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom 3. Define atomic number as it relates to subatomic particles 4. Define atomic mass as it relates to subatomic particles. 5. Dr ...
The Periodic Table PP
... • Have some characteristics of metals and have some characteristics of non-metals ...
... • Have some characteristics of metals and have some characteristics of non-metals ...
How is the Periodic Table organized?
... physical properties are found to show a repeating, or periodic, pattern. • Elements within a family have similar properties. ...
... physical properties are found to show a repeating, or periodic, pattern. • Elements within a family have similar properties. ...
b. matching
... 24) ____________________________________ is used to make smoke bombs, pyrotechnics and matches. OXYGEN GROUP 25) The Oxygen Group is Group #_____________ on the periodic table. 26) The common e- configuration for the nitrogen group is__________________. 27) The elements in the nitrogen group have __ ...
... 24) ____________________________________ is used to make smoke bombs, pyrotechnics and matches. OXYGEN GROUP 25) The Oxygen Group is Group #_____________ on the periodic table. 26) The common e- configuration for the nitrogen group is__________________. 27) The elements in the nitrogen group have __ ...
Chemistry Definitions
... liquid to gaseous water and carbon dioxide or when iron corrodes it mixes with other elements (mostly oxygen) When a chemical change occurs, the atoms that make up the substance are rearranged to form a new compound. ...
... liquid to gaseous water and carbon dioxide or when iron corrodes it mixes with other elements (mostly oxygen) When a chemical change occurs, the atoms that make up the substance are rearranged to form a new compound. ...
Periodic Table Trends
... added to the outermost shell. For example, sodium has one electron in shell 3, followed by magnesium which has two electrons in shell 3. ...
... added to the outermost shell. For example, sodium has one electron in shell 3, followed by magnesium which has two electrons in shell 3. ...
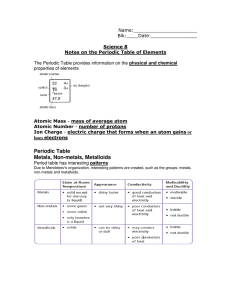
Periodic Table Metals, Non
... Atomic Mass - mass of average atom Atomic Number - number of protons Ion Charge - electric charge that forms when an atom gains or loses electrons ...
... Atomic Mass - mass of average atom Atomic Number - number of protons Ion Charge - electric charge that forms when an atom gains or loses electrons ...
Periodic Table
... valance shell. Atoms will often take, loose or share electrons on order to fill the valance. All atoms that have the same # of electrons behave in a similar fashion. The atoms with fewer electrons on the valance and/or the fewer electrons needed to fill the valance are very reactive and combine easi ...
... valance shell. Atoms will often take, loose or share electrons on order to fill the valance. All atoms that have the same # of electrons behave in a similar fashion. The atoms with fewer electrons on the valance and/or the fewer electrons needed to fill the valance are very reactive and combine easi ...
Chapter 22- Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... iv. ______________________________ is the weighted-average mass of an element’s isotopes. v. Average atomic mass is closest to its most a_______________ isotope. The Periodic Table a. Elements are organized in the _________________ by increasing atomic number. i. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev ...
... iv. ______________________________ is the weighted-average mass of an element’s isotopes. v. Average atomic mass is closest to its most a_______________ isotope. The Periodic Table a. Elements are organized in the _________________ by increasing atomic number. i. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev ...
Chapter 22- Properties of Atoms and the Periodic
... iv. ______________________________ is the weighted-average mass of an element’s isotopes. v. Average atomic mass is closest to its most a_______________ isotope. The Periodic Table a. Elements are organized in the _________________ by increasing atomic number. i. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev ...
... iv. ______________________________ is the weighted-average mass of an element’s isotopes. v. Average atomic mass is closest to its most a_______________ isotope. The Periodic Table a. Elements are organized in the _________________ by increasing atomic number. i. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev ...
Notes - RCSD
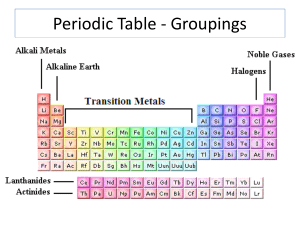
... Group 18 is called the Noble Gases. These gases are completely unreactive (they do not make compounds with any other elements). The large block of elements in the middle of the Periodic Table is called the Transition Metals. These metals are very good conductors and are not very reactive, which ...
... Group 18 is called the Noble Gases. These gases are completely unreactive (they do not make compounds with any other elements). The large block of elements in the middle of the Periodic Table is called the Transition Metals. These metals are very good conductors and are not very reactive, which ...
The Periodic Table of Elements
... They are highly reactive but are slightly less reactive and harder than the Group 1 metals. The reactivity of both Group 1 and 2 metals increases with increasing atomic number. ...
... They are highly reactive but are slightly less reactive and harder than the Group 1 metals. The reactivity of both Group 1 and 2 metals increases with increasing atomic number. ...
General Structure of the Periodic Table
... In the sixty-seven years from Dalton's formulation of atomic weight to Mendeleyev's periodic table many scientists had tried to create a working organizational structure for the elements. Mendeleyev succeeded where others failed because he realized that there existed a number of as yet unknown eleme ...
... In the sixty-seven years from Dalton's formulation of atomic weight to Mendeleyev's periodic table many scientists had tried to create a working organizational structure for the elements. Mendeleyev succeeded where others failed because he realized that there existed a number of as yet unknown eleme ...
CPA Study Guide for Chapter 6 Test The Periodic Table Know the
... Be able to predict the charge on an ion based on the atoms tendency to obtain a noble gas electron configuration Be able to write/identify an element form its electron configuration AND locate the position on the Periodic Table from the outer electron configuration Recall that two trends (ionization ...
... Be able to predict the charge on an ion based on the atoms tendency to obtain a noble gas electron configuration Be able to write/identify an element form its electron configuration AND locate the position on the Periodic Table from the outer electron configuration Recall that two trends (ionization ...
Periodic Table of Elements – (155 points)
... 2. These are the metals you are probably most familiar: copper, tin, zinc, __________, nickel, _____________, and __________________. 3. They are good ____________________ of heat and electricity. 4. The compounds of transition metals are usually _____________________ colored and are often used to c ...
... 2. These are the metals you are probably most familiar: copper, tin, zinc, __________, nickel, _____________, and __________________. 3. They are good ____________________ of heat and electricity. 4. The compounds of transition metals are usually _____________________ colored and are often used to c ...
Slide 1 - Herricks
... Electronegativity- The ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound As you move across a period EN increases because nuclear charge increases and shielding effect remains constant so the nucleus is able to attract electrons better. As you move down a group EN decreases be ...
... Electronegativity- The ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound As you move across a period EN increases because nuclear charge increases and shielding effect remains constant so the nucleus is able to attract electrons better. As you move down a group EN decreases be ...
Chapter 6 review
... a. Ne, O, C, Be c. K, Se, Br, Kr b. C, Si, Ge, Sn d. He, Ne, Ar, Kr 3. A positive ion (cation), like K+1 has a _larger/smaller_ radius than the neutral atom of potassium. 4. A negative ion (anion), like Br-1 has a _larger/smaller_ radius than the neutral atom of bromine. 5. Circle the ion in each pa ...
... a. Ne, O, C, Be c. K, Se, Br, Kr b. C, Si, Ge, Sn d. He, Ne, Ar, Kr 3. A positive ion (cation), like K+1 has a _larger/smaller_ radius than the neutral atom of potassium. 4. A negative ion (anion), like Br-1 has a _larger/smaller_ radius than the neutral atom of bromine. 5. Circle the ion in each pa ...
Quiz name: Unit 2 Review (so far)
... In the article we read "A Number's Game", scientists were making element 119 by: A ...
... In the article we read "A Number's Game", scientists were making element 119 by: A ...
Revision map for the Periodic Table
... 1. The Periodic Table is a way of arranging what we know about the chemical elements. 2. Each element in the Periodic Table is a different type of atom. 3. Each element has a different atomic number. 4. The Periodic Table is arranged in atomic number order. 5. Each atom has an atomic number. 6. An e ...
... 1. The Periodic Table is a way of arranging what we know about the chemical elements. 2. Each element in the Periodic Table is a different type of atom. 3. Each element has a different atomic number. 4. The Periodic Table is arranged in atomic number order. 5. Each atom has an atomic number. 6. An e ...
Periodic Table - Jefferson Lab
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
8.2 Families and Periods of the Periodic Table Lesson Objectives
... of carbon and silicon. Instead, arsenic matched the chemical characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus. Mendeleev placed arsenic in the column which matched arsenic’s chemistry and assumed that there was an undiscovered element that would fit chemically with the carbon column. As a result, Mendeleev ...
... of carbon and silicon. Instead, arsenic matched the chemical characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus. Mendeleev placed arsenic in the column which matched arsenic’s chemistry and assumed that there was an undiscovered element that would fit chemically with the carbon column. As a result, Mendeleev ...
Chapter 10
... (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium) 8. Alkaline-earth metal-one of the elements of Group 2 of the periodic table (beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium) 9. Halogen-one of the elements of Group 17 of the periodic table (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodi ...
... (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium) 8. Alkaline-earth metal-one of the elements of Group 2 of the periodic table (beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium) 9. Halogen-one of the elements of Group 17 of the periodic table (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodi ...