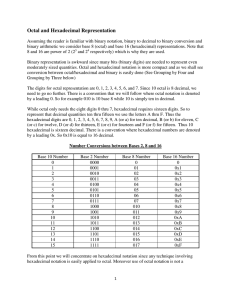
Octal and Hexadecimal Representation
... 8 and 16 are power of 2 (23 and 24 respectively) which is why they are used. Binary representation is awkward since many bits (binary digits) are needed to represent even moderately sized quantities. Octal and hexadecimal notation is more compact and as we shall see conversion between octal/hexadeci ...
... 8 and 16 are power of 2 (23 and 24 respectively) which is why they are used. Binary representation is awkward since many bits (binary digits) are needed to represent even moderately sized quantities. Octal and hexadecimal notation is more compact and as we shall see conversion between octal/hexadeci ...
CIS541_08_MonteCarlo
... • Problem: What is the probability that 10 dice throws add up exactly to 32? • Exact Way. Calculate this exactly by counting all possible ways of making 32 from 10 dice. • Approximate (Lazy) Way. Simulate throwing the dice (say 500 times), count the number of times the results add up to 32, and divi ...
... • Problem: What is the probability that 10 dice throws add up exactly to 32? • Exact Way. Calculate this exactly by counting all possible ways of making 32 from 10 dice. • Approximate (Lazy) Way. Simulate throwing the dice (say 500 times), count the number of times the results add up to 32, and divi ...
Grade 6 – Number and Operation
... checking induced errors and the reasonableness of the solution. CLE 3103.1.3 Develop inductive and deductive reasoning to independently make and evaluate mathematical arguments and construct appropriate proofs; include various types of reasoning, logic, and intuition. CLE 3103.1.4 Move flexibly betw ...
... checking induced errors and the reasonableness of the solution. CLE 3103.1.3 Develop inductive and deductive reasoning to independently make and evaluate mathematical arguments and construct appropriate proofs; include various types of reasoning, logic, and intuition. CLE 3103.1.4 Move flexibly betw ...
nov 7-10
... c. Recognize when ordered pairs are reflections of each other on the coordinate plane across one axis, both axes, or the origin. d. Plot rational numbers on number lines and ordered pairs on coordinate planes. 6.NS.7 Understand and apply the concepts of comparing, ordering, and finding absolute valu ...
... c. Recognize when ordered pairs are reflections of each other on the coordinate plane across one axis, both axes, or the origin. d. Plot rational numbers on number lines and ordered pairs on coordinate planes. 6.NS.7 Understand and apply the concepts of comparing, ordering, and finding absolute valu ...
Elementary mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. The most basic topics in elementary mathematics are arithmetic and geometry. Beginning in the last decades of the 20th century, there has been an increased emphasis on problem solving. Elementary mathematics is used in everyday life in such activities as making change, cooking, buying and selling stock, and gambling. It is also an essential first step on the path to understanding science.In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics are algebra and trigonometry. Calculus, even though it is often taught to advanced secondary school students, is usually considered college level mathematics.