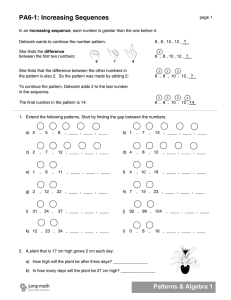
Pepperell Middle School
... • apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide rational numbers. • understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distribut ...
... • apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide rational numbers. • understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distribut ...
17(2)
... occur and all relatively prime pairs a, o will occur. For all elements of this same sequence that appear as SUMMENGLIED, that same element will be relatively prime to all smaller-valued elements that are STAMMGLIED. Stern pointed out that this is also a result of (6). (9) The last row in which the n ...
... occur and all relatively prime pairs a, o will occur. For all elements of this same sequence that appear as SUMMENGLIED, that same element will be relatively prime to all smaller-valued elements that are STAMMGLIED. Stern pointed out that this is also a result of (6). (9) The last row in which the n ...
McCallum ch 08
... So the domain of f is the set of all values on the input axis for which there is a corresponding point on the graph. For example, Figure 8.1 shows the graph of k( x) x 1, which we saw in Example 1(d) with domain x ≥ 1. The graph has no portion to the left of x = 1, starts at (1, 0), and has poin ...
... So the domain of f is the set of all values on the input axis for which there is a corresponding point on the graph. For example, Figure 8.1 shows the graph of k( x) x 1, which we saw in Example 1(d) with domain x ≥ 1. The graph has no portion to the left of x = 1, starts at (1, 0), and has poin ...
10 - Greedy Algorithms
... Input: A backpack of capacity C A set of n materials, each one with weight wi and value vi Output: The allocation of materials to the backpack that maximizes the transported value. The materials can be ”broken” em smaller pieces, that is, we can decide to take only quantity xi of object i, with 0 ≤ ...
... Input: A backpack of capacity C A set of n materials, each one with weight wi and value vi Output: The allocation of materials to the backpack that maximizes the transported value. The materials can be ”broken” em smaller pieces, that is, we can decide to take only quantity xi of object i, with 0 ≤ ...
open ppt file
... Given a simplex tableau, 1. Numbers of variables. Determine the number of basic variables and the number of nonbasic variables. These numbers do not change during the simplex process. 2. Selecting basic variables. A variable can be selected as a basic variable only if it corresponds to a column in t ...
... Given a simplex tableau, 1. Numbers of variables. Determine the number of basic variables and the number of nonbasic variables. These numbers do not change during the simplex process. 2. Selecting basic variables. A variable can be selected as a basic variable only if it corresponds to a column in t ...
Elementary mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. The most basic topics in elementary mathematics are arithmetic and geometry. Beginning in the last decades of the 20th century, there has been an increased emphasis on problem solving. Elementary mathematics is used in everyday life in such activities as making change, cooking, buying and selling stock, and gambling. It is also an essential first step on the path to understanding science.In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics are algebra and trigonometry. Calculus, even though it is often taught to advanced secondary school students, is usually considered college level mathematics.