eighth/homework2016-17/homework 19
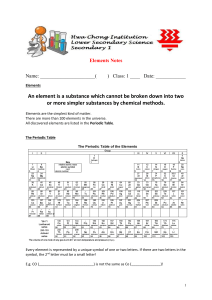
... 7. An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus. _____________________ 8. Formed when an atom loses or gains one or more electrons. ______________ 9. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. _____________ 10. A table showing a re ...
... 7. An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus. _____________________ 8. Formed when an atom loses or gains one or more electrons. ______________ 9. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. _____________ 10. A table showing a re ...
Chapter 4: Energy Guided Reading
... Read the indicated sections and answer the following questions. They are IN ORDER from the text. Page 506-511 1. What are the particles that make up the atom and where are they located? Particles that make up atoms include protons and neutrons, which are located in the nucleus, and electrons, which ...
... Read the indicated sections and answer the following questions. They are IN ORDER from the text. Page 506-511 1. What are the particles that make up the atom and where are they located? Particles that make up atoms include protons and neutrons, which are located in the nucleus, and electrons, which ...
The Chinese High School
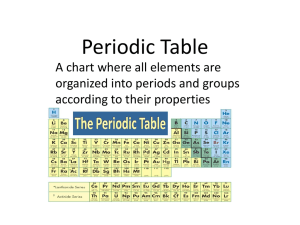
... Elements have been placed systematically into the Periodic Table according to their properties. Scientists have classified elements into 2 main groups, the metals and non-metals. Each vertical column is called a _____________________. Each group’s number is reflected at the top of the periodic table ...
... Elements have been placed systematically into the Periodic Table according to their properties. Scientists have classified elements into 2 main groups, the metals and non-metals. Each vertical column is called a _____________________. Each group’s number is reflected at the top of the periodic table ...
File
... b. magnesium 4. Which subatomicparticle plays the greatestpart in determining the propertiesof an element? c. neutron a. proton d. none of the above b. electron 5. Which of the following elementsis a transition metal? c. tellurium a. cesium d. tin b. copper 6. Which of the following groupingscontain ...
... b. magnesium 4. Which subatomicparticle plays the greatestpart in determining the propertiesof an element? c. neutron a. proton d. none of the above b. electron 5. Which of the following elementsis a transition metal? c. tellurium a. cesium d. tin b. copper 6. Which of the following groupingscontain ...
atomic number
... element has. For instance, hydrogen has 1 proton, so it’s atomic number is 1. The atomic number is unique to that element. No two elements have the same atomic number. ...
... element has. For instance, hydrogen has 1 proton, so it’s atomic number is 1. The atomic number is unique to that element. No two elements have the same atomic number. ...
Atomic and Molecular Structure – Standard 1 Review
... 1e.1 What did Rutherford’s gold foil experiment reveal about the structure of the atom? ...
... 1e.1 What did Rutherford’s gold foil experiment reveal about the structure of the atom? ...
File
... 5. Identify which scientist did each of the following. a. Named small part of matter after Greek word atamos b. Discovered electrons c. Discovered dense, positively charged nucleus d. Proposed atoms were indestructible particles shaped like a solid sphere e. Proposed that electrons move in spherical ...
... 5. Identify which scientist did each of the following. a. Named small part of matter after Greek word atamos b. Discovered electrons c. Discovered dense, positively charged nucleus d. Proposed atoms were indestructible particles shaped like a solid sphere e. Proposed that electrons move in spherical ...
Ways the Periodic Table is Organized
... table is organized. Be sure to give examples as well as the definition: A: Groups (p. 22) B: Periods (p. 22) C: Reactivity (p. 26) ...
... table is organized. Be sure to give examples as well as the definition: A: Groups (p. 22) B: Periods (p. 22) C: Reactivity (p. 26) ...
PERIODIC TABLE quiz study guide
... 10. What do the periods on the periodic table tell us about those atoms? ...
... 10. What do the periods on the periodic table tell us about those atoms? ...
Groups of the Periodic Table
... 14. Look at the graphs of the melting and boiling points. What trend (pattern) do you notice as we move across each row on the periodic table? ...
... 14. Look at the graphs of the melting and boiling points. What trend (pattern) do you notice as we move across each row on the periodic table? ...
The Periodic Table Chemistry – Leaving Cert Quick Notes
... The Periodic Table An element is a substance that cannot be split into simpler substances by chemical means. Humphry Davy isolated potassium and sodium from their hydroxide compounds. Henry Moseley used the concept of atomic number to derive another definition for an element: a substance all of tho ...
... The Periodic Table An element is a substance that cannot be split into simpler substances by chemical means. Humphry Davy isolated potassium and sodium from their hydroxide compounds. Henry Moseley used the concept of atomic number to derive another definition for an element: a substance all of tho ...
ELEMENTS and THEIR PROPERTIES
... PROPERTIES OF NONMETALS- usually gases or brittle solids at room temperature; are not malleable or ductile; usually poor conductors of heat and electricity; usually not lustrous Ionic compounds- form when nonmetals gain electrons from metals and become negative ions Covalent compounds- form when non ...
... PROPERTIES OF NONMETALS- usually gases or brittle solids at room temperature; are not malleable or ductile; usually poor conductors of heat and electricity; usually not lustrous Ionic compounds- form when nonmetals gain electrons from metals and become negative ions Covalent compounds- form when non ...
Test Question
... Use the Periodic Table on page 38 to answer Question 66. Question 66 (7 marks) (a) ...
... Use the Periodic Table on page 38 to answer Question 66. Question 66 (7 marks) (a) ...
ATOMS ELEMENTS PERIODIC TABLE MOLECULES COMPOUNDS
... • What is the difference between a compound and a molecule? • A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. • Molecular hydrogen (H2), mole ...
... • What is the difference between a compound and a molecule? • A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. • Molecular hydrogen (H2), mole ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... Most of the elements are classified as metals. Properties of elements change as you go across a period. Alkali Metals I- most reactive metals Alkaline Earth Metals II- not as reactive as Alkali Metals Halogens (VII)- most reactive non-metals; “salt formers” Noble Gases (VIII)- colorless, odorless ga ...
... Most of the elements are classified as metals. Properties of elements change as you go across a period. Alkali Metals I- most reactive metals Alkaline Earth Metals II- not as reactive as Alkali Metals Halogens (VII)- most reactive non-metals; “salt formers” Noble Gases (VIII)- colorless, odorless ga ...
5.1 Structure of the Periodic Table
... Atomic Number = Proton Number Because atoms are electrically neutral, the atomic number is also the number of electrons. Atomic Number = Electron Number The mass number tells you the number of protons and neutrons in an atom. By subtracting the atomic number from the mass number, you can determine t ...
... Atomic Number = Proton Number Because atoms are electrically neutral, the atomic number is also the number of electrons. Atomic Number = Electron Number The mass number tells you the number of protons and neutrons in an atom. By subtracting the atomic number from the mass number, you can determine t ...
Chemistry Study Guide - Atomic structure and the Periodic Table 2010
... b. How can you use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. 7. The organization of the periodic table is based on the properties of the elements and reflects the structure of atoms. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Identify regions of the periodic table that correspo ...
... b. How can you use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. 7. The organization of the periodic table is based on the properties of the elements and reflects the structure of atoms. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Identify regions of the periodic table that correspo ...
Name: Per: _____ Date: ______ Unit 5 Redemption Packet: The
... 22. Circle the element in each pair that has the greater ionization energy. a) Lithium, boron b) Magnesium, strontium c) Cesium, aluminum 23. Arrange the following groups of elements in order of increasing ionization energy. a) Be, Mg, Sr ...
... 22. Circle the element in each pair that has the greater ionization energy. a) Lithium, boron b) Magnesium, strontium c) Cesium, aluminum 23. Arrange the following groups of elements in order of increasing ionization energy. a) Be, Mg, Sr ...
ReviewCat1 - greenslime.info
... Conductivity - ability to transfer heat and/or electricity Density - measure of a materials mass per unit volume (m/v) Luster - describes how a material reflect light Malleability - materials flexibility without breaking Metals - good conductors of heat/electricity Metalloids - have properties of bo ...
... Conductivity - ability to transfer heat and/or electricity Density - measure of a materials mass per unit volume (m/v) Luster - describes how a material reflect light Malleability - materials flexibility without breaking Metals - good conductors of heat/electricity Metalloids - have properties of bo ...
Chapter 12 The Periodic Table
... silvery in their pure form and are highly reactive. This group includes the elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K). ...
... silvery in their pure form and are highly reactive. This group includes the elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K). ...
The Atom and how it is organized - Cashmere
... The atoms of all elements are made up of a central nucleus with orbiting electrons. ◦ A nucleus is made up of positively charged PROTONS and neutral NEUTRONS. ◦ ELECTRONS are negatively charged and orbit around the nucleus. ...
... The atoms of all elements are made up of a central nucleus with orbiting electrons. ◦ A nucleus is made up of positively charged PROTONS and neutral NEUTRONS. ◦ ELECTRONS are negatively charged and orbit around the nucleus. ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.