chem 1405 chapter -5
... These are the elements of the 8A group. They have completely filled sub shells in the valence shell. 3. Transition Metals ( d - block elements) They are the elements of the groups IB and 3B through 8B. All of them are metals with incompletely filled (n-1) d sub shells. Elements of 2B have completely ...
... These are the elements of the 8A group. They have completely filled sub shells in the valence shell. 3. Transition Metals ( d - block elements) They are the elements of the groups IB and 3B through 8B. All of them are metals with incompletely filled (n-1) d sub shells. Elements of 2B have completely ...
Medical Chemistry Lecture By : Asst. LectTariq Al Mgheer of
... left. Near this line are the metalloids. These elements such as silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge), have some properties that are similar to those of nonmetals and some that are similar to those of metals. Only 90 of the 106 elements are found in nature. The others are prepared in the laboratory by ins ...
... left. Near this line are the metalloids. These elements such as silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge), have some properties that are similar to those of nonmetals and some that are similar to those of metals. Only 90 of the 106 elements are found in nature. The others are prepared in the laboratory by ins ...
Topic 3-Periodicity
... Obtain evidence for scientific theories by making and testing predictions based on them—scientists organize subjects based on structure and function; the periodic table is a key example of this. Early models of the periodic table from Mendeleev, and later Moseley, allowed for the prediction of prope ...
... Obtain evidence for scientific theories by making and testing predictions based on them—scientists organize subjects based on structure and function; the periodic table is a key example of this. Early models of the periodic table from Mendeleev, and later Moseley, allowed for the prediction of prope ...
Families of elements
... Will gain one electron to become stable -1 ions Reaction of chlorine (a halogen) with sodium (an alkali metal) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1xT4OFS03jE ...
... Will gain one electron to become stable -1 ions Reaction of chlorine (a halogen) with sodium (an alkali metal) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1xT4OFS03jE ...
Section 6.1 Development of the Modern Periodic Table
... • All group 1 elements have one valence electron. ...
... • All group 1 elements have one valence electron. ...
Naming Compounds Essential Question
... Essential Question: What are the rules for naming a compound and writing its formula? Vocabulary: monatomic ion polyatomic ion ...
... Essential Question: What are the rules for naming a compound and writing its formula? Vocabulary: monatomic ion polyatomic ion ...
Naming Compounds and Formula Writing
... One exception is we don’t write mono- if there is only one of the first element. No double vowels when writing names (oa oo) ...
... One exception is we don’t write mono- if there is only one of the first element. No double vowels when writing names (oa oo) ...
Periodic Table
... However, each succeeding shell is further from the nucleus, and is shielded from the nuclear pull by inner electrons. It is thus easier to remove electrons from outer shells which are less attracted to the nucleus. ...
... However, each succeeding shell is further from the nucleus, and is shielded from the nuclear pull by inner electrons. It is thus easier to remove electrons from outer shells which are less attracted to the nucleus. ...
Chapter 5 Section 3: Electron Configuration and Periodic Properties
... energy. When energy is absorbed it is represented by a positive number and the ion is unstable and usually decays (breaks apart back to the element). Periodic Trend for Electron Affinity – It is easier to add ...
... energy. When energy is absorbed it is represented by a positive number and the ion is unstable and usually decays (breaks apart back to the element). Periodic Trend for Electron Affinity – It is easier to add ...
version
... All elements possess from very low to very high metallic character. The scale is from Fr to F. Fr has the most metallic character and F has the least. In groups, metallic character increases with atomic number because each successive element gets closest to Fr. In periods, metallic charact ...
... All elements possess from very low to very high metallic character. The scale is from Fr to F. Fr has the most metallic character and F has the least. In groups, metallic character increases with atomic number because each successive element gets closest to Fr. In periods, metallic charact ...
- Williamsburg High School for
... As atomic number increases within Group 15 on the Periodic Table, atomic radius ...
... As atomic number increases within Group 15 on the Periodic Table, atomic radius ...
Chemistry
... Atoms that have a filled outer shell are stable (Noble gases) all other atoms become stable by forming bonds to fill their outer shell Atoms fill their outer shell by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons with one or more atoms Ionic bonds are formed when one atom takes one or more electron from ano ...
... Atoms that have a filled outer shell are stable (Noble gases) all other atoms become stable by forming bonds to fill their outer shell Atoms fill their outer shell by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons with one or more atoms Ionic bonds are formed when one atom takes one or more electron from ano ...
Periodicity
... The outermost “s” and “p” electrons, which are largely responsible for an atom’s chemical behavior, are called valence electrons. • The elements in a group have similar properties because they have the same number of valence electrons (which means similar electron configurations). • To save space i ...
... The outermost “s” and “p” electrons, which are largely responsible for an atom’s chemical behavior, are called valence electrons. • The elements in a group have similar properties because they have the same number of valence electrons (which means similar electron configurations). • To save space i ...
Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry
... malleable = able to be hammered into thin sheets; ductile = able to be drawn into fine wire 3. List three properties of nonmetals. has a low density, low melting point, and is a poor conductor of heat and electricity 4. Solid nonmetals, such as _carbon_ and _sulfur_, have a _dull_ appearance. They _ ...
... malleable = able to be hammered into thin sheets; ductile = able to be drawn into fine wire 3. List three properties of nonmetals. has a low density, low melting point, and is a poor conductor of heat and electricity 4. Solid nonmetals, such as _carbon_ and _sulfur_, have a _dull_ appearance. They _ ...
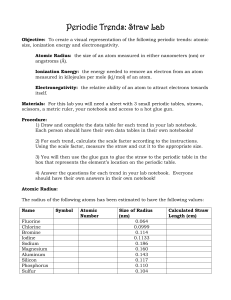
Periodic Trends: Straw Lab
... of the atom’s radius going down a group on the periodic table. 2) Why does this relationship make sense in relation to what you know about elements on the periodic table? 3) In a sentence, describe the relationship between atomic number and the size of each atom’s radius when going across a period o ...
... of the atom’s radius going down a group on the periodic table. 2) Why does this relationship make sense in relation to what you know about elements on the periodic table? 3) In a sentence, describe the relationship between atomic number and the size of each atom’s radius when going across a period o ...
groups - Northside Middle School
... Soft, silvery Good conductor of electricity React violently with water React with halogens to form salts ...
... Soft, silvery Good conductor of electricity React violently with water React with halogens to form salts ...
TCSS Physical Science Unit 2 – Atomic Structure Information
... Georgia Performance Standards: SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. a. Examine the structure of the atom in terms of: proton, electron, and neutron locations; atomic mass and atomic number; atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes); explain the relationshi ...
... Georgia Performance Standards: SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. a. Examine the structure of the atom in terms of: proton, electron, and neutron locations; atomic mass and atomic number; atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes); explain the relationshi ...
CHEM 1405 CHAPTER 5
... shells in the valence shell. 3. Transition Metals ( d - block elements) They are the elements of the groups IB and 3B through 8B. All of them are metals with incompletely filled (n-1) d sub shells. Elements of 2B have completely filled (n-1) d sub shells. But are studied along with transition metals ...
... shells in the valence shell. 3. Transition Metals ( d - block elements) They are the elements of the groups IB and 3B through 8B. All of them are metals with incompletely filled (n-1) d sub shells. Elements of 2B have completely filled (n-1) d sub shells. But are studied along with transition metals ...
The Periodic Law
... period. However, the 6th period transition elements, are about the same size as the 5th period transition elements. • This is due to the lanthanide contraction, the placement of the lanthanides after the 6s sublevel. The expected increase in size ...
... period. However, the 6th period transition elements, are about the same size as the 5th period transition elements. • This is due to the lanthanide contraction, the placement of the lanthanides after the 6s sublevel. The expected increase in size ...
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE p
... The small size of the atoms of N, O and F results in their high electonegativity values. This is reflected in the formation of relatively strong hydrogen bonds in X – H....Y, where X and Y may be N, O or F. Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen differ from other elements of their respective groups due to thei ...
... The small size of the atoms of N, O and F results in their high electonegativity values. This is reflected in the formation of relatively strong hydrogen bonds in X – H....Y, where X and Y may be N, O or F. Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen differ from other elements of their respective groups due to thei ...
Station 1: The Periodic Table 1a. Students know how to relate the
... o IE increases from left to right because the elements increase in nuclear charge in this direction. o IE decreases from top to bottom because as the atom’s shells get further away from the nucleus they are less attracted to it. Electronegativity increases from left to right and decreases from top ...
... o IE increases from left to right because the elements increase in nuclear charge in this direction. o IE decreases from top to bottom because as the atom’s shells get further away from the nucleus they are less attracted to it. Electronegativity increases from left to right and decreases from top ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.