Periodicity Jeopardy
... Ge hadn’t yet been discovered, so he left a place for it Some elements (potassium, for example) did not “fit” according to their atomic mass ...
... Ge hadn’t yet been discovered, so he left a place for it Some elements (potassium, for example) did not “fit” according to their atomic mass ...
Unit 5
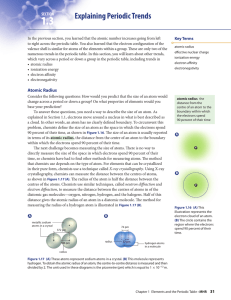
... _________________________ is the amount of energy needed to pull an electron away from an isolated atom. ...
... _________________________ is the amount of energy needed to pull an electron away from an isolated atom. ...
chapter 17 - keishabrady
... PS 2b An element is composed of a single type of atom. When elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements with similar properties. This “Periodic Table” is a consequence ...
... PS 2b An element is composed of a single type of atom. When elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements with similar properties. This “Periodic Table” is a consequence ...
Chapter 3
... Knowing the electron configuration, we can identify valence electrons and begin to predict the kinds of reactions that the elements will undergo. Elements in the last family, the noble gases, have either two or eight valence electrons. Their most important properties are their extreme stability and ...
... Knowing the electron configuration, we can identify valence electrons and begin to predict the kinds of reactions that the elements will undergo. Elements in the last family, the noble gases, have either two or eight valence electrons. Their most important properties are their extreme stability and ...
Families and Periods of the Periodic Table - CK
... The ten elements formed by filling in the 3d orbitals, as well as all other elements that have between 1 to 10 electrons in d orbitals, are called the transition elements. These elements, in general, differ from each other in the electron structure of the next-to-last energy level. For the most part ...
... The ten elements formed by filling in the 3d orbitals, as well as all other elements that have between 1 to 10 electrons in d orbitals, are called the transition elements. These elements, in general, differ from each other in the electron structure of the next-to-last energy level. For the most part ...
Chapter 3. Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
... Knowing the electron configuration, we can identify valence electrons and begin to predict the kinds of reactions that the elements will undergo. Elements in the last family, the noble gases, have either two or eight valence electrons. Their most important properties are their extreme stability and ...
... Knowing the electron configuration, we can identify valence electrons and begin to predict the kinds of reactions that the elements will undergo. Elements in the last family, the noble gases, have either two or eight valence electrons. Their most important properties are their extreme stability and ...
Chapter3
... Br) and (S Se Te).1865: Newlands – "law of octaves", about 55 elements: pattern of reactivity follows after 8 elements. However, no one had found a clear "order" in their properties until Mendeleev, Dmitri (1834-1907) arranged 63 then known elements in the order of increasing atomic mass in a period ...
... Br) and (S Se Te).1865: Newlands – "law of octaves", about 55 elements: pattern of reactivity follows after 8 elements. However, no one had found a clear "order" in their properties until Mendeleev, Dmitri (1834-1907) arranged 63 then known elements in the order of increasing atomic mass in a period ...
Chapter 5
... b. In a third-period element, the highest occupied energy level is the third main energy level, n = 3. The 1s, 2s, and 2p sublevels are completely filled. This element has the following configuration: 1s22s22p63s1 or [Ne]3s1 Because it is in Group 1, this element is likely to be more reactive than t ...
... b. In a third-period element, the highest occupied energy level is the third main energy level, n = 3. The 1s, 2s, and 2p sublevels are completely filled. This element has the following configuration: 1s22s22p63s1 or [Ne]3s1 Because it is in Group 1, this element is likely to be more reactive than t ...
Periods and Blocks of the Periodic Table
... b. In a third-period element, the highest occupied energy level is the third main energy level, n = 3. The 1s, 2s, and 2p sublevels are completely filled. This element has the following configuration: 1s22s22p63s1 or [Ne]3s1 Because it is in Group 1, this element is likely to be more reactive than t ...
... b. In a third-period element, the highest occupied energy level is the third main energy level, n = 3. The 1s, 2s, and 2p sublevels are completely filled. This element has the following configuration: 1s22s22p63s1 or [Ne]3s1 Because it is in Group 1, this element is likely to be more reactive than t ...
Chapter 6: The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... who is shown in Figure 6-2, proposed an organization scheme for the elements. Newlands noticed that when the elements were arranged by increasing atomic mass, their properties repeated every eighth element. In other words, the first and eighth elements had similar properties, the second and ninth el ...
... who is shown in Figure 6-2, proposed an organization scheme for the elements. Newlands noticed that when the elements were arranged by increasing atomic mass, their properties repeated every eighth element. In other words, the first and eighth elements had similar properties, the second and ninth el ...
LETTER TO THE EDITOR: “Cheese or Flu?” William B. Jensen
... between 1 March and 12 March 1869, thus allowing Mendeleev plenty of time to attend the meeting of the Russian Chemical Society on the 18th of March (8). According to this account, the cheese inspection trip was pertinent not because it interfered with Mendeleev's presence at the meeting but because ...
... between 1 March and 12 March 1869, thus allowing Mendeleev plenty of time to attend the meeting of the Russian Chemical Society on the 18th of March (8). According to this account, the cheese inspection trip was pertinent not because it interfered with Mendeleev's presence at the meeting but because ...
tro2_ppt_lecture_02 - Louisiana Tech University
... Isotopes are elements whose atoms differ in mass only. – They differ in mass because these elemental atoms have different number of neutrons. – They are the same element because they have the same number of protons (atomic number). – They are chemically identical. ...
... Isotopes are elements whose atoms differ in mass only. – They differ in mass because these elemental atoms have different number of neutrons. – They are the same element because they have the same number of protons (atomic number). – They are chemically identical. ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
... Isotopes are elements whose atoms differ in mass only. – They differ in mass because these elemental atoms have different number of neutrons. – They are the same element because they have the same number of protons (atomic number). – They are chemically identical. ...
... Isotopes are elements whose atoms differ in mass only. – They differ in mass because these elemental atoms have different number of neutrons. – They are the same element because they have the same number of protons (atomic number). – They are chemically identical. ...
Periodic Trends - MathewsClassroom
... The periodicity of properties of the elements is caused by the periodicity in electronic structure. The noble gases are chemically unreactive, or nearly so, because their electronic structures are stable--their atoms hold their quota of electrons strongly, have no affinity for more electrons, and ha ...
... The periodicity of properties of the elements is caused by the periodicity in electronic structure. The noble gases are chemically unreactive, or nearly so, because their electronic structures are stable--their atoms hold their quota of electrons strongly, have no affinity for more electrons, and ha ...
effective nuclear charge
... • The notion of Zeff explains this effect: For a manyelectron atom, the energies of orbitals with the same n value increase with increasing l value. – Ex) Carbon atom (1s22s22p2): The energy of the 2p orbital (l = 1) is higher than that of the 2s (l = 0) orbital. – This difference in energies is due ...
... • The notion of Zeff explains this effect: For a manyelectron atom, the energies of orbitals with the same n value increase with increasing l value. – Ex) Carbon atom (1s22s22p2): The energy of the 2p orbital (l = 1) is higher than that of the 2s (l = 0) orbital. – This difference in energies is due ...
File atoms1
... All of the above examples are considered matter because they have mass and take up space. Can you think of anything that would not be considered matter? ...
... All of the above examples are considered matter because they have mass and take up space. Can you think of anything that would not be considered matter? ...
Unit Description and Student Understandings
... Can students interpret models of atoms (Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model, Rutherford’s Model, Bohr Model, and Electron Cloud Model)? Can students list the major components of an atom and provide the charge for each? Can students recognize and explain patterns, simple periodic tendencies, and the relatio ...
... Can students interpret models of atoms (Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model, Rutherford’s Model, Bohr Model, and Electron Cloud Model)? Can students list the major components of an atom and provide the charge for each? Can students recognize and explain patterns, simple periodic tendencies, and the relatio ...
Chapter 4 notes
... Strategy Isoelectronic series are species with identical electron configurations but different nuclear charges. Determine the number of electrons in each species. The radii of isoelectronic series members decreases with increasing nuclear charge. Solution The isoelectronic series includes K+, Ar, P3 ...
... Strategy Isoelectronic series are species with identical electron configurations but different nuclear charges. Determine the number of electrons in each species. The radii of isoelectronic series members decreases with increasing nuclear charge. Solution The isoelectronic series includes K+, Ar, P3 ...
Chapter 6.3 Periodic Trends
... Sodium chloride (table salt) produced the geometric pattern in the photograph. Such a pattern can be used to calculate the position of nuclei in a solid. You will learn how properties such as atomic size are related to the location of elements in the periodic table. ...
... Sodium chloride (table salt) produced the geometric pattern in the photograph. Such a pattern can be used to calculate the position of nuclei in a solid. You will learn how properties such as atomic size are related to the location of elements in the periodic table. ...
Slide 1
... Alkali metals are so named because they are metals that react with water to make alkaline solutions. All have a single valence electron Alkali metals are usually stored in oil to keep them from reacting with the oxygen and water in the air. Because of their high reactivity, Alkali metals are never f ...
... Alkali metals are so named because they are metals that react with water to make alkaline solutions. All have a single valence electron Alkali metals are usually stored in oil to keep them from reacting with the oxygen and water in the air. Because of their high reactivity, Alkali metals are never f ...
Electron Configuration and Periodic Properties
... what is occurring. The first electron is removed from a neutral atom. However, the second electron is removed from a positive ion, so it takes more energy to remove it. Therefore, it is harder to remove each additional electron because it is being removed from an even more positive ion. The electron ...
... what is occurring. The first electron is removed from a neutral atom. However, the second electron is removed from a positive ion, so it takes more energy to remove it. Therefore, it is harder to remove each additional electron because it is being removed from an even more positive ion. The electron ...
Chemistry Part - teko classes bhopal
... compounds are low. Forces of attraction between these molecules of organic compounds are not very strong/ As these compound are largely non conductors of electricity hence the bonding in these compound does not give rise to any ions. The reactivity of elements if explained at their tendency to attai ...
... compounds are low. Forces of attraction between these molecules of organic compounds are not very strong/ As these compound are largely non conductors of electricity hence the bonding in these compound does not give rise to any ions. The reactivity of elements if explained at their tendency to attai ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.