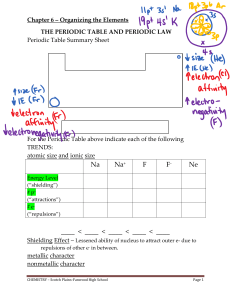
chem 1405 chapter -5
... These are the elements of the 8A group. They have completely filled sub shells in the valence shell. 3. Transition Metals ( d - block elements) They are the elements of the groups IB and 3B through 8B. All of them are metals with incompletely filled (n-1) d sub shells. Elements of 2B have completely ...
... These are the elements of the 8A group. They have completely filled sub shells in the valence shell. 3. Transition Metals ( d - block elements) They are the elements of the groups IB and 3B through 8B. All of them are metals with incompletely filled (n-1) d sub shells. Elements of 2B have completely ...
Periodic_Tendancies
... Down the Periodic Table •Family: Are arranged vertically down the periodic table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) •These elements have the same number electrons in the outer most shells, the valence shell. ...
... Down the Periodic Table •Family: Are arranged vertically down the periodic table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) •These elements have the same number electrons in the outer most shells, the valence shell. ...
Unit 3 Activity Exploring Periodic Trends… MORE! Name: Directions
... 1. Obtain a laptop and go to the website: http://www.ptable.com/ 2. Click the blue “properties” tab located at the top of the screen. 3. You will use the interactive tools and this worksheet to continue to learn about the trends (patterns) that exist within the periodic table. 4. You may use Google ...
... 1. Obtain a laptop and go to the website: http://www.ptable.com/ 2. Click the blue “properties” tab located at the top of the screen. 3. You will use the interactive tools and this worksheet to continue to learn about the trends (patterns) that exist within the periodic table. 4. You may use Google ...
Chapter 6 PP
... atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the e ...
... atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the e ...
Document
... atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the e ...
... atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the e ...
ch 6 ppt - Madison County Schools
... atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the e ...
... atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the e ...
D. - Telluride Middle/High School
... atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the e ...
... atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the e ...
The Development of the Periodic Table - wths
... The measure of how much an atom wants to gain an electron For most atoms, energy is released ...
... The measure of how much an atom wants to gain an electron For most atoms, energy is released ...
Name
... 6.1: Development of the Periodic Table 1) History of the Periodic Table – By the end of the 1700’ scientists had identified only 30 elements By the mid 1800’s with the assistance of electricity and spectroscopy additional elements were identified by using their line spectra and about 65 elements had ...
... 6.1: Development of the Periodic Table 1) History of the Periodic Table – By the end of the 1700’ scientists had identified only 30 elements By the mid 1800’s with the assistance of electricity and spectroscopy additional elements were identified by using their line spectra and about 65 elements had ...
Chapter 5- The Periodic Law
... 3. The elements in the periodic table fit into patterns better when they were arranged in increasing order according to nuclear charge, or the number of protons in the nucleus. 3. Moseley’s work led to both the modern definition of atomic number and the recognition that atomic number, not atomic mas ...
... 3. The elements in the periodic table fit into patterns better when they were arranged in increasing order according to nuclear charge, or the number of protons in the nucleus. 3. Moseley’s work led to both the modern definition of atomic number and the recognition that atomic number, not atomic mas ...
Topic 3 Periodic Trends Notes 14-15
... Nature of Science: Obtain evidence of scientific theories by making and testing predictions based on them – scientists organize subjects based on structure and function; the periodic table is a key example of this. Early models of the periodic table from Mendeleev, and later Moseley, allowed for the ...
... Nature of Science: Obtain evidence of scientific theories by making and testing predictions based on them – scientists organize subjects based on structure and function; the periodic table is a key example of this. Early models of the periodic table from Mendeleev, and later Moseley, allowed for the ...
Concerning Electronegativity as a Basic Elemental Property and
... are dozens of methods for empirically quantifying electronegativity including: the original thermochemical technique (Pauling 1932), numerical averaging of the ionisation potential & electron affinity (Mulliken 1934), effective nuclear charge & covalent radius analysis (Sanderson 1955) and the avera ...
... are dozens of methods for empirically quantifying electronegativity including: the original thermochemical technique (Pauling 1932), numerical averaging of the ionisation potential & electron affinity (Mulliken 1934), effective nuclear charge & covalent radius analysis (Sanderson 1955) and the avera ...
Periodic Trends (Section 6.3).
... AOD C.3.1 Define atomic radii, ionization energy, electronegativity, and energy levels. AOD C.3.2 Recognize periodic trends of elements, including the number of valence electrons, atomic size, and reactivity. ...
... AOD C.3.1 Define atomic radii, ionization energy, electronegativity, and energy levels. AOD C.3.2 Recognize periodic trends of elements, including the number of valence electrons, atomic size, and reactivity. ...
Chapter 5 - EZWebSite
... Group IIA elements are called alkaline earth metals. All of their electron configurations end in s2. Harder, denser, and stronger than alkali metals. Higher melting points, and are less reactive, but still too reactive to be found in nature. ...
... Group IIA elements are called alkaline earth metals. All of their electron configurations end in s2. Harder, denser, and stronger than alkali metals. Higher melting points, and are less reactive, but still too reactive to be found in nature. ...
ד"סב Chemistry Chapter 4 What is John Newland`s law of octaves
... ● Conductors of heat and electricity ● Metallic luster ● Very reactive with water and oxygen ○ Stored in oil and many layers of protective covering to prevent these reactions ● 1 valence electron ● Very reactive because they're close to an octete ● Very reactive with group 17 (halogens) Their reacti ...
... ● Conductors of heat and electricity ● Metallic luster ● Very reactive with water and oxygen ○ Stored in oil and many layers of protective covering to prevent these reactions ● 1 valence electron ● Very reactive because they're close to an octete ● Very reactive with group 17 (halogens) Their reacti ...
Intro To The Periodic Table
... • Periodic Law - the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers • *When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, elements with similar properties occur at regular ...
... • Periodic Law - the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers • *When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, elements with similar properties occur at regular ...
Periodic Trend Notes
... Reactive (not as reactive as Groups 1 or 2), can be free elements Highest melting points Electron Configuration ns2(n-1)dx where x is column in d-block Form variable valence state ions Always form Cations Examples: Co, Fe, Pt, etc ...
... Reactive (not as reactive as Groups 1 or 2), can be free elements Highest melting points Electron Configuration ns2(n-1)dx where x is column in d-block Form variable valence state ions Always form Cations Examples: Co, Fe, Pt, etc ...
Chapter 6
... • The periodic law states that the properties of elements recur in a repeating pattern when arranged according to increasing atomic number. • With the introduction of the concept of electron energy levels by Niels Bohr, the periodic table took ...
... • The periodic law states that the properties of elements recur in a repeating pattern when arranged according to increasing atomic number. • With the introduction of the concept of electron energy levels by Niels Bohr, the periodic table took ...
Ch. 6 PPT
... Ionization Energy = The energy need to remove an electron (to make a negative charge) KC 18 : Decreases within a group (gets easier to steal an electron as you go down the table) Increases across a period (gets more difficult to steal an electron as they get closer to a full shell) 2nd Ionization E ...
... Ionization Energy = The energy need to remove an electron (to make a negative charge) KC 18 : Decreases within a group (gets easier to steal an electron as you go down the table) Increases across a period (gets more difficult to steal an electron as they get closer to a full shell) 2nd Ionization E ...
Mendeleev`s Periodic Table - Scotch Plains
... representative elements, transition metals, or inner transition metals. After reading Lesson 6.2, answer the following questions. ...
... representative elements, transition metals, or inner transition metals. After reading Lesson 6.2, answer the following questions. ...
Chapter 5 study guide - Peoria Public Schools
... 1. Describe the contribution of each of the following to the development of the periodic table: a. Dobereiner b. Newlands c. Mendeleev d. Moseley 2. State Mendeleev's periodic law. 3. Describe how Mendeleev's periodic table is organized. 4. Explain was wrong with Mendeleev's periodic law? 5. State t ...
... 1. Describe the contribution of each of the following to the development of the periodic table: a. Dobereiner b. Newlands c. Mendeleev d. Moseley 2. State Mendeleev's periodic law. 3. Describe how Mendeleev's periodic table is organized. 4. Explain was wrong with Mendeleev's periodic law? 5. State t ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... What does a group tell us about valence electrons and ion formation? ...
... What does a group tell us about valence electrons and ion formation? ...
History of the Periodic Table Chapter 6.1 Who developed the first
... advised to revise the periodic table. • After examining the properties of the elements, Seaborg was convinced that the elements were part of the inner transition elements because they behaved similarly to other transition metals. • Instead of creating a new system, he integrated the elements into a ...
... advised to revise the periodic table. • After examining the properties of the elements, Seaborg was convinced that the elements were part of the inner transition elements because they behaved similarly to other transition metals. • Instead of creating a new system, he integrated the elements into a ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.