Chapter 6 Reading Guide
... 4. What were Dobereiner’s triads? 5. What pattern did he notice about the triads? 6. What are the two reasons Mendeleev gets more credit than Meyer for the periodic table? 7. What approach did Mendelleev take to organizing the elements? 8. How did he eventually organize the elements? 9. What were th ...
... 4. What were Dobereiner’s triads? 5. What pattern did he notice about the triads? 6. What are the two reasons Mendeleev gets more credit than Meyer for the periodic table? 7. What approach did Mendelleev take to organizing the elements? 8. How did he eventually organize the elements? 9. What were th ...
Alexandre-Emile Béguyer de Chancourtois
... carbon dioxide from a sample of air and was left with a gas 19 times heavier than hydrogen, very unreactive and with an unknown emission spectrum. He called this gas Argon. In 1895 he discovered helium as a decay product of uranium and matched it to the emission spectrum of an unknown element in the ...
... carbon dioxide from a sample of air and was left with a gas 19 times heavier than hydrogen, very unreactive and with an unknown emission spectrum. He called this gas Argon. In 1895 he discovered helium as a decay product of uranium and matched it to the emission spectrum of an unknown element in the ...
Periodic Table
... increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties. Elements with similar chemical and physical properties are in the same column or group in the PT. ...
... increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties. Elements with similar chemical and physical properties are in the same column or group in the PT. ...
Periodic Table History & Organization
... Ch. 5 - The Periodic Table II. Organization of the Elements ...
... Ch. 5 - The Periodic Table II. Organization of the Elements ...
Elements of the Periodic Table… What`s in a Name?
... If you think naming a puppy is difficult, you should try naming a new element! First, you need to think of an appropriate name and then you need approval from the ACS (American Chemical Society) and the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry). Once these organizations agree on a na ...
... If you think naming a puppy is difficult, you should try naming a new element! First, you need to think of an appropriate name and then you need approval from the ACS (American Chemical Society) and the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry). Once these organizations agree on a na ...
Name PERIODIC TABLE WORKSHEET
... As you go down a group, the elements generally become (--m~-/-le.~ metallic. The majority of elements in the periodic table are (metals / nonmetals ), Elements in the periodic table are arranged according to their An element with both metallic and nonmetallic properties is called a Chemistry IF87.66 ...
... As you go down a group, the elements generally become (--m~-/-le.~ metallic. The majority of elements in the periodic table are (metals / nonmetals ), Elements in the periodic table are arranged according to their An element with both metallic and nonmetallic properties is called a Chemistry IF87.66 ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of Elements - GCG-42
... Table of the Elements. Historically, several people contributed to this effort in the late 19th century: –Dobereiner- “triads”: Ca, Sr, Ba; Li, Na, K –Newlands- similarity between every eighth element –Mendeleev (1870) - Arranged elements according to atomic mass. Similar elements were arranged toge ...
... Table of the Elements. Historically, several people contributed to this effort in the late 19th century: –Dobereiner- “triads”: Ca, Sr, Ba; Li, Na, K –Newlands- similarity between every eighth element –Mendeleev (1870) - Arranged elements according to atomic mass. Similar elements were arranged toge ...
Section 15.1
... Physical properties include color, texture, density, brittleness, and state (solid, liquid, or gas). Melting point, boiling point, and specific heat are also physical properties. ...
... Physical properties include color, texture, density, brittleness, and state (solid, liquid, or gas). Melting point, boiling point, and specific heat are also physical properties. ...
9/98 scerri 7p dom - PubContent test page
... the table did not appear in print until 1870 because of a publisher’s delay—a factor that contributed to an acrimonious dispute for priority that ensued between Lothar Meyer and Mendeleev. Around the same time, Mendeleev assembled his own periodic table while he, too, was writing a textbook of chemi ...
... the table did not appear in print until 1870 because of a publisher’s delay—a factor that contributed to an acrimonious dispute for priority that ensued between Lothar Meyer and Mendeleev. Around the same time, Mendeleev assembled his own periodic table while he, too, was writing a textbook of chemi ...
Periodic Table of the Elements
... become like Group 18 Noble Gases and have 8 electrons in the valence shell (Octet Rule) ...
... become like Group 18 Noble Gases and have 8 electrons in the valence shell (Octet Rule) ...
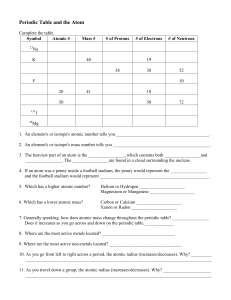
3.08_Periodic Table and the Atom
... 22. Elements of Groups 17 are called ________________________________. 23. The most active element in Group 17 is ________________________________. 24. Elements of Groups 18 are called ________________________________. 25. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Metals? ________________ 26. ...
... 22. Elements of Groups 17 are called ________________________________. 23. The most active element in Group 17 is ________________________________. 24. Elements of Groups 18 are called ________________________________. 25. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Metals? ________________ 26. ...
Document
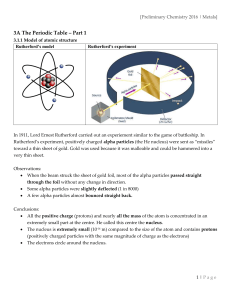
... (the nucleus), and Borh (planetary model of the atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern theory Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear atom. Identify the major components (protons, neutrons, and electrons) of the nuclear atom and explain ...
... (the nucleus), and Borh (planetary model of the atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern theory Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear atom. Identify the major components (protons, neutrons, and electrons) of the nuclear atom and explain ...
Chapter 6 Review
... 2. Who was the scientist that first arranged the elements into a periodic table? 3. He arranged the elements according to their what? 4. In the modern periodic table the elements are arranged according to their ____________. 5. When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there i ...
... 2. Who was the scientist that first arranged the elements into a periodic table? 3. He arranged the elements according to their what? 4. In the modern periodic table the elements are arranged according to their ____________. 5. When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there i ...
Periodic Table How did Dmitri Mendeleev arrange the periodic table?
... • As you go from left to right, atomic number increases by 1 – number of protons increases by 1 – number of electrons also increases by 1 in the same valence shell ...
... • As you go from left to right, atomic number increases by 1 – number of protons increases by 1 – number of electrons also increases by 1 in the same valence shell ...
Chapter 2
... John Dalton and the Atomic Theory of Matter • 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. • 2. All atoms of a given element are alike and differ from the atoms of any other element. • 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in fixed proportions. • 4 ...
... John Dalton and the Atomic Theory of Matter • 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. • 2. All atoms of a given element are alike and differ from the atoms of any other element. • 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in fixed proportions. • 4 ...
Periodic TABLE: Tables: PT, Table S
... Periodic TABLE: Tables: PT, Table S 3.1u Elements are substances that are composed of atoms that have the same atomic number. Elements cannot be broken down by chemical change. 3.1v Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, ...
... Periodic TABLE: Tables: PT, Table S 3.1u Elements are substances that are composed of atoms that have the same atomic number. Elements cannot be broken down by chemical change. 3.1v Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, ...
Chapter 6 Test Review
... i. When an anion forms, more electrons are transferred to it. ii. Elements is Groups 17A (-1), 16A (-2), 15A (-3) gain electrons to form anions. iii. Anions have a larger radius than do the atoms form which they from. Searching for an Organizing Principle As more and more elements were discovered sc ...
... i. When an anion forms, more electrons are transferred to it. ii. Elements is Groups 17A (-1), 16A (-2), 15A (-3) gain electrons to form anions. iii. Anions have a larger radius than do the atoms form which they from. Searching for an Organizing Principle As more and more elements were discovered sc ...
Dimitri Mendeleev- The father of the modern periodic table. Russian
... tablefrom actinium to lawrencium (atomic numbers 89–103). All are radioactive heavy metals; and only the first four (actinium, thorium, protactinium, and uranium) occur in nature. The other 11 (the transuranium elements) are unstable and are produced only artificially. ...
... tablefrom actinium to lawrencium (atomic numbers 89–103). All are radioactive heavy metals; and only the first four (actinium, thorium, protactinium, and uranium) occur in nature. The other 11 (the transuranium elements) are unstable and are produced only artificially. ...
The Periodic Table - Lincoln Park High School
... Families on the Periodic Table • Columns are also grouped into families. • Families may be one column, or several columns put together. • Families have names rather than numbers. ...
... Families on the Periodic Table • Columns are also grouped into families. • Families may be one column, or several columns put together. • Families have names rather than numbers. ...
Atomic Radius - Atomic radius is simply the radius of
... Dmitri Mendeleev In 1869 Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer (Germany) published nearly identical classification schemes for elements known to date. The periodic table is base on the similarity of properties and reactivities exhibited by certain elements. Later, Henri Moseley ( England,1887-1915) establishe ...
... Dmitri Mendeleev In 1869 Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer (Germany) published nearly identical classification schemes for elements known to date. The periodic table is base on the similarity of properties and reactivities exhibited by certain elements. Later, Henri Moseley ( England,1887-1915) establishe ...
The Periodic Law (Unit #5) Study Guide 1. Who is credited with
... 3. Henry Moseley found that elements in the periodic table fit into patterns better when arranged in increasing order according to nuclear charge or _atomic number______. 4. The _periodic_______ law states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their _ato ...
... 3. Henry Moseley found that elements in the periodic table fit into patterns better when arranged in increasing order according to nuclear charge or _atomic number______. 4. The _periodic_______ law states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their _ato ...
Chapter 3 Introduction to the Periodic Table
... The energy level of an atom’s valence electrons indicate the period in which it is found. A representative element’s group number and the number of valence electrons it contains are equal (with a few exceptions). Atoms can gain or lose one or more electrons and acquire a net charge. ...
... The energy level of an atom’s valence electrons indicate the period in which it is found. A representative element’s group number and the number of valence electrons it contains are equal (with a few exceptions). Atoms can gain or lose one or more electrons and acquire a net charge. ...
Dmitri Mendeleev

Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev (/ˌmɛndəlˈeɪəf/; Russian: Дми́трий Ива́нович Менделе́ев; IPA: [ˈdmʲitrʲɪj ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ mʲɪndʲɪˈlʲejɪf]; 8 February 1834 – 2 February 1907 O.S. 27 January 1834 – 20 January 1907) was a Russian chemist and inventor. He formulated the Periodic Law, created his own version of the periodic table of elements, and used it to correct the properties of some already discovered elements and also to predict the properties of eight elements yet to be discovered.