Covers material through Today`s lecture
... Human: Met Lys Try Thr Ser… Mouse: Met Asn Ala Thr His… • From this data, Kimura estimated evolutionary rates for each protein in the various lineages ...
... Human: Met Lys Try Thr Ser… Mouse: Met Asn Ala Thr His… • From this data, Kimura estimated evolutionary rates for each protein in the various lineages ...
Avian Influenza - Commonwealth of Learning
... Avian influenza is caused by influenza A viruses. Some viruses have the capacity to cross the species barrier form birds to humans. The strains that have caused diseases in humans are of subtypes H5N1, H7N7, H9N2. These subtypes also have pandemic avian influenza potential. The AI viruses lose infec ...
... Avian influenza is caused by influenza A viruses. Some viruses have the capacity to cross the species barrier form birds to humans. The strains that have caused diseases in humans are of subtypes H5N1, H7N7, H9N2. These subtypes also have pandemic avian influenza potential. The AI viruses lose infec ...
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) presentation
... This can lead to death from infections, secondary diseases from opportunistic bacteria and/or viruses that are usually harmless to people, or many different types of cancers. Common diseases associated with HIV infection: ...
... This can lead to death from infections, secondary diseases from opportunistic bacteria and/or viruses that are usually harmless to people, or many different types of cancers. Common diseases associated with HIV infection: ...
HIV INFECTION
... 1% with <400 copies/mL, and it was > 30 % with >100,000 copies/mL . (ZDV) therapy that reduced these levels to <500 copies/mL also minimized the risk of transmission although ZDV is effective in reducing transmission across all HIV RNA levels. Maternal infusions of HIV-1 hyperimmune globulin did not ...
... 1% with <400 copies/mL, and it was > 30 % with >100,000 copies/mL . (ZDV) therapy that reduced these levels to <500 copies/mL also minimized the risk of transmission although ZDV is effective in reducing transmission across all HIV RNA levels. Maternal infusions of HIV-1 hyperimmune globulin did not ...
Evolutionary Algorithms
... population of video clips. The evolutionary model is more flexible, the system has improved functionalities, and the use of creative video editing is further explored as a process to support the production of digital video art (Teresa Chambela, 2010). Genetic algorithms are probably the most popular ...
... population of video clips. The evolutionary model is more flexible, the system has improved functionalities, and the use of creative video editing is further explored as a process to support the production of digital video art (Teresa Chambela, 2010). Genetic algorithms are probably the most popular ...
Week 7 - Natural Selection and Genetic Variation for Allozymes
... features of the population before the selective event and then again after it. The strength of selection is inferred from the difference in the characteristics of the population before versus after selection. Natural selection is not sufficient to produce evolutionary change. Populations change only ...
... features of the population before the selective event and then again after it. The strength of selection is inferred from the difference in the characteristics of the population before versus after selection. Natural selection is not sufficient to produce evolutionary change. Populations change only ...
Module 1
... time three landmark discoveries came together that formed the founding stone of what we call today as medical science. The first discovery came from Louis Pasture (1822-1895) who gave the spontaneous generation theory from his famous swan-neck flask experiment. The second discovery came from Robert ...
... time three landmark discoveries came together that formed the founding stone of what we call today as medical science. The first discovery came from Louis Pasture (1822-1895) who gave the spontaneous generation theory from his famous swan-neck flask experiment. The second discovery came from Robert ...
Mendelian Genetics in Populations II
... Nearly neutral theory – 2 • Imagine a species in which effective population size, N, is 500. If the selection coefficient, s, against a mutant heterozygote is 0.0005, then 4Ns = 1.0, which qualifies as “small”, and the mutation is effectively neutral • On the other hand, the same selection coeffici ...
... Nearly neutral theory – 2 • Imagine a species in which effective population size, N, is 500. If the selection coefficient, s, against a mutant heterozygote is 0.0005, then 4Ns = 1.0, which qualifies as “small”, and the mutation is effectively neutral • On the other hand, the same selection coeffici ...
Genetic Algorithms (GAs)
... Biological life is in control of its own means of reproduction... But this autonomy of design and manufacture has not yet been realized artificially… Here we report the results of a combined computational and experimental approach in which simple electromechanical systems are evolved through simulat ...
... Biological life is in control of its own means of reproduction... But this autonomy of design and manufacture has not yet been realized artificially… Here we report the results of a combined computational and experimental approach in which simple electromechanical systems are evolved through simulat ...
File - Patterson Science
... What additional item does HIV have that is not found in the influenza virus? Describe how HIV reproduces when it is infectious and causing disease. Describe how HIV could form a “provirus” ...
... What additional item does HIV have that is not found in the influenza virus? Describe how HIV reproduces when it is infectious and causing disease. Describe how HIV could form a “provirus” ...
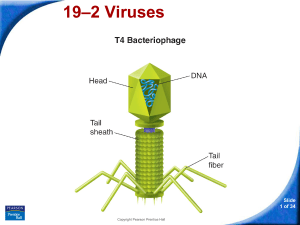
Viruses - mrsteeves
... of living things. c. Viruses can reproduce independently if they contain DNA. d. Viruses cannot reproduce unless they infect a living cell. Slide 29 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... of living things. c. Viruses can reproduce independently if they contain DNA. d. Viruses cannot reproduce unless they infect a living cell. Slide 29 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
Name - IISME Community Site
... 6. When was H1N1 first identified in the United States? _______________________ ...
... 6. When was H1N1 first identified in the United States? _______________________ ...
Document
... This equation is similar to one we learned earlier but 2Ne is replaced by Nef as mtDNA is maternally inherited and genetic diversity is lost at a rate of 1/Nef. The mtDNA diversity in southern elephant seals is 0.980 (assumed to represent H0), while that in northern elephant seals is 0.409 (Ht). Ma ...
... This equation is similar to one we learned earlier but 2Ne is replaced by Nef as mtDNA is maternally inherited and genetic diversity is lost at a rate of 1/Nef. The mtDNA diversity in southern elephant seals is 0.980 (assumed to represent H0), while that in northern elephant seals is 0.409 (Ht). Ma ...
HIV test methods and applications
... 90% of HIV-1 infections belong to HIV-1 group M. Within group M there are known to be at least nine genetically distinct subtypes (or clades) of HIV-1. These are subtypes A, B, C, D, F, G, H, J and K. Occasionally, two viruses of different subtypes can meet in the cell of an infected person and mix ...
... 90% of HIV-1 infections belong to HIV-1 group M. Within group M there are known to be at least nine genetically distinct subtypes (or clades) of HIV-1. These are subtypes A, B, C, D, F, G, H, J and K. Occasionally, two viruses of different subtypes can meet in the cell of an infected person and mix ...
Collection - E
... gram staining the smear. The elative numbers of polymorphs and squamous epithelial cells may be seen. If there are less them 10 polymorphs/ squam the specimen is mainly saliva in suspected case of tuberculosis, acid-fast staining is done. ...
... gram staining the smear. The elative numbers of polymorphs and squamous epithelial cells may be seen. If there are less them 10 polymorphs/ squam the specimen is mainly saliva in suspected case of tuberculosis, acid-fast staining is done. ...
Molecular Evolution
... Thus, a protein in which the active sites constitute only 1% of its sequence will be less constrained, and therefore will evolve more quickly than a protein that devotes 50% of its sequence to performing specific biochemical or physiological tasks. ...
... Thus, a protein in which the active sites constitute only 1% of its sequence will be less constrained, and therefore will evolve more quickly than a protein that devotes 50% of its sequence to performing specific biochemical or physiological tasks. ...
biology b242 - evolution of genetic diversity
... Do genes always evolve until they become fixed (invariant in a population), or become immediately lost because they are disfavoured? If so, most of the time, populations would be invariant and no change would occur. However, in nature things are very different ... ...
... Do genes always evolve until they become fixed (invariant in a population), or become immediately lost because they are disfavoured? If so, most of the time, populations would be invariant and no change would occur. However, in nature things are very different ... ...
Respiratory Infections
... • Subtypes (H1 - H3: N1 or N2) determined by viral hemagglutinin & neuraminidase in lipid envelope – eg., H3N2 ...
... • Subtypes (H1 - H3: N1 or N2) determined by viral hemagglutinin & neuraminidase in lipid envelope – eg., H3N2 ...
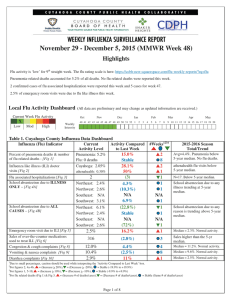
Table 1. Cuyahoga County Influenza Data Dashboard
... particular influenza season. This condition became reportable in January 2009. B) Influenza-associated Pediatric Mortality (ODRS): Influenza-associated pediatric mortalities are reported into ODRS by CCBH and hospital staff. Pediatric deaths can be an indicator of the severity of illness during the ...
... particular influenza season. This condition became reportable in January 2009. B) Influenza-associated Pediatric Mortality (ODRS): Influenza-associated pediatric mortalities are reported into ODRS by CCBH and hospital staff. Pediatric deaths can be an indicator of the severity of illness during the ...
Sexual Selection - Cathedral High School
... describes and predicts genotype and allele frequencies in a non-evolving population (equilibrium) Evolution = change in allele frequencies in a population – hypothetical: what conditions would NOT cause allele frequencies to change? – non-evolving population REMOVE all agents of evolutionary change ...
... describes and predicts genotype and allele frequencies in a non-evolving population (equilibrium) Evolution = change in allele frequencies in a population – hypothetical: what conditions would NOT cause allele frequencies to change? – non-evolving population REMOVE all agents of evolutionary change ...
Massachusetts Department of Public Health (MDPH)
... 2. Active surveillance and testing for new illness and cases: Educate staff about the signs and symptoms of influenza-like illness. The ILI line list found on the MDPH website (can be used to collect and manage relevant information about ill residents and staff. 3. Respiratory hygiene/cough etiquett ...
... 2. Active surveillance and testing for new illness and cases: Educate staff about the signs and symptoms of influenza-like illness. The ILI line list found on the MDPH website (can be used to collect and manage relevant information about ill residents and staff. 3. Respiratory hygiene/cough etiquett ...
幻灯片 1
... Unlocking Clues to Spread of 1918 Flu Virus But Dr. Jeffery Taubenberger, chief of the molecular pathology department at the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology in Washington, had an idea for finding that ancient virus. He recalled that his institute had a warehouse of autopsy tissue, established b ...
... Unlocking Clues to Spread of 1918 Flu Virus But Dr. Jeffery Taubenberger, chief of the molecular pathology department at the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology in Washington, had an idea for finding that ancient virus. He recalled that his institute had a warehouse of autopsy tissue, established b ...
Viruses
... come in a variety of shapes due to their protein covering. They are responsible for many diseases. They are classified by shape, the kind of hereditary material they have, the kind of organisms they infect, and their method of reproduction. ...
... come in a variety of shapes due to their protein covering. They are responsible for many diseases. They are classified by shape, the kind of hereditary material they have, the kind of organisms they infect, and their method of reproduction. ...
Viral vector type - Office of the Gene Technology Regulator
... transduce human cells unless all structural & accessory genes deleted and transcriptionally inactive ...
... transduce human cells unless all structural & accessory genes deleted and transcriptionally inactive ...
Annual Report, October 2011, 272 KB PDF
... We began by determining if there were natural geographic breaks in the GOA POP population that are detectable from the survey and catch data. Based on estimates of neighborhood size from the genetic data, we established levels of spatial groupings – regional, statistical area, and smaller neighborho ...
... We began by determining if there were natural geographic breaks in the GOA POP population that are detectable from the survey and catch data. Based on estimates of neighborhood size from the genetic data, we established levels of spatial groupings – regional, statistical area, and smaller neighborho ...
Viral phylodynamics
Viral phylodynamics is defined as the study of how epidemiological, immunological, and evolutionary processes act and potentially interact to shape viral phylogenies.Since the coining of the term in 2004, research on viral phylodynamics has focused on transmission dynamics in an effort to shed light on how these dynamics impact viral genetic variation. Transmission dynamics can be considered at the level of cells within an infected host, individual hosts within a population, or entire populations of hosts.Many viruses, especially RNA viruses, rapidly accumulate genetic variation because of short generation times and high mutation rates.Patterns of viral genetic variation are therefore heavily influenced by how quickly transmission occurs and by which entities transmit to one another.Patterns of viral genetic variation will also be affected by selection acting on viral phenotypes.Although viruses can differ with respect to many phenotypes, phylodynamic studies have to date tended to focus on a limited number of viral phenotypes.These include virulence phenotypes, phenotypes associated with viral transmissibility, cell or tissue tropism phenotypes, and antigenic phenotypes that can facilitate escape from host immunity.Due to the impact that transmission dynamics and selection can have on viral genetic variation, viral phylogenies can therefore be used to investigate important epidemiological, immunological, and evolutionary processes, such as epidemic spread, spatio-temporal dynamics including metapopulation dynamics, zoonotic transmission, tissue tropism, and antigenic drift.The quantitative investigation of these processes through the consideration of viral phylogenies is the central aim of viral phylodynamics.