Significant Events Of The Last 125 Years
... Thomas H. Huxley's Biogenesis and Abiogenesis address is the first clear statement of the basic outlines of modern Darwinian science on the question of the origin of life. The terms "biogenesis" (for life only from pre-existing life) and "abiogenesis" (for life from nonliving materials, what had pre ...
... Thomas H. Huxley's Biogenesis and Abiogenesis address is the first clear statement of the basic outlines of modern Darwinian science on the question of the origin of life. The terms "biogenesis" (for life only from pre-existing life) and "abiogenesis" (for life from nonliving materials, what had pre ...
PICORNAVIRIDAE
... vertebrates and are responsible for many important diseases in humans and animals. • Picornaviruses are responsible for a wide range of clinical diseases resulting from multiple factors such as receptor specificity, tissue-specific susceptibility, virulence and the mechanisms of transmission. • Pico ...
... vertebrates and are responsible for many important diseases in humans and animals. • Picornaviruses are responsible for a wide range of clinical diseases resulting from multiple factors such as receptor specificity, tissue-specific susceptibility, virulence and the mechanisms of transmission. • Pico ...
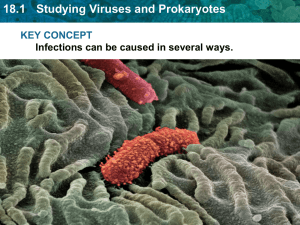
18.1 Studying Viruses and Prokaryotes
... Structure Viruses and Reproduction 18.1Viral Studying and Prokaryotes Viral Structure Nucleic acid • Either DNA or RNA, but not both • Helical, closed loop, or a long strand • Protein coat surrounds nucleic acid (capsid) • Some have a membrane like structure outside capsid called an envelope • Ex: i ...
... Structure Viruses and Reproduction 18.1Viral Studying and Prokaryotes Viral Structure Nucleic acid • Either DNA or RNA, but not both • Helical, closed loop, or a long strand • Protein coat surrounds nucleic acid (capsid) • Some have a membrane like structure outside capsid called an envelope • Ex: i ...
3 Virus Replication Cycles
... adapt to their hosts have been able to exist in nature. This chapter focuses on experiments such as one-step growth curves, which are used to study virus–host interactions. These studies have provided information about the events that occur at each step of the infection cycle (attachment, penetratio ...
... adapt to their hosts have been able to exist in nature. This chapter focuses on experiments such as one-step growth curves, which are used to study virus–host interactions. These studies have provided information about the events that occur at each step of the infection cycle (attachment, penetratio ...
like - bYTEBoss
... • Viruses are so small they only have enough genes for the protein coat and enzymes that allow the virus to take over its host cell. • Viruses have some characteristics of living things – like genetic material, but they lack three things – they are not made of cells, they cannot make proteins by the ...
... • Viruses are so small they only have enough genes for the protein coat and enzymes that allow the virus to take over its host cell. • Viruses have some characteristics of living things – like genetic material, but they lack three things – they are not made of cells, they cannot make proteins by the ...
Significant Events Of The Last 125 Years
... Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which causes diphtheria. Loeffler later shows that the bacterium secretes a soluble substance that affects organs beyond sites where there is physical evidence of the organism. Ulysse Gayon and Gabriel Dupetit isolate in pure culture two strains of denitrifying bacteria. ...
... Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which causes diphtheria. Loeffler later shows that the bacterium secretes a soluble substance that affects organs beyond sites where there is physical evidence of the organism. Ulysse Gayon and Gabriel Dupetit isolate in pure culture two strains of denitrifying bacteria. ...
1- الوضع الوبائى لحمى الوادي المتصدع في مصر والمملكة العربية
... Objective: The present study aimed to investigate the clinical and clinicopathological findings of .arthritic camel calf associated with mycoplasma infection in district areas of Saudi Arabia Metho حقائق وبائية: مرض فيروس زيكا-5 Zika virus disease is a disease caused by Zika virus leads to symp ...
... Objective: The present study aimed to investigate the clinical and clinicopathological findings of .arthritic camel calf associated with mycoplasma infection in district areas of Saudi Arabia Metho حقائق وبائية: مرض فيروس زيكا-5 Zika virus disease is a disease caused by Zika virus leads to symp ...
The Silver Ion (Ag+),
... dangerous “superbugs” like MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with its growing number of strains) and newly emerging pandemic threats, such as Influenza A (H1N1), bird flu (H5N1 virus) and SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome). Research at Washington University School of Medicine i ...
... dangerous “superbugs” like MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with its growing number of strains) and newly emerging pandemic threats, such as Influenza A (H1N1), bird flu (H5N1 virus) and SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome). Research at Washington University School of Medicine i ...
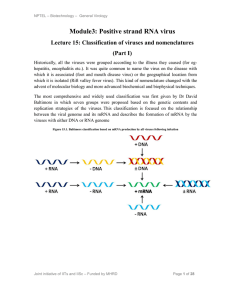
Module3: Positive strand RNA virus
... Group 3, ds RNA viruses- Replicating through RNA Group 4, ssRNA viruses (+) polarity, (sense to mRNAs) - Replicating through RNA Group 5, ssRNA viruses (-) polarity, (antisense to mRNAs) - Replicating through RNA Group 6, RNA-retroid genomes (RNA -> DNA -> RNA) - Replicating using reverse transcript ...
... Group 3, ds RNA viruses- Replicating through RNA Group 4, ssRNA viruses (+) polarity, (sense to mRNAs) - Replicating through RNA Group 5, ssRNA viruses (-) polarity, (antisense to mRNAs) - Replicating through RNA Group 6, RNA-retroid genomes (RNA -> DNA -> RNA) - Replicating using reverse transcript ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 7. The generation time of a bacterial population is the time it takes for a bacterial population to double. 8. Competence is related towards transformation. 9. Xanthomonas citri is a rod shaped, monotrichous and anaerobic bacterium. 10. Water can be purified by exposure to UV. ...
... 7. The generation time of a bacterial population is the time it takes for a bacterial population to double. 8. Competence is related towards transformation. 9. Xanthomonas citri is a rod shaped, monotrichous and anaerobic bacterium. 10. Water can be purified by exposure to UV. ...
43. Tumor Viruses
... chemically treated cells, and these genes are expressed with high efficiency. There is another mechanism of carcinogenesis involving cellular genes, namely, mutation of a tumor suppressor gene. A well-documented example is the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene, which normally acts as a suppressor o ...
... chemically treated cells, and these genes are expressed with high efficiency. There is another mechanism of carcinogenesis involving cellular genes, namely, mutation of a tumor suppressor gene. A well-documented example is the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene, which normally acts as a suppressor o ...
“All the World`s a Phage” The Role of Bacterial Viruses in
... Bacterial viruses, or bacteriophages, play several important roles in microbial communities. Results from environmental sampling of bacteriophages over the past decade or so suggests that there are probably on the order of 1031 bacteriophages in the biosphere, making them by far the most abundant or ...
... Bacterial viruses, or bacteriophages, play several important roles in microbial communities. Results from environmental sampling of bacteriophages over the past decade or so suggests that there are probably on the order of 1031 bacteriophages in the biosphere, making them by far the most abundant or ...
Bacterial and Viral Infections
... adhesion molecules (NCAMs) found in human neural tissues (see Chapter 14). The group C capsule has proven to be a successful vaccine antigen in human populations, whereas the group B capsule is essentially nonimmunogenic. Another challenge posed to host immunity by certain pathogens is the great div ...
... adhesion molecules (NCAMs) found in human neural tissues (see Chapter 14). The group C capsule has proven to be a successful vaccine antigen in human populations, whereas the group B capsule is essentially nonimmunogenic. Another challenge posed to host immunity by certain pathogens is the great div ...
Camellia Viruses - Atlantic Coast Camellia Society
... associated with Camellia yellow mottle disease were graft-transmissible. Therefore according to plant pathologists/virologists the disease must be associated with infection by a virus. Hence the name. ...
... associated with Camellia yellow mottle disease were graft-transmissible. Therefore according to plant pathologists/virologists the disease must be associated with infection by a virus. Hence the name. ...
Microorganisms Informational Text with Questions
... break down the food so that it can be used as energy to move around. Ciliates: This group of protozoa are called ciliates because they are lined with tiny hairs called cilia. These hairs are used for movement. The hairs are also used in feeding. They carry the food to the mouth region. Enzymes then ...
... break down the food so that it can be used as energy to move around. Ciliates: This group of protozoa are called ciliates because they are lined with tiny hairs called cilia. These hairs are used for movement. The hairs are also used in feeding. They carry the food to the mouth region. Enzymes then ...
Microbiology - Cape Cod Community College
... Terms: photosynthetic pigment, unicellular, macroscopic. Commercial uses of red and brown algae. For the dinoflagellates, harmful algal blooms, and their health consequences with general symptoms. Lichens as algal/fungal symbiosis. ...
... Terms: photosynthetic pigment, unicellular, macroscopic. Commercial uses of red and brown algae. For the dinoflagellates, harmful algal blooms, and their health consequences with general symptoms. Lichens as algal/fungal symbiosis. ...
Chapter 14
... several strains of E. coli that have been involved in human illness. Blue-green bacteria and prochlorobacteria are explored next, and the human relevance of blue-green bacteria is examined. The chapter concludes with an overview of the nature, reproduction, and human relevance of viruses. ...
... several strains of E. coli that have been involved in human illness. Blue-green bacteria and prochlorobacteria are explored next, and the human relevance of blue-green bacteria is examined. The chapter concludes with an overview of the nature, reproduction, and human relevance of viruses. ...
1 Introduction - Libreria Universo
... identifying Vibrio as a cause of cholera, as well as work in India and Africa on malaria, plague, typhus, trypanosomiasis and tickborne spirochaete infections. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1905, and continued his work on bacteriology and serology until his death in 19 ...
... identifying Vibrio as a cause of cholera, as well as work in India and Africa on malaria, plague, typhus, trypanosomiasis and tickborne spirochaete infections. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1905, and continued his work on bacteriology and serology until his death in 19 ...
Simultaneous recovery of bacteria and viruses from contaminated
... hepatitis A virus (HAV) strain HM-175 (ATCC# VR-1402) and the feline calicivirus (FCV) strain F9 (ATCC VR-782), propagated in FRhK-4, MA-104 and CrFK cells respectively as previously described (Ansari et al., 1988; Bidawid et al., 2003; Mbithi et al., 1990), were also used. Viral suspensions of each ...
... hepatitis A virus (HAV) strain HM-175 (ATCC# VR-1402) and the feline calicivirus (FCV) strain F9 (ATCC VR-782), propagated in FRhK-4, MA-104 and CrFK cells respectively as previously described (Ansari et al., 1988; Bidawid et al., 2003; Mbithi et al., 1990), were also used. Viral suspensions of each ...
Gapped dsDNA genomes
... The bigger surprise: thousands of different virions, seemingly infinite complexity of infec*ons But a finite number of viral genomes ...
... The bigger surprise: thousands of different virions, seemingly infinite complexity of infec*ons But a finite number of viral genomes ...
RNA dependent synthesis of DNA and RNA
... RNA synthesis. This lack of sensitivity suggested that there was a virus specific enzyme that could copy RNA from an RNA template and not from a DNA template. The most famous example of RDRP is the polio virus. The virus is made up of RNA which enters the cell through receptor-mediated endocytosis. ...
... RNA synthesis. This lack of sensitivity suggested that there was a virus specific enzyme that could copy RNA from an RNA template and not from a DNA template. The most famous example of RDRP is the polio virus. The virus is made up of RNA which enters the cell through receptor-mediated endocytosis. ...
Microbiology 1: Bacterial Properties
... The bacterial cell is infected by bacteriophages (viruses which infect bacteria) ...
... The bacterial cell is infected by bacteriophages (viruses which infect bacteria) ...
MICROBIOLOGY EXAM III SIMPLE COMPLETION: Each of the
... A. Clone the entire CF gene from each patient and determine the DNA sequence of the cloned gene in each case. B. Design a bacteriophage luciferase assay that will detect function of the CF gene. C. Choose two oligonucleotide primers that immediately flank the known CF deletion, amplify the region by ...
... A. Clone the entire CF gene from each patient and determine the DNA sequence of the cloned gene in each case. B. Design a bacteriophage luciferase assay that will detect function of the CF gene. C. Choose two oligonucleotide primers that immediately flank the known CF deletion, amplify the region by ...
Introduction to viruses

A virus is a biological agent that reproduces inside the cells of living hosts. When infected by a virus, a host cell is forced to produce many thousands of identical copies of the original virus, at an extraordinary rate. Unlike most living things, viruses do not have cells that divide; new viruses are assembled in the infected host cell. But unlike still simpler infectious agents, viruses contain genes, which gives them the ability to mutate and evolve. Over 5,000 species of viruses have been discovered.The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids—pieces of DNA that can move between cells—while others may have evolved from bacteria. A virus consists of two or three parts: genes, made from either DNA or RNA, long molecules that carry genetic information; a protein coat that protects the genes; and in some viruses, an envelope of fat that surrounds and protects them when they are not contained within a host cell. Viruses vary in shape from the simple helical and icosahedral to more complex structures. Viruses range in size from 20 to 300 nanometres; it would take 30,000 to 750,000 of them, side by side, to stretch to 1 centimetre (0.39 in).Viruses spread in many ways. Just as many viruses are very specific as to which host species or tissue they attack, each species of virus relies on a particular method for propagation. Plant viruses are often spread from plant to plant by insects and other organisms, known as vectors. Some viruses of animals, including humans, are spread by exposure to infected bodily fluids. Viruses such as influenza are spread through the air by droplets of moisture when people cough or sneeze. Viruses such as norovirus are transmitted by the faecal–oral route, which involves the contamination of hands, food and water. Rotavirus is often spread by direct contact with infected children. The human immunodeficiency virus, HIV, is transmitted by bodily fluids transferred during sex. Others, such as the Dengue virus, are spread by blood-sucking insects.Viral infections can cause disease in humans, animals and even plants. However, they are usually eliminated by the immune system, conferring lifetime immunity to the host for that virus. Antibiotics have no effect on viruses, but antiviral drugs have been developed to treat life-threatening infections. Vaccines that produce lifelong immunity can prevent some viral infections.