Reading Guide for Week 5
... acids, nucleotides, fatty acids, glycerol, and monosaccharides). In this reading guide we’ll put those subunits together to make macromolecules through the processes of DNA replication, transcription, and translation, and put those macromolecules together to make cellular structures (for example: pr ...
... acids, nucleotides, fatty acids, glycerol, and monosaccharides). In this reading guide we’ll put those subunits together to make macromolecules through the processes of DNA replication, transcription, and translation, and put those macromolecules together to make cellular structures (for example: pr ...
Bacteria/Virses
... reported estimates that about 75-80% of sexually active Americans will be infected with HPV at some point in their lifetime. ...
... reported estimates that about 75-80% of sexually active Americans will be infected with HPV at some point in their lifetime. ...
Viruses (1)
... Discovery of the tobacco mosaic disease (Iwanowski 1892): Infectous agent of the tobacco mosaic disease passes through filter that retain bacteria. Contagium vivum fluidum (Beijerink1898): Suggested that the pathogen is a distinct living agent Agent of foot and mouth disease is filterable (Loeffler ...
... Discovery of the tobacco mosaic disease (Iwanowski 1892): Infectous agent of the tobacco mosaic disease passes through filter that retain bacteria. Contagium vivum fluidum (Beijerink1898): Suggested that the pathogen is a distinct living agent Agent of foot and mouth disease is filterable (Loeffler ...
Pathogens – Bacteria & Viruses
... its tail fibers. The sheath then contracts, injecting the contents of the head (DNA) into the host. The viral DNA makes the bacteria manufacture more copies of the virus. TEM X40,000. ...
... its tail fibers. The sheath then contracts, injecting the contents of the head (DNA) into the host. The viral DNA makes the bacteria manufacture more copies of the virus. TEM X40,000. ...
A. invades the host cell to reproduce B. - Problem
... the e ectiveness of three di erent mouthwashes in destroying bacteria. He covered the surface of the nutrient agar in four petri dishes with bacteria found in the human mouth. One paper disk, 1 centimeter in diameter, that had been soaked in a speci c mouthwash was placed on the agar surface of plat ...
... the e ectiveness of three di erent mouthwashes in destroying bacteria. He covered the surface of the nutrient agar in four petri dishes with bacteria found in the human mouth. One paper disk, 1 centimeter in diameter, that had been soaked in a speci c mouthwash was placed on the agar surface of plat ...
3. Viruses 2010
... Human Health What makes viruses so challenging? 1. Most are difficult to treat and are not destroyed by sulfa drugs or antibiotics that have been so effective at treating bacterial illnesses. 2. Some viruses remain dormant for years before symptoms appear (due to the lysogenic cycle) ...
... Human Health What makes viruses so challenging? 1. Most are difficult to treat and are not destroyed by sulfa drugs or antibiotics that have been so effective at treating bacterial illnesses. 2. Some viruses remain dormant for years before symptoms appear (due to the lysogenic cycle) ...
Are Viruses Alive
... molecules that can do nothing by themselves. Viruses are right on the border between living and nonliving. There are many non-living things that demonstrate characteristics of living things. Some biologists currently see the virus as a nonliving infectious particle. Other biologists disagree and sug ...
... molecules that can do nothing by themselves. Viruses are right on the border between living and nonliving. There are many non-living things that demonstrate characteristics of living things. Some biologists currently see the virus as a nonliving infectious particle. Other biologists disagree and sug ...
Are Viruses Alive
... All other living things also grow or get bigger. A virus does nothing inside its protein coat; therefore it does not grow. But some scientists argue that a virus's growth occurs inside the host cell where parts of viruses are built during reproduction. Plants and animals react to the environment. A ...
... All other living things also grow or get bigger. A virus does nothing inside its protein coat; therefore it does not grow. But some scientists argue that a virus's growth occurs inside the host cell where parts of viruses are built during reproduction. Plants and animals react to the environment. A ...
AP Biology 12 Viruses
... A. Viruses are two-dimensional, rather than threedimensional. FALSE B. The viral genome may be single- or double-stranded. TRUE C. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites. TRUE D. An isolated virus is unable to replicate its genes or regenerate ATP. TRUE ...
... A. Viruses are two-dimensional, rather than threedimensional. FALSE B. The viral genome may be single- or double-stranded. TRUE C. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites. TRUE D. An isolated virus is unable to replicate its genes or regenerate ATP. TRUE ...
Chapter 36: Picornaviruses (Enterovirus & Rhinovirus Groups)
... secretory IgA antibodies in the intestine, which then becomes resistant to reinfection. Both killed-virus and live-virus vaccines induce antibodies and protect the central nervous system from subsequent invasion by wild virus. ...
... secretory IgA antibodies in the intestine, which then becomes resistant to reinfection. Both killed-virus and live-virus vaccines induce antibodies and protect the central nervous system from subsequent invasion by wild virus. ...
Viruses, Prions, and Viroids:
... Viral genetic material and viral capsids ______________ Host range temporarily altered ...
... Viral genetic material and viral capsids ______________ Host range temporarily altered ...
Supplementary Figures - PowerPoint
... Supplementary Figure 4 | Effect of HA mutations on SAα2,6Gal recognition. Mutations found in the HA of A/Vietnam/30408/05clone7 were introduced individually or in combination into the reference VN1194 HA. Direct binding activity to sialylglycopolymers containing either α2,3-linked (blue) or α2,6-lin ...
... Supplementary Figure 4 | Effect of HA mutations on SAα2,6Gal recognition. Mutations found in the HA of A/Vietnam/30408/05clone7 were introduced individually or in combination into the reference VN1194 HA. Direct binding activity to sialylglycopolymers containing either α2,3-linked (blue) or α2,6-lin ...
Slide 1
... structural subunits surrounding the virus nucleic acid. • Although viruses are metabolically inert, in some viruses, one or more key enzymes are present within the virion. ...
... structural subunits surrounding the virus nucleic acid. • Although viruses are metabolically inert, in some viruses, one or more key enzymes are present within the virion. ...
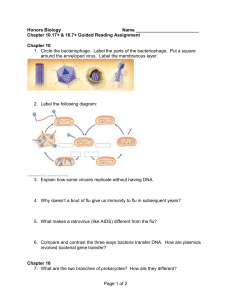
5echap10n16guidedreading
... 1. Circle the bacteriophage. Label the parts of the bacteriophage. Put a square around the enveloped virus. Label the membranous layer. ...
... 1. Circle the bacteriophage. Label the parts of the bacteriophage. Put a square around the enveloped virus. Label the membranous layer. ...
Master/PhD position in cell biology of virus infection at the University
... skin or mucosa, to reach its receptors and initiate infection. We aim to characterize physical barriers, signaling pathways and receptors that are involved in the viral entry process. The establishment of a protocol for ex vivo infection of epidermal sheets allows us to study virus entry into the ep ...
... skin or mucosa, to reach its receptors and initiate infection. We aim to characterize physical barriers, signaling pathways and receptors that are involved in the viral entry process. The establishment of a protocol for ex vivo infection of epidermal sheets allows us to study virus entry into the ep ...
File
... a cell. In a lytic infection, viral genes are quickly transcribed and new viruses are made by the host cell. In a lysogenic infection, the host cell is not immediately taken over; viral nucleic acid is inserted into the host cell’s DNA and may be inactive for a long time. 3. What’s the difference be ...
... a cell. In a lytic infection, viral genes are quickly transcribed and new viruses are made by the host cell. In a lysogenic infection, the host cell is not immediately taken over; viral nucleic acid is inserted into the host cell’s DNA and may be inactive for a long time. 3. What’s the difference be ...
6 Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents
... variable; such viruses are said to have binal symmetry C. Viral envelopes and enzymes 1. Envelopes are membrane structures surrounding some (but not all) viruses a. Lipids and carbohydrates are usually derived from the host membranes b. Proteins are virus-specific c. Many have protruding glycoprotei ...
... variable; such viruses are said to have binal symmetry C. Viral envelopes and enzymes 1. Envelopes are membrane structures surrounding some (but not all) viruses a. Lipids and carbohydrates are usually derived from the host membranes b. Proteins are virus-specific c. Many have protruding glycoprotei ...
Viral Plant Pathogens
... approximately 1000 species and phytopathogenic. Viral species with slightly different variants are designated as strains. Virons are individual particles and are inert Tobacco mosaic virus – 200,000+X carriers of the genome and are assembled inside the host cell. The genome of an organism is it whol ...
... approximately 1000 species and phytopathogenic. Viral species with slightly different variants are designated as strains. Virons are individual particles and are inert Tobacco mosaic virus – 200,000+X carriers of the genome and are assembled inside the host cell. The genome of an organism is it whol ...
Chapter 20 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea
... The viruses are a biological enigma. They have a DNA or RNA genome, but they can reproduce only by using the metabolic machinery of a host cell. Viruses are noncellular, and therefore cannot be assigned a two-part binomial name, as are organisms. In 1884, Pasteur suspected something smaller than bac ...
... The viruses are a biological enigma. They have a DNA or RNA genome, but they can reproduce only by using the metabolic machinery of a host cell. Viruses are noncellular, and therefore cannot be assigned a two-part binomial name, as are organisms. In 1884, Pasteur suspected something smaller than bac ...
Viruses - Chap 13 partI
... electron microscope. Plating efficiency with bacteriophage is usually > 50% but with some animal viruses may be <1% The plaque procedure may be used to prepare pure viral strains Cell cultures may also be used to titre virus – infection with viruses leads to cellular deterioration - known as the ...
... electron microscope. Plating efficiency with bacteriophage is usually > 50% but with some animal viruses may be <1% The plaque procedure may be used to prepare pure viral strains Cell cultures may also be used to titre virus – infection with viruses leads to cellular deterioration - known as the ...
Viruses Lecture 16 Fall 2008
... • Ability of virus to mutate – RNA viruses have very high mutation rate – copy errors are not corrected by proofreading • Dissemination from small isolated human populations • Virus spreads from other animals to human population – “Spanish flu” pandemic of 1918 • 40 million people died ...
... • Ability of virus to mutate – RNA viruses have very high mutation rate – copy errors are not corrected by proofreading • Dissemination from small isolated human populations • Virus spreads from other animals to human population – “Spanish flu” pandemic of 1918 • 40 million people died ...
Plant Viruses - rci.rutgers.edu
... different hosts • No “rules” about virus families that may or may not be present in a given kingdom • Some types of viruses are found more commonly in some kingdoms than in others – Many plant viruses contain ssRNA genomes – Many fungal viruses contain dsRNA genomes – Many bacterial viruses contain ...
... different hosts • No “rules” about virus families that may or may not be present in a given kingdom • Some types of viruses are found more commonly in some kingdoms than in others – Many plant viruses contain ssRNA genomes – Many fungal viruses contain dsRNA genomes – Many bacterial viruses contain ...
Bacteria and Viruses
... Bacteriophage • Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria • Bacteriophage – Head – capsid and DNA – Tail – with fibers to attach to ...
... Bacteriophage • Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria • Bacteriophage – Head – capsid and DNA – Tail – with fibers to attach to ...
History of virology

The history of virology – the scientific study of viruses and the infections they cause – began in the closing years of the 19th century. Although Louis Pasteur and Edward Jenner developed the first vaccines to protect against viral infections, they did not know that viruses existed. The first evidence of the existence of viruses came from experiments with filters that had pores small enough to retain bacteria. In 1892, Dmitry Ivanovsky used one of these filters to show that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious to healthy tobacco plants despite having been filtered. Martinus Beijerinck called the filtered, infectious substance a ""virus"" and this discovery is considered to be the beginning of virology. By the 20th century many viruses were discovered.