Study Guide for Exam 6 Part I – The Trait Perspective in Personality
... Post traumatic stress disorder (also note pt personal growth) What is a somatoform disorder? Recognize an example of conversion disorder. What are characteristics of dissociative disorders? What is dissociative identity disorder? What evidence suggests that it is ‘more than role-playing’? What are m ...
... Post traumatic stress disorder (also note pt personal growth) What is a somatoform disorder? Recognize an example of conversion disorder. What are characteristics of dissociative disorders? What is dissociative identity disorder? What evidence suggests that it is ‘more than role-playing’? What are m ...
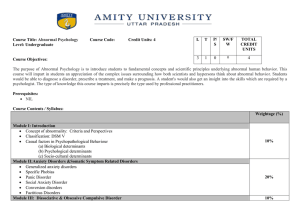
L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 3 1 0 0 4 Course Title
... Describe the diagnostic criteria, symptoms, course, incidence, prevalence, etiology, prognosis, and correlates of major mental disorders. Evaluate biological, social, learning, and developmental influences on psychopathology. Apply diagnostic criteria and case formulations to the assessment and diag ...
... Describe the diagnostic criteria, symptoms, course, incidence, prevalence, etiology, prognosis, and correlates of major mental disorders. Evaluate biological, social, learning, and developmental influences on psychopathology. Apply diagnostic criteria and case formulations to the assessment and diag ...
Child and Adolescent Psychopathology
... • Provides instructions to teachers and peers regarding specific behavioral changes (e.g., teachers taught to diffuse their frustrations by providing positive comments) ...
... • Provides instructions to teachers and peers regarding specific behavioral changes (e.g., teachers taught to diffuse their frustrations by providing positive comments) ...
Dissociative, Personality, and Somatoform Disorders
... Personality Disorders- Disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They usually occur without anxiety, depression, or delusions. These personalities are the extreme compared to normal variation and some say are a result of failure to establish ...
... Personality Disorders- Disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They usually occur without anxiety, depression, or delusions. These personalities are the extreme compared to normal variation and some say are a result of failure to establish ...
Word - University of Maine Farmington
... Professional Credentials - Name, title, and professional credentials of the evaluator, including information about license or certification, area of specialization, employment, and state or province in which the individual practices. Professionals generally considered qualified to evaluate and diagn ...
... Professional Credentials - Name, title, and professional credentials of the evaluator, including information about license or certification, area of specialization, employment, and state or province in which the individual practices. Professionals generally considered qualified to evaluate and diagn ...
Chapter 14 Review
... Major Depressive Disorder Number one reason people seek mental health services is depression Worthlessness Two weeks of the major depressive disorder signs Compared to men, women are more likely to be diagnosed as suffering from depression Western individualism is most clearly responsible ...
... Major Depressive Disorder Number one reason people seek mental health services is depression Worthlessness Two weeks of the major depressive disorder signs Compared to men, women are more likely to be diagnosed as suffering from depression Western individualism is most clearly responsible ...
Dissociative Disorders
... Dr. Robert Hare describes his EEG studies and later SPECT (single photon emission computerized tomography) studies on language processing by psychopathic persons, and reflects on what these results ...
... Dr. Robert Hare describes his EEG studies and later SPECT (single photon emission computerized tomography) studies on language processing by psychopathic persons, and reflects on what these results ...
2. Personality Disorders
... – Identity disturbance, unstable self-image or sense of self • Chronic feelings of emptiness – Impulsivity in at least 2 areas (e.g. spending, sex, substance abuse, reckless driving, binge eating) ...
... – Identity disturbance, unstable self-image or sense of self • Chronic feelings of emptiness – Impulsivity in at least 2 areas (e.g. spending, sex, substance abuse, reckless driving, binge eating) ...
File
... mistaken impression or wrong idea, but the word also implies action - the action of fooling with a wrong impression or idea or the condition of being fooled or deceived. Some examples are: In an allusion to her profession, she named her cat Webster. / He suffers from the delusion that he is a great ...
... mistaken impression or wrong idea, but the word also implies action - the action of fooling with a wrong impression or idea or the condition of being fooled or deceived. Some examples are: In an allusion to her profession, she named her cat Webster. / He suffers from the delusion that he is a great ...
Chapter 14- Abnormal Behavior
... Dissociative Amnesia: sudden loss of memory for personal information that is not due to normal forgetfulness • Fugue: forming a new identity ...
... Dissociative Amnesia: sudden loss of memory for personal information that is not due to normal forgetfulness • Fugue: forming a new identity ...
Semi-final written exam in Psychiatry
... and psychiatric disorders.EEG and event related potentials in PsychiatryOrganic mental disorders: diagnosis and treatment.Classification of mental disorders.Substance abuse: diagnosis and treatment.Alcohol abuse and dependence: diagnosis and treatment.Consultation and liason psychiatry.Psychosomatic ...
... and psychiatric disorders.EEG and event related potentials in PsychiatryOrganic mental disorders: diagnosis and treatment.Classification of mental disorders.Substance abuse: diagnosis and treatment.Alcohol abuse and dependence: diagnosis and treatment.Consultation and liason psychiatry.Psychosomatic ...
Psychopathology
... Psychopathology is the disease of the brain, no different than any other disease of the body. Learning- Psychopathology is learned or acquired. Psychoanalytical- The result of childhood fixations during psychosexual development ...
... Psychopathology is the disease of the brain, no different than any other disease of the body. Learning- Psychopathology is learned or acquired. Psychoanalytical- The result of childhood fixations during psychosexual development ...
Mental Disorders and Treatment Schedule
... identify the criteria for judging whether behavior is psychologically disordered describe the symptoms of generalized anxiety, phobic, and obsessive-compulsive disorders distinguish between a conversion disorder and hypochondriasis describe the characteristics and possible causes of amnesia, fugue, ...
... identify the criteria for judging whether behavior is psychologically disordered describe the symptoms of generalized anxiety, phobic, and obsessive-compulsive disorders distinguish between a conversion disorder and hypochondriasis describe the characteristics and possible causes of amnesia, fugue, ...
Current Tri II Course Schedule
... Overview to Clinical Psychology: Psychological Theories: Psychoanalytic, Behavioral, Humanistic, Systems, Cognitive ...
... Overview to Clinical Psychology: Psychological Theories: Psychoanalytic, Behavioral, Humanistic, Systems, Cognitive ...
Chapter 13: Psychological Disorders Abnormal Behavior: The
... A sudden loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting Dissociative Fugue When a person lose their memory for their entire lives along with their sense of personal identity ...
... A sudden loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting Dissociative Fugue When a person lose their memory for their entire lives along with their sense of personal identity ...
Person Class Notes Behaviorism:
... -- Payoff: gaining some psychological score from the game. *People are adept at playing games and finding ppl who will play the games with them. Positions: - before children are 8 years old, they develop a concept about their own worth. - also formulate ideas about the worth of others. - decision ma ...
... -- Payoff: gaining some psychological score from the game. *People are adept at playing games and finding ppl who will play the games with them. Positions: - before children are 8 years old, they develop a concept about their own worth. - also formulate ideas about the worth of others. - decision ma ...
Part 2 2011
... Recurrent suicidal behavior, gestures or threats or selfmutilating behaviour Identity disturbance, unstable self-image or sense of self Impulsivity in at least 2 areas (e.g. spending, sex, substance abuse, reckless driving, binge eating) ...
... Recurrent suicidal behavior, gestures or threats or selfmutilating behaviour Identity disturbance, unstable self-image or sense of self Impulsivity in at least 2 areas (e.g. spending, sex, substance abuse, reckless driving, binge eating) ...
Abnormal Psychology
... – Freud saw the neurotic disorders as ways of dealing with anxiety • Psychotic disorder – person loses contact with reality – experiences irrational ideas and distorted perceptions ...
... – Freud saw the neurotic disorders as ways of dealing with anxiety • Psychotic disorder – person loses contact with reality – experiences irrational ideas and distorted perceptions ...
Borderline Personality Disorder
... Typical characteristics of Borderline Personality Disorder described in depth: 1. Disturbance in self-concept. People with BPD base their self-image on what others say or how others react to them. Self-concept fluctuates due to mood swings and contradictory inconsistent thoughts about oneself. 2. Un ...
... Typical characteristics of Borderline Personality Disorder described in depth: 1. Disturbance in self-concept. People with BPD base their self-image on what others say or how others react to them. Self-concept fluctuates due to mood swings and contradictory inconsistent thoughts about oneself. 2. Un ...
Abnormal Psychology
... – Reactions to medications – Physical health – Faking illness (secondary gain) ...
... – Reactions to medications – Physical health – Faking illness (secondary gain) ...
Chapter 9
... -Personality traits exaggerated to the point that they cause dysfunction in their relationships -DSM IV classified as Axis II -They do not believe there is anything wrong with them, but rather their problems occur by other people or events ...
... -Personality traits exaggerated to the point that they cause dysfunction in their relationships -DSM IV classified as Axis II -They do not believe there is anything wrong with them, but rather their problems occur by other people or events ...
Impulsivity
Impulsivity (or impulsiveness) is a multifactorial construct that involves a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences. Impulsive actions are typically ""poorly conceived, prematurely expressed, unduly risky, or inappropriate to the situation that often result in undesirable consequences,"" which imperil long-term goals and strategies for success. A functional variety of impulsivity has also been suggested, which involves action without much forethought in appropriate situations that can and does result in desirable consequences. ""When such actions have positive outcomes, they tend not to be seen as signs of impulsivity, but as indicators of boldness, quickness, spontaneity, courageousness, or unconventionality"" Thus, the construct of impulsivity includes at least the two independent components of, first: acting without an appropriate amount of deliberation, which may or may not be functional; and, second: choosing short-term gains over long-term ones.Impulsivity is both a facet of personality as well as a major component of various disorders, including ADHD, substance use disorders, bipolar disorder, antisocial personality disorder, and borderline personality disorder. Impulsiveness may also be a factor in procrastination. Abnormal patterns of impulsivity have also been noted instances of acquired brain injury and neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiological findings suggest that there are specific brain regions involved in impulsive behavior, although different brain networks may contribute to different manifestations of impulsivity, and that genetics may play a role.Many actions contain both impulsive and compulsive features, but impulsivity and compulsivity are functionally distinct. Impulsivity and compulsivity are interrelated in that each exhibits a tendency to act prematurely or without considered thought and often include negative outcomes. Compulsivity may be on a continuum with compulsivity on one end and impulsivity on the other, but research has been contradictory on this point. Compulsivity occurs in response to a perceived risk or threat, impulsivity occurs in response to a perceived immediate gain or benefit, and, whereas compulsivity involves repetitive actions, impulsivity involves unplanned reactions.