Canada in the 30`s the build up to WWII Due 18th Nov
... Total state control of society (Hitler Youth, ...
... Total state control of society (Hitler Youth, ...
Section 2: War in Europe
... Benito Mussolini was establishing a totalitarism regime in Italy Seized power, taking advantage of high unemployment, inflation Middle-class fear of communism Creates Fascist Party Strong public speaker Italian national pride 921 Mussolini established the Fascist party Focused on natio ...
... Benito Mussolini was establishing a totalitarism regime in Italy Seized power, taking advantage of high unemployment, inflation Middle-class fear of communism Creates Fascist Party Strong public speaker Italian national pride 921 Mussolini established the Fascist party Focused on natio ...
World War II
... Acted as totalitarian dictator – controlled aspects of daily life Silenced and even killed any who spoke against him ...
... Acted as totalitarian dictator – controlled aspects of daily life Silenced and even killed any who spoke against him ...
Fascism Reading
... the German workers to promote antiSemitism, hostility and hatred towards the Jews, and enforcement of racial “purification.” Hitler also promoted national expansion and claimed that Germany needed more lebensraum, or “living space.” Hitler believed that in order for Germany to survive they must expa ...
... the German workers to promote antiSemitism, hostility and hatred towards the Jews, and enforcement of racial “purification.” Hitler also promoted national expansion and claimed that Germany needed more lebensraum, or “living space.” Hitler believed that in order for Germany to survive they must expa ...
Chapter 14 The Coming of War - Mr Russell FCHS
... Totalitarianism in Italy direct result of WWI/treaties Italy on winning side Doesn’t get land it wanted Depression = high unemployment = communist ...
... Totalitarianism in Italy direct result of WWI/treaties Italy on winning side Doesn’t get land it wanted Depression = high unemployment = communist ...
WW II: The Rise of Dictators
... • In 1927 he began a massive effort to industrialize the country. • As a result of Stalin’s policies in the 1930’s, millions of Russians either were executed or died from hunger during the forced collectivization of Soviet agriculture or brutal conditions in labor camps called Gulags in Siberia • Ma ...
... • In 1927 he began a massive effort to industrialize the country. • As a result of Stalin’s policies in the 1930’s, millions of Russians either were executed or died from hunger during the forced collectivization of Soviet agriculture or brutal conditions in labor camps called Gulags in Siberia • Ma ...
Fascism Rises in Europe
... • Promised to revive Italian economy and rebuild military • Founded Fascist Party in 1919 – popularity increases as conditions worsen • Italy disappointed with territorial gains from WWI • Inflation and unemployment = social unrest • Fear Communist revolution – win support of upper and middle class ...
... • Promised to revive Italian economy and rebuild military • Founded Fascist Party in 1919 – popularity increases as conditions worsen • Italy disappointed with territorial gains from WWI • Inflation and unemployment = social unrest • Fear Communist revolution – win support of upper and middle class ...
File - Mrs. Ward World History
... opposition parties Mussolini built up the military to create new jobs He planned to conquer new territories in North Africa for Italy, creating a new Roman Empire ...
... opposition parties Mussolini built up the military to create new jobs He planned to conquer new territories in North Africa for Italy, creating a new Roman Empire ...
The Treaty of Versailles
... Germany: There were three examples of aggression that led to World War Two. First, and probably the largest, were the warlike acts of Adolf Hitler and the NAZIS. Hitler came to power in Germany promising to rebuild the defeated country. Soon, he had increased the size of the army, and began taking o ...
... Germany: There were three examples of aggression that led to World War Two. First, and probably the largest, were the warlike acts of Adolf Hitler and the NAZIS. Hitler came to power in Germany promising to rebuild the defeated country. Soon, he had increased the size of the army, and began taking o ...
Totalitarian
... opposition parties Mussolini built up the military to create new jobs He planned to conquer new territories in North Africa for Italy, creating a new Roman Empire ...
... opposition parties Mussolini built up the military to create new jobs He planned to conquer new territories in North Africa for Italy, creating a new Roman Empire ...
WWII Timeline PowerPoint
... • Mussolini wanted to rule the countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea (including the northern parts of Africa) to build a “new Roman Empire.” • Tojo wanted to rule Asia and the South Pacific. – This led to the invasion of their respective areas and was the primary reason for World War II. – Alt ...
... • Mussolini wanted to rule the countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea (including the northern parts of Africa) to build a “new Roman Empire.” • Tojo wanted to rule Asia and the South Pacific. – This led to the invasion of their respective areas and was the primary reason for World War II. – Alt ...
File - MR. GREGORSKI`S WEB PAGE
... • Sooner will a camel pass through a needle's eye than a great man be 'discovered' by an election. • -Adolf Hitler with his twist on Mark 10:25 (Mein Kampf) ...
... • Sooner will a camel pass through a needle's eye than a great man be 'discovered' by an election. • -Adolf Hitler with his twist on Mark 10:25 (Mein Kampf) ...
WWII - Les Cheneaux Community Schools
... Created the National Socialist Party: Nazis Hitler: Tremendous motivator of the masses Restore national pride Promised order out of chaos. Germany’s problems blamed on the Jews, International Bankers, Communists, Old German Leaders, and nations who signed the Treaty of Versailles ...
... Created the National Socialist Party: Nazis Hitler: Tremendous motivator of the masses Restore national pride Promised order out of chaos. Germany’s problems blamed on the Jews, International Bankers, Communists, Old German Leaders, and nations who signed the Treaty of Versailles ...
Name - Edison
... Europe: WWI – WWII When WWI ended in 1918, President Woodrow Wilson had announced, “Everything for which America fought has been accomplished.” Wilson had hoped that the US could “aid in the establishment of just democracy throughout the world.” Instead, the treaty that ended the war, along with the ...
... Europe: WWI – WWII When WWI ended in 1918, President Woodrow Wilson had announced, “Everything for which America fought has been accomplished.” Wilson had hoped that the US could “aid in the establishment of just democracy throughout the world.” Instead, the treaty that ended the war, along with the ...
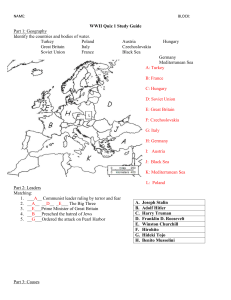
NAME: BLOCK: WWII Quiz 1 Study Guide Part 1: Geography Identify
... Treaty of Versailles (must include reparations) – Germany was forced to pay high reparations after WWII. They were also resentful towards the Allied powers. Japan felt excluded from the negotiations, and wanted to prove their power. How did post WWI Europe set the stage for WWII? Explain two histori ...
... Treaty of Versailles (must include reparations) – Germany was forced to pay high reparations after WWII. They were also resentful towards the Allied powers. Japan felt excluded from the negotiations, and wanted to prove their power. How did post WWI Europe set the stage for WWII? Explain two histori ...
ItalianFascism - SWR Global History
... To Fascists, the individual was unimportant except as a member of the state. Men were urged to be ruthless, selfless warriors for the glory of Italy. Women were pushed out of paying jobs. Instead, Mussolini called on women to “win the battle of motherhood.” Those who bore more than 14 children were ...
... To Fascists, the individual was unimportant except as a member of the state. Men were urged to be ruthless, selfless warriors for the glory of Italy. Women were pushed out of paying jobs. Instead, Mussolini called on women to “win the battle of motherhood.” Those who bore more than 14 children were ...
RISE OF DICTATORS
... intimidating opponents and causing violence – Hitler promised to fix the economic problems and to overturn the Treaty of Versailles and bring glory back to Germany since Germans were the master race – By 1933 the Nazi party gained the majority of seats in the German parliament and Hitler was named ...
... intimidating opponents and causing violence – Hitler promised to fix the economic problems and to overturn the Treaty of Versailles and bring glory back to Germany since Germans were the master race – By 1933 the Nazi party gained the majority of seats in the German parliament and Hitler was named ...
Fascist Dictatorships in Italy and Germany
... Kaiser's abdication, Germany became a republic The German federal republic became known as the Weimar Republic Weimar is where they drafted ...
... Kaiser's abdication, Germany became a republic The German federal republic became known as the Weimar Republic Weimar is where they drafted ...
Fascism, Mussolini, and the Corporate State
... invaded Poland which began World War II. Both England and France courted Italy, but in 1940, Mussolini joined Germany as the Axis (soon joined by Japan), after the surrender of France to Germany. Mussolini thought it would be a brief war. Italy’s role was to control the Mediterranean, including Lib ...
... invaded Poland which began World War II. Both England and France courted Italy, but in 1940, Mussolini joined Germany as the Axis (soon joined by Japan), after the surrender of France to Germany. Mussolini thought it would be a brief war. Italy’s role was to control the Mediterranean, including Lib ...
File
... democratic processes. In some countries people turned to extremist groups. One was communism. Another was a new political movement known as fascism. Fascism was different from communism because it had no plan of action. Most fascist believed in an extreme type of nationalism that included war as a w ...
... democratic processes. In some countries people turned to extremist groups. One was communism. Another was a new political movement known as fascism. Fascism was different from communism because it had no plan of action. Most fascist believed in an extreme type of nationalism that included war as a w ...
World History - WordPress.com
... 12. Which European battle was the last offensive attack by the Germans? 13. Francisco Franco of Spain was the leader of which group? 14. What happened at the Munich Conference? 15. What happened on D-Day? 16. In which nation was the pre-war government allowed to return to power after WWII? 17. What ...
... 12. Which European battle was the last offensive attack by the Germans? 13. Francisco Franco of Spain was the leader of which group? 14. What happened at the Munich Conference? 15. What happened on D-Day? 16. In which nation was the pre-war government allowed to return to power after WWII? 17. What ...
Rise_of_Totalitarian_Dictators (1)
... wanted to overthrow the & quickly rose to disloyal Weimar Republic power in the party The Nazis created their own miliMa called the Brown Shirts Hitler planned a march on Munich but he ...
... wanted to overthrow the & quickly rose to disloyal Weimar Republic power in the party The Nazis created their own miliMa called the Brown Shirts Hitler planned a march on Munich but he ...
Fascism in Europe

Fascism in Europe was composed of numerous ideologies present during the 20th century which all developed their own differences from each other. Fascism was born in Italy and subsequently, across Europe several movements which took influence from it emerged. Purists assert that the term ""Fascism"" should only be used in relation to the National Fascist Party under Benito Mussolini in Italy.However, commonly the following European ideologies are also described as forms of, or strongly related to fascism. The Falange in Spain under Francisco Franco, the Austrofascism in Austria under Engelbert Dollfuß, the 4th of August Regime in Greece under Ioannis Metaxas, the Sanation in Poland under Józef Piłsudski, the National Legionary State in Romania under Ion Antonescu, the Ustaše in Croatia under Ante Pavelic during the Interwar period and World War II, the Estado Novo in Portugal under António de Oliveira Salazar, and the Nazi Party of Germany under Adolf Hitler.The most striking difference is the racialist and anti-Semitic ideology present in Nazism but not the other ideologies. Fascism was founded on the principle of nationalist unity, against the divisionist class war ideology of Socialism and Communism. Thus the majority of the regimes viewed racialism as counter productive to unity, with Mussolini asserting that ""National pride has no need of the delirium of race"".Italian Fascism was expansionist in its desires, looking to create a New Roman Empire. As was Nazi Germany, who looked to expand its borders. The same cannot be said for the other ideologies who focused almost exclusively on internal matters. This led to some countries, such as Spain or Portugal, remaining neutral in World War II, rather than being Axis powers, while Metaxas's Greece fought against the Axis, due to Italy's invasion. It is widely accepted that the Nazis murdered the Austrofascist dictator, causing an uneasy relationship between Fascism and Nazism at an early stage.The question of religion also poses considerable conflicting differences, some forms of fascism, particularly the Falange and Estado Novo were devoutly Christian. Thus the occultist and pagan elements of Nazism, were directly opposed to the Christian element found in the vast majority of fascism movements of the 20th century.