Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... into the end of the digestive tract and ejected though the anus. Senses: Arthropods have specialized sense organs that allow them to be sensitive to changes in their environments. These include changes in light, sound, scents, chemicals, potential mates, food proximity, touch, air currents, and body ...
... into the end of the digestive tract and ejected though the anus. Senses: Arthropods have specialized sense organs that allow them to be sensitive to changes in their environments. These include changes in light, sound, scents, chemicals, potential mates, food proximity, touch, air currents, and body ...
Phylum Arthropoda “Jointed Legs”
... daddy-long-legs & others. Chelicera- Pointed appendage used to grasp food. Pedipalps- Second Pair of appendages. Function as touch organs. ...
... daddy-long-legs & others. Chelicera- Pointed appendage used to grasp food. Pedipalps- Second Pair of appendages. Function as touch organs. ...
1 Organismal Final Study Guide Fall 2015 Organism
... o Raptorial Pedipalps modified for grasping (raptorial) Order Araneae o Spiders o Silk= spinnerets o Chelicerae- fangs, venomous o Male pedipalps are modified for copulation o Narrow waist Order Pseudoscorpiones o All small o Lacking tail o No metasoma or sting o Venom through chelicerae o Sil ...
... o Raptorial Pedipalps modified for grasping (raptorial) Order Araneae o Spiders o Silk= spinnerets o Chelicerae- fangs, venomous o Male pedipalps are modified for copulation o Narrow waist Order Pseudoscorpiones o All small o Lacking tail o No metasoma or sting o Venom through chelicerae o Sil ...
FINAL REVIEW GUIDE
... Know the parts of the starfish. This will be part of the Lab Practical Know how water moves through the water vascular system ...
... Know the parts of the starfish. This will be part of the Lab Practical Know how water moves through the water vascular system ...
File
... hollow dorsal nerve cord: central nervous system, arising from infolding of ectodermal tissue early in embryonic development, which serves to coordinate sensory input and motor response; differentiates into tripartite brain & spinal cord in most chordates pharyngeal slits: arise from lateral grooves ...
... hollow dorsal nerve cord: central nervous system, arising from infolding of ectodermal tissue early in embryonic development, which serves to coordinate sensory input and motor response; differentiates into tripartite brain & spinal cord in most chordates pharyngeal slits: arise from lateral grooves ...
Arthropods - Killeen Independent School District
... without pedicel Presence of external segmentation of abdomen 4 pairs of long, spindly legs ...
... without pedicel Presence of external segmentation of abdomen 4 pairs of long, spindly legs ...
File
... Gathering and Responding to Information Skeletons vary widely from phylum to phylum. Some invertebrates, such as earthworms, have skeletons that are flexible and function through the use of fluid pressure. Insects and some other invertebrates have external skeletons. The hard shell of a lobster is ...
... Gathering and Responding to Information Skeletons vary widely from phylum to phylum. Some invertebrates, such as earthworms, have skeletons that are flexible and function through the use of fluid pressure. Insects and some other invertebrates have external skeletons. The hard shell of a lobster is ...
Animals Part I - CCRI Faculty Web
... – Over 1 million species have been described 30 million may exist (mostly insects) – Appendages are for: Walking, swimming, reproduction, eating, sensory reception – Exoskeleton of chitin (must molt to grow) – Well-developed nervous system Brain and ventral nerve cord Sense organs ...
... – Over 1 million species have been described 30 million may exist (mostly insects) – Appendages are for: Walking, swimming, reproduction, eating, sensory reception – Exoskeleton of chitin (must molt to grow) – Well-developed nervous system Brain and ventral nerve cord Sense organs ...
ANIMAL DIVERSITY
... • The muscular foot of the Molluscs is used for locomotion • The form of the foot is modified in each group to meet their own specific needs – ___________________________ MOLLUSCAN MANTLE & SHELL • The mantle is the tissue responsible for ___________________________ • The ancestral shell is thought ...
... • The muscular foot of the Molluscs is used for locomotion • The form of the foot is modified in each group to meet their own specific needs – ___________________________ MOLLUSCAN MANTLE & SHELL • The mantle is the tissue responsible for ___________________________ • The ancestral shell is thought ...
Chapter # 13 Notes
... soft bodied with a leathery covering which makes them different from all other echinoderms have tentacles around their mouth rows of tube feet on their upper and lower surfaces when threatened they can expel their internal organs which regenerate in a few weeks Value of Echinoderms: feed o ...
... soft bodied with a leathery covering which makes them different from all other echinoderms have tentacles around their mouth rows of tube feet on their upper and lower surfaces when threatened they can expel their internal organs which regenerate in a few weeks Value of Echinoderms: feed o ...
Section 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
... • Open circulatory system – a heart pumps fluid containing oxygen and nutrients through vessels into the body cavity. – The fluid provides oxygen and nutrients as it washes across the ...
... • Open circulatory system – a heart pumps fluid containing oxygen and nutrients through vessels into the body cavity. – The fluid provides oxygen and nutrients as it washes across the ...
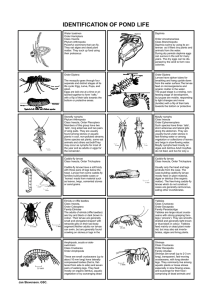
Identification of Pondlife
... dark. Some leeches take blood from animals such as frogs, fish and turtles, while others do not feed on blood but prey on other invertebrates or scavenge for their food. ...
... dark. Some leeches take blood from animals such as frogs, fish and turtles, while others do not feed on blood but prey on other invertebrates or scavenge for their food. ...
Animals: Vertebrates
... b. A ________ within the egg nourishes the developing embryo until it hatches and can feed itself c. This self-contained, drought resistant _________________ allowed reptiles to complete their life cycles on land, similar to what the seed did for plants 3. Reproduction is via _________ fertilization ...
... b. A ________ within the egg nourishes the developing embryo until it hatches and can feed itself c. This self-contained, drought resistant _________________ allowed reptiles to complete their life cycles on land, similar to what the seed did for plants 3. Reproduction is via _________ fertilization ...
m5zn_72f62a9797e3098
... All reptiles have: Dry, scaly skin – helps prevent loss of body water in dry environments. Terrestrial eggs – first animals to develop amniotic eggs that didn’t need to be deposited in water Respire using lungs. Closed circulatory system. Heart = two atria; one or two ventricles. Interna ...
... All reptiles have: Dry, scaly skin – helps prevent loss of body water in dry environments. Terrestrial eggs – first animals to develop amniotic eggs that didn’t need to be deposited in water Respire using lungs. Closed circulatory system. Heart = two atria; one or two ventricles. Interna ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... living animals, and molecular data illustrates that they are the closest living relatives of animals. 4. A choanoflagellate is a single cell, 3–10 μm in diameter, with a flagellum surrounded by a collar of 30–40 microvilli. 5. As the water moves through the microvilli, they engulf bacteria and debri ...
... living animals, and molecular data illustrates that they are the closest living relatives of animals. 4. A choanoflagellate is a single cell, 3–10 μm in diameter, with a flagellum surrounded by a collar of 30–40 microvilli. 5. As the water moves through the microvilli, they engulf bacteria and debri ...
Classification - WordPress.com
... • Have a backbone •Most lay eggs •Their eggs have no shells •They use gills, lungs and skin to breathe •They have a three chamber heart •They are cold blooded •They have four legs •They use webbed feet ...
... • Have a backbone •Most lay eggs •Their eggs have no shells •They use gills, lungs and skin to breathe •They have a three chamber heart •They are cold blooded •They have four legs •They use webbed feet ...
Final Review #1
... Carangiform-front half body rigid, back half moves Ostraciiform-only caudal fin moves Appendicular-appendages move angulliform- most of body used 48.What are the three types of instability? Describe. Roll- move side to side Pitch-up and down movement yaw- tendency to go right or left 49.The two forc ...
... Carangiform-front half body rigid, back half moves Ostraciiform-only caudal fin moves Appendicular-appendages move angulliform- most of body used 48.What are the three types of instability? Describe. Roll- move side to side Pitch-up and down movement yaw- tendency to go right or left 49.The two forc ...
Evolution of Animals
... A crown of cilia (corona) causes a rotating motion; this organ of locomotion also directs food to the mouth. They can dessicate for lengthy periods of time and thus are called “resurrection animacules.” E. Molluscs 1. Molluscs (phylum Mollusca) live in marine, freshwater and terrestrial environments ...
... A crown of cilia (corona) causes a rotating motion; this organ of locomotion also directs food to the mouth. They can dessicate for lengthy periods of time and thus are called “resurrection animacules.” E. Molluscs 1. Molluscs (phylum Mollusca) live in marine, freshwater and terrestrial environments ...
File - Taran D. Thompson
... b. sand dollars c. sea cuccumbers d. sea urchins e. all of these 26. ______________ separates the visceral mass from the secreted shell in mollusks a. mantle b. radula c. caecum d. foot e. esophagus 27. Only class of mollusk that does not have a radula a. Cephalopods b. Gastropods c. Uropods d. Biva ...
... b. sand dollars c. sea cuccumbers d. sea urchins e. all of these 26. ______________ separates the visceral mass from the secreted shell in mollusks a. mantle b. radula c. caecum d. foot e. esophagus 27. Only class of mollusk that does not have a radula a. Cephalopods b. Gastropods c. Uropods d. Biva ...
Animal Diversity Handout
... • ___________________________ – sponges • ___________________________ – jellyfish, anemones, corals, hydra • ___________________________ – planaria, tapeworms, flukes • ___________________________ – segmented worms • ___________________________ – snails, slugs, clams, squid, octopus • ______________ ...
... • ___________________________ – sponges • ___________________________ – jellyfish, anemones, corals, hydra • ___________________________ – planaria, tapeworms, flukes • ___________________________ – segmented worms • ___________________________ – snails, slugs, clams, squid, octopus • ______________ ...
Worksheet - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Starfish are an important part of shoreline ecosystems. In one experiment, a starfish (Pisaster ochraceous) was removed from an area. This starfish was a predator of many mussel species in that location. With the starfish removed, it was thought that the mussels would achieve greater diversity. On t ...
... Starfish are an important part of shoreline ecosystems. In one experiment, a starfish (Pisaster ochraceous) was removed from an area. This starfish was a predator of many mussel species in that location. With the starfish removed, it was thought that the mussels would achieve greater diversity. On t ...
Unit 4 Part 2 Outline Animal Diversity
... Earthworms are hermaphroditic. Comparison with Clam Worm The comparison of the marine clam worm with the terrestrial earthworm highlights the manner in which earthworms are adapted to life on land. Leeches Leeches have no setae and each body ring has several transverse grooves. Among their modificat ...
... Earthworms are hermaphroditic. Comparison with Clam Worm The comparison of the marine clam worm with the terrestrial earthworm highlights the manner in which earthworms are adapted to life on land. Leeches Leeches have no setae and each body ring has several transverse grooves. Among their modificat ...
Chapter XXII —Subphylum Crustacea
... dominant class of arthropods on land, the class Crustacea dominates the water. Several features distinguish crustaceans from insects. Another difference between crustaceans and insects is that crustaceans continue to molt after they become adults. Most of the 35,000 known species of crustaceans are ...
... dominant class of arthropods on land, the class Crustacea dominates the water. Several features distinguish crustaceans from insects. Another difference between crustaceans and insects is that crustaceans continue to molt after they become adults. Most of the 35,000 known species of crustaceans are ...
Chapter 36: Comparing Vertebrates
... positioned on either side of the vertebral column Contract in waves, one after another Make the body bend rapidly back and forth Amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals The position of the limbs relative to the body shifts toward the center The movement of the vertebral column when the anim ...
... positioned on either side of the vertebral column Contract in waves, one after another Make the body bend rapidly back and forth Amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals The position of the limbs relative to the body shifts toward the center The movement of the vertebral column when the anim ...
Terrestrial locomotion

Terrestrial locomotion has evolved as animals adapted from aquatic to terrestrial environments. Locomotion on land raises different problems than that in water, with reduced friction being replaced by the effects of gravity.There are three basic forms of locomotion found among terrestrial animalsLegged - Moving by using appendagesLimbless locomotion - moving without legs, primarily using the body itself as a propulsive structure.Rolling - rotating the body over the substrate