Histidine protein kinases: key signal transducers outside the animal
... the H-box histidine in the opposing subunit [3]. Many HPKs also have phosphatase activity which dephosphorylates the response regulator and opposes kinase function [3,13] (for details see the Mechanism section); phosphatase activity is mediated by the dimerization domain in these HPKs. The catalytic ...
... the H-box histidine in the opposing subunit [3]. Many HPKs also have phosphatase activity which dephosphorylates the response regulator and opposes kinase function [3,13] (for details see the Mechanism section); phosphatase activity is mediated by the dimerization domain in these HPKs. The catalytic ...
Document
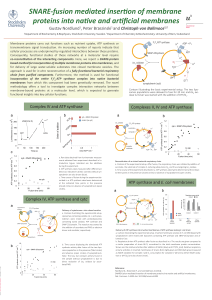
... Membrane proteins carry out func ons such as nutrient uptake, ATP synthesis or transmembrane signal transduc on. An increasing number of reports indicate that cellular processes are underpinned by regulated interac ons between these proteins. Consequently, func onal studies of these networks at a mo ...
... Membrane proteins carry out func ons such as nutrient uptake, ATP synthesis or transmembrane signal transduc on. An increasing number of reports indicate that cellular processes are underpinned by regulated interac ons between these proteins. Consequently, func onal studies of these networks at a mo ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... cyclase types I, III and VIII are stimulated by Ca 2+/calmodulin, an increase in cellular Ca2+ levels, which can result from either increased entry of Ca 2+ into the cell or increased release of Ca2+ from internal stores, would be expected to activate these enzymes. The actions of Ca 2+/calmodulin a ...
... cyclase types I, III and VIII are stimulated by Ca 2+/calmodulin, an increase in cellular Ca2+ levels, which can result from either increased entry of Ca 2+ into the cell or increased release of Ca2+ from internal stores, would be expected to activate these enzymes. The actions of Ca 2+/calmodulin a ...
File - Martin Ray Arcibal
... bond is broken, energy is released, which powers the endergonic reaction that comes afterwards. ...
... bond is broken, energy is released, which powers the endergonic reaction that comes afterwards. ...
Chapter 18 Classification Chapter Vocabulary Review
... Multiple Choice On the lines provided, write the letter of the answer that best completes the sentence or answers the question. 5. The method of grouping organisms into categories that represent lines of evolutionary descent is called a. taxonomy. c. binomial nomenclature. b. cladistic analysis. d. ...
... Multiple Choice On the lines provided, write the letter of the answer that best completes the sentence or answers the question. 5. The method of grouping organisms into categories that represent lines of evolutionary descent is called a. taxonomy. c. binomial nomenclature. b. cladistic analysis. d. ...
ATP - acpsd.net
... When the phosphate is removed, ATP becomes ______________—adenosine _________________phosphate A phosphate is released into the cytoplasm and energy is released. ADP is a lower energy molecule than ATP, but can be converted to ATP by the addition of a phosphate group. ATP → ADP + phosphate + ...
... When the phosphate is removed, ATP becomes ______________—adenosine _________________phosphate A phosphate is released into the cytoplasm and energy is released. ADP is a lower energy molecule than ATP, but can be converted to ATP by the addition of a phosphate group. ATP → ADP + phosphate + ...
assignment
... We notice that the two arabinose transport systems are redundant in the sense that they both transport arabinose, but they are not identical. The ara F, G, H multi-component system couples arabinose transport to ATP hydrolysis. The ara E system couples transport to proton transport (i.e. proton sym ...
... We notice that the two arabinose transport systems are redundant in the sense that they both transport arabinose, but they are not identical. The ara F, G, H multi-component system couples arabinose transport to ATP hydrolysis. The ara E system couples transport to proton transport (i.e. proton sym ...
Ecto-enzymes ofmammary gland and its tumours
... number of cell types. Its external location suggests that it is different from previously described ATPases, which are found at the interior surface of plasma membranes and often supply the energy requirement for transport functions. In the human erythrocyte membrane, the best-studied membrane model ...
... number of cell types. Its external location suggests that it is different from previously described ATPases, which are found at the interior surface of plasma membranes and often supply the energy requirement for transport functions. In the human erythrocyte membrane, the best-studied membrane model ...
Lecture 5
... Predict how glucose moves into intestinal cells when glucose concentration is higher in the gut than in the intestinal cells after a meal: A) through a glucose channel B) directly through the lipid bilayer C) via Na+-glucose cotransport fueled by the Na+/K+ pump D) through the ATP-fueled Na+/K+ pump ...
... Predict how glucose moves into intestinal cells when glucose concentration is higher in the gut than in the intestinal cells after a meal: A) through a glucose channel B) directly through the lipid bilayer C) via Na+-glucose cotransport fueled by the Na+/K+ pump D) through the ATP-fueled Na+/K+ pump ...
No Slide Title
... major mediator of cAMP action. PKA specifically phosphorylates serine or threonine residues preferably in the following amino acid sequence: Arg - Arg - X Ser (or Thr) - Y, ( where X is a small residue and Y is a large hydrophobic residue). Most kinases rely primarily on the amino acid sequence surr ...
... major mediator of cAMP action. PKA specifically phosphorylates serine or threonine residues preferably in the following amino acid sequence: Arg - Arg - X Ser (or Thr) - Y, ( where X is a small residue and Y is a large hydrophobic residue). Most kinases rely primarily on the amino acid sequence surr ...
Renal tubular transp..
... gradient after binding with a specific carrier protein in the membrane. Needs a carrier. ...
... gradient after binding with a specific carrier protein in the membrane. Needs a carrier. ...
The Internal Repeats in the Na /Ca2+ Exchanger
... eukaryotic Na⫹/Ca2⫹ exchangers (1). All proteins in this family have an internal repeat in their membrane domain that presumably has arisen from a primordial gene duplication event. A strongly conserved and functionally important so-called ␣-motif that spans two of the predicted transmembrane helice ...
... eukaryotic Na⫹/Ca2⫹ exchangers (1). All proteins in this family have an internal repeat in their membrane domain that presumably has arisen from a primordial gene duplication event. A strongly conserved and functionally important so-called ␣-motif that spans two of the predicted transmembrane helice ...
Gene7-26
... a signal transduction pathway is activated. The classic second messenger is cyclic AMP, which is generated when adenylate cyclase is activated by a G protein (when the G protein itself was activated by a transmembrane receptor). Signal transduction describes the process by which a receptor interacts ...
... a signal transduction pathway is activated. The classic second messenger is cyclic AMP, which is generated when adenylate cyclase is activated by a G protein (when the G protein itself was activated by a transmembrane receptor). Signal transduction describes the process by which a receptor interacts ...
Section Review 18-3 (worksheet page 1)
... 2. The three domains are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. 3. Monera was divided into two kingdoms because scientists have come to recognize profound differences among two broad groups of Monera. 4. Members of the kingdom Protista display the greatest variety, sharing characteristics with plants, fung ...
... 2. The three domains are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. 3. Monera was divided into two kingdoms because scientists have come to recognize profound differences among two broad groups of Monera. 4. Members of the kingdom Protista display the greatest variety, sharing characteristics with plants, fung ...
Section Review 18-3 (worksheet page 1)
... 2. The three domains are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. 3. Monera was divided into two kingdoms because scientists have come to recognize profound differences among two broad groups of Monera. 4. Members of the kingdom Protista display the greatest variety, sharing characteristics with plants, fung ...
... 2. The three domains are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. 3. Monera was divided into two kingdoms because scientists have come to recognize profound differences among two broad groups of Monera. 4. Members of the kingdom Protista display the greatest variety, sharing characteristics with plants, fung ...
WORKSHEET 16.3 Building the Tree of Life
... Researchers found that microorganisms were very different from plants and animals. They were placed in their own kingdom, called Protista. Then, yeast, molds, and mushrooms were separated from plants and placed in their own kingdom, called Fungi. Because bacteria lack nuclei, mitochondria, and chlor ...
... Researchers found that microorganisms were very different from plants and animals. They were placed in their own kingdom, called Protista. Then, yeast, molds, and mushrooms were separated from plants and placed in their own kingdom, called Fungi. Because bacteria lack nuclei, mitochondria, and chlor ...
013368718X_CH18_285
... Researchers found that microorganisms were very different from plants and animals. They were placed in their own kingdom, called Protista. Then, yeast, molds, and mushrooms were separated from plants and placed in their own kingdom, called Fungi. Because bacteria lack nuclei, mitochondria, and chlor ...
... Researchers found that microorganisms were very different from plants and animals. They were placed in their own kingdom, called Protista. Then, yeast, molds, and mushrooms were separated from plants and placed in their own kingdom, called Fungi. Because bacteria lack nuclei, mitochondria, and chlor ...
bacteria
... colleagues began to cluster prokarotes into taxonomic groups based on comparisons of nucleic acid sequences. • Especially useful was the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (SSU-rRNA) because all organisms have ribosomes. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... colleagues began to cluster prokarotes into taxonomic groups based on comparisons of nucleic acid sequences. • Especially useful was the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (SSU-rRNA) because all organisms have ribosomes. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
013368718X_CH18_285-298.indd
... Researchers found that microorganisms were very different from plants and animals. They were placed in their own kingdom, called Protista. Then, yeast, molds, and mushrooms were separated from plants and placed in their own kingdom, called Fungi. Because bacteria lack nuclei, mitochondria, and chlor ...
... Researchers found that microorganisms were very different from plants and animals. They were placed in their own kingdom, called Protista. Then, yeast, molds, and mushrooms were separated from plants and placed in their own kingdom, called Fungi. Because bacteria lack nuclei, mitochondria, and chlor ...
Regulation of Lung Ion Transport Faculty: O`Grady, Ingbar This
... regulation of alveolar epithelial function during lung development, injury and repair. Most studies focus on Na,K-ATPase and other ion transport proteins, with additional interest in epithelial migration, matrix interactions, and apoptosis. A major goal is to develop therapeutic strategies to upregu ...
... regulation of alveolar epithelial function during lung development, injury and repair. Most studies focus on Na,K-ATPase and other ion transport proteins, with additional interest in epithelial migration, matrix interactions, and apoptosis. A major goal is to develop therapeutic strategies to upregu ...
3did: a catalog of domain-based interactions of
... occur, we need to incorporate high-resolution molecular/ atomic details, which are currently available in the Protein Data Bank [PDB, (4)]. Several efforts over the last years aimed at mining the data in the PDB to provide a comprehensive structural characterization of protein interaction networks ( ...
... occur, we need to incorporate high-resolution molecular/ atomic details, which are currently available in the Protein Data Bank [PDB, (4)]. Several efforts over the last years aimed at mining the data in the PDB to provide a comprehensive structural characterization of protein interaction networks ( ...
Structural and enzymatic characterization of a glycoside hydrolase
... [6]. In contrast with anaerobic species, such as the Clostridia, the enzymes of C. japonicus that target polysaccharides integral to the plant cell walls do not form large membrane-attached cellulosome complexes [7], but are instead either secreted into the medium or attached to the cell membrane as ...
... [6]. In contrast with anaerobic species, such as the Clostridia, the enzymes of C. japonicus that target polysaccharides integral to the plant cell walls do not form large membrane-attached cellulosome complexes [7], but are instead either secreted into the medium or attached to the cell membrane as ...
Protons and how they are transported by proton pumps
... the cavity, which now forms the deep end of a long exit pathway. Arg655 is suggested to play a key role in proton release and proton pumping against high membrane potentials [25]. The positive charge of Arg655, now approaching Asp684, will favor proton release from Asp684 and at the same time inhibi ...
... the cavity, which now forms the deep end of a long exit pathway. Arg655 is suggested to play a key role in proton release and proton pumping against high membrane potentials [25]. The positive charge of Arg655, now approaching Asp684, will favor proton release from Asp684 and at the same time inhibi ...
- University of East Anglia
... depicted as arrow molecules. In multi-subunit proteins, particularly those that are known to have allosteric mechanism, this depiction is particularly interesting as it may show how a movement is communicated to other parts. An interesting finding from the original work showed that domains do not co ...
... depicted as arrow molecules. In multi-subunit proteins, particularly those that are known to have allosteric mechanism, this depiction is particularly interesting as it may show how a movement is communicated to other parts. An interesting finding from the original work showed that domains do not co ...
Enzymes
... reaction, attaches to the enzyme that catalyses the first reaction and inhibits that enzyme This is called end-product inhibition The enzyme that is inhibited is an example of an allosteric enzyme This is a type of noncompetitive inhibition that controls reactions in the body ...
... reaction, attaches to the enzyme that catalyses the first reaction and inhibits that enzyme This is called end-product inhibition The enzyme that is inhibited is an example of an allosteric enzyme This is a type of noncompetitive inhibition that controls reactions in the body ...
P-type ATPase

The P-type ATPases, also known as E1-E2 ATPases, are a large group of evolutionarily related ion and lipid pumps that are found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. They are α-helical bundle primary transporters referred to as P-type ATPases because they catalyze auto- (or self-) phosphorylation of a key conserved aspartate residue within the pump. In addition, they all appear to interconvert between at least two different conformations, denoted by E1 and E2.Most members of this transporter family are specific for the pumping of a large array of cations, however one subfamily is involved in flipping phospholipids to maintain the asymmetric nature of the biomembrane.Prominent examples of P-type ATPases are the sodium-potassium pump (Na+,K+-ATPase), the plasma membrane proton pump (H+-ATPase), the proton-potassium pump (H+,K+-ATPase), and the calcium pump (Ca2+-ATPase).