Natural selection
... rate of bacteria, algae, and aquatic plants. – Toxic algae can kill fish and poison humans. – An increase in the number of plants and algae results in lowered oxygen concentrations, creating “dead zones.” ...
... rate of bacteria, algae, and aquatic plants. – Toxic algae can kill fish and poison humans. – An increase in the number of plants and algae results in lowered oxygen concentrations, creating “dead zones.” ...
Community Properties
... Community change over time -- succession • If you have a community that is disturbed by some agent (e.g. fire, plowing, landslide, flooding), the community structure in that community is altered. Gradually the community will rebuild itself, tending towards a more stable structure that can be suppor ...
... Community change over time -- succession • If you have a community that is disturbed by some agent (e.g. fire, plowing, landslide, flooding), the community structure in that community is altered. Gradually the community will rebuild itself, tending towards a more stable structure that can be suppor ...
Ch4 Revision - Population Ecology
... environment brought about by the organisms themselves. Through succession, the organisms tend to get bigger and more complex, whilst the biodiversity also rises. Pioneer species are those that first colonise bare soil or rock. They can withstand the harsh environment, and include lichens and mosses ...
... environment brought about by the organisms themselves. Through succession, the organisms tend to get bigger and more complex, whilst the biodiversity also rises. Pioneer species are those that first colonise bare soil or rock. They can withstand the harsh environment, and include lichens and mosses ...
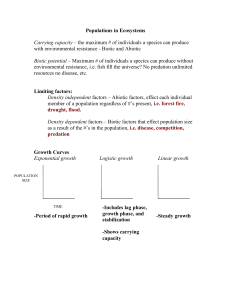
Populations in Ecosystems
... member of a population regardless of #’s present, i.e. forest fire, drought, flood. Density dependent factors – Biotic factors that effect population size as a result of the #’s in the population, i.e. disease, competition, predation ...
... member of a population regardless of #’s present, i.e. forest fire, drought, flood. Density dependent factors – Biotic factors that effect population size as a result of the #’s in the population, i.e. disease, competition, predation ...
An Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Chapter 50
... The study of the distribution of organisms past and present is called biogeography. There are several factors that influence (limit) an organism’s distribution. 1) dispersal: the movement of individuals away from high population or area of origin. Dispersal can be seen when organisms move to areas w ...
... The study of the distribution of organisms past and present is called biogeography. There are several factors that influence (limit) an organism’s distribution. 1) dispersal: the movement of individuals away from high population or area of origin. Dispersal can be seen when organisms move to areas w ...
Lecture 1
... 3. Evolution cannot explain the presence of complex structures in organisms, such as eyes or flagella, that must operate as a unit. 4. While it is clear that evolution can explain changes within species, it cannot explain how new species or groups of species may have arisen. 5. While Darwin proposed ...
... 3. Evolution cannot explain the presence of complex structures in organisms, such as eyes or flagella, that must operate as a unit. 4. While it is clear that evolution can explain changes within species, it cannot explain how new species or groups of species may have arisen. 5. While Darwin proposed ...
Ecology Drives the Worldwide Distribution of
... animal habitat. The additional direct sunlight (versus higher latitudes) leads to more captured energy, which can be used in photosynthesis to promote plant life. The sun also is out longer during the day in tropical climates then higher latitudes. This extra sun light time also would foster animal ...
... animal habitat. The additional direct sunlight (versus higher latitudes) leads to more captured energy, which can be used in photosynthesis to promote plant life. The sun also is out longer during the day in tropical climates then higher latitudes. This extra sun light time also would foster animal ...
Product factsheet - EU BON European Biodiversity Portal
... hybrid models require fine-scale occurrence data and a set of environmental variables to fit the SDMs. Atlas data can be provided independently or can be created from the fine-scale occurrence data, using the ‘downscale’ package. ...
... hybrid models require fine-scale occurrence data and a set of environmental variables to fit the SDMs. Atlas data can be provided independently or can be created from the fine-scale occurrence data, using the ‘downscale’ package. ...
The Five Themes of Geography student notes
... Guided Notes with Powerpoint Presentation First things first… Geography is: a _____________ that deals with the _____________________ , distribution, and ________________________ of the diverse physical, _________________, and cultural features of the Earth’s _________________. ...
... Guided Notes with Powerpoint Presentation First things first… Geography is: a _____________ that deals with the _____________________ , distribution, and ________________________ of the diverse physical, _________________, and cultural features of the Earth’s _________________. ...
Chapter 6 Objective Questions
... take care of your aquarium and you decided you would toss it out, fish, plants, and all into the Chatahoochee River. No one would care and no one would know that YOU did it, so what’s the harm, right? Well, if you float the Chat these days you will see clumps of an aquatic plant called Anacharis (El ...
... take care of your aquarium and you decided you would toss it out, fish, plants, and all into the Chatahoochee River. No one would care and no one would know that YOU did it, so what’s the harm, right? Well, if you float the Chat these days you will see clumps of an aquatic plant called Anacharis (El ...
What`s the Impact?
... eat plants for food and other animals eat the animals that eat plants. Some organisms, such as fungi and bacteria, break down dead organisms (both plants or plants parts and animals) and therefore operate as “decomposers.” Decomposition eventually restores (recycles) some materials back to the soil. ...
... eat plants for food and other animals eat the animals that eat plants. Some organisms, such as fungi and bacteria, break down dead organisms (both plants or plants parts and animals) and therefore operate as “decomposers.” Decomposition eventually restores (recycles) some materials back to the soil. ...
Lesson 5.3 Ecological Communities
... • Three hundred trout are needed to support one man for a year. The trout, in turn, must consume 90,000 frogs, that must consume 27 million grasshoppers that live off of 1,000 tons of grass. • G. Tyler Miller, Jr ...
... • Three hundred trout are needed to support one man for a year. The trout, in turn, must consume 90,000 frogs, that must consume 27 million grasshoppers that live off of 1,000 tons of grass. • G. Tyler Miller, Jr ...
Ecology, interdependence, ecological model, biosphere, ecosystem
... possesses all characteristics of life. ...
... possesses all characteristics of life. ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... things maintain a stable ________________ environment. Taken as a group living things ____________ over ___________ (evolution). o Page 20 Some of the levels at which life can be studied include ______________, cells, ________________, _______________ of a single kind of organism, __________________ ...
... things maintain a stable ________________ environment. Taken as a group living things ____________ over ___________ (evolution). o Page 20 Some of the levels at which life can be studied include ______________, cells, ________________, _______________ of a single kind of organism, __________________ ...
Interactions Among Living Things
... Carrying capacity – the largest population that an environment can support. When a population grows larger than its carrying capacity, limiting factors in the environment cause individuals to die off or leave, returning the population to a size that the environment can support. ...
... Carrying capacity – the largest population that an environment can support. When a population grows larger than its carrying capacity, limiting factors in the environment cause individuals to die off or leave, returning the population to a size that the environment can support. ...
Population
... • Unfortunately, the toads became extinct within 25 years. - Due to global warming’s drying effect on the forest ...
... • Unfortunately, the toads became extinct within 25 years. - Due to global warming’s drying effect on the forest ...
mark scheme
... 2. Describe some of the selection pressures that affect the sizes of populations. Competition for the available food and living space between different species and within the same species occurs. Within species, competition for mates occurs. Other selection pressures could involve the abiotic factor ...
... 2. Describe some of the selection pressures that affect the sizes of populations. Competition for the available food and living space between different species and within the same species occurs. Within species, competition for mates occurs. Other selection pressures could involve the abiotic factor ...
Limiting Factors of Population Growth
... Introduced Invasive Species 2nd biggest threat to biodiversity after habitat destruction!!! ...
... Introduced Invasive Species 2nd biggest threat to biodiversity after habitat destruction!!! ...
TE Notes word version
... Some have proposed that the earth’s various forms of life control or at least influence its chemical cycles and other earth-sustaining processes. The strong Gaia hypothesis: life controls the earth’s life-sustaining processes. The weak Gaia hypothesis: life influences the earth’s life-sustaini ...
... Some have proposed that the earth’s various forms of life control or at least influence its chemical cycles and other earth-sustaining processes. The strong Gaia hypothesis: life controls the earth’s life-sustaining processes. The weak Gaia hypothesis: life influences the earth’s life-sustaini ...
Biogeography

Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area. Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals.Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, geology, and physical geography.Modern biogeographic research combines information and ideas from many fields, from the physiological and ecological constraints on organismal dispersal to geological and climatological phenomena operating at global spatial scales and evolutionary time frames.The short-term interactions within a habitat and species of organisms describe the ecological application of biogeography. Historical biogeography describes the long-term, evolutionary periods of time for broader classifications of organisms. Early scientists, beginning with Carl Linnaeus, contributed theories to the contributions of the development of biogeography as a science. Beginning in the mid-18th century, Europeans explored the world and discovered the biodiversity of life. Linnaeus initiated the ways to classify organisms through his exploration of undiscovered territories.The scientific theory of biogeography grows out of the work of Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859), Hewett Cottrell Watson (1804–1881), Alphonse de Candolle (1806–1893), Alfred Russel Wallace (1823–1913), Philip Lutley Sclater (1829–1913) and other biologists and explorers.