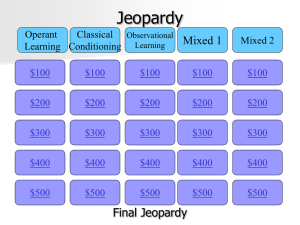
Unit 2: Vocab List and Objectives
... Overview: Psychology is an empirical discipline. Psychologists develop knowledge by doing research. Research provides guidance for psychologists who develop theories to explain behavior and who apply theories to solve problems in behavior. AP Learning Objectives: ● Differentiate types of research (e ...
... Overview: Psychology is an empirical discipline. Psychologists develop knowledge by doing research. Research provides guidance for psychologists who develop theories to explain behavior and who apply theories to solve problems in behavior. AP Learning Objectives: ● Differentiate types of research (e ...
Unit 2 Understanding the Individual 2.5 Learning approach Students
... Describe how learning theory can be used to explain gender development/behaviour with particular reference to modelling, reinforcement and behaviour shaping. ...
... Describe how learning theory can be used to explain gender development/behaviour with particular reference to modelling, reinforcement and behaviour shaping. ...
Behaviorism PP Slides
... conditions - we are who are we are because we’ve been conditioned to be that way. With enough effort, we can identify the cause of the deviant behavior and change the environment so that the deviant behavior is eliminated. ...
... conditions - we are who are we are because we’ve been conditioned to be that way. With enough effort, we can identify the cause of the deviant behavior and change the environment so that the deviant behavior is eliminated. ...
Notes_1_bcsd Intro to Psych research design
... implications -real life cases offer opportunity for insights one could never or would never attempt to gain through artificially designing an experiment -in-depth understanding of single cases will allow for general conclusions about other similar cases -Ex: Phineas Gage -research method involving q ...
... implications -real life cases offer opportunity for insights one could never or would never attempt to gain through artificially designing an experiment -in-depth understanding of single cases will allow for general conclusions about other similar cases -Ex: Phineas Gage -research method involving q ...
chapter - Human Kinetics
... in Physical Education • The terms of this contract are detailed below: • The student will earn one point for every positive statement or action made to or about an opponent during participation in the class basketball unit. Student must earn 10 points to qualify for free time in the gym on Friday af ...
... in Physical Education • The terms of this contract are detailed below: • The student will earn one point for every positive statement or action made to or about an opponent during participation in the class basketball unit. Student must earn 10 points to qualify for free time in the gym on Friday af ...
Operant Conditioning
... Operant conditioning uses operant or voluntary behavior Ask: Is the behavior something the animal can control? Does the animal have a choice in how to behave? ...
... Operant conditioning uses operant or voluntary behavior Ask: Is the behavior something the animal can control? Does the animal have a choice in how to behave? ...
139 Chapter 13 Assignment
... 12. Social-Learning theory: Behavior-environment-behavior interaction- what is it? 13. Rotter and the concept of behavior potential: The likelihood that a given behavior would occur in a given situation. The behavioral potential is based on expectancy- that is- expectation that the behavior be reinf ...
... 12. Social-Learning theory: Behavior-environment-behavior interaction- what is it? 13. Rotter and the concept of behavior potential: The likelihood that a given behavior would occur in a given situation. The behavioral potential is based on expectancy- that is- expectation that the behavior be reinf ...
New Directions in Conditioning
... • Natural predispositions constrain capacity for operant conditioning • Facilitated conditioning – Reinforce natural behaviors ...
... • Natural predispositions constrain capacity for operant conditioning • Facilitated conditioning – Reinforce natural behaviors ...
Learning Red
... 2 – Which will lead to faster learning – immediate or delayed reinforcement? 3 – What is secondary (or conditioned) reinforcement? 4 – Gambling on a slot machine is an example of what type of reinforcement schedule? 5 – Lars, a shoe salesman, is paid every two weeks. He is paid on what type of reinf ...
... 2 – Which will lead to faster learning – immediate or delayed reinforcement? 3 – What is secondary (or conditioned) reinforcement? 4 – Gambling on a slot machine is an example of what type of reinforcement schedule? 5 – Lars, a shoe salesman, is paid every two weeks. He is paid on what type of reinf ...
1 - Cinnaminson School District
... controlled situation, such as a laboratory. o Case studies are detailed investigations of one subject. One concern is the generalizability of the results. o Surveys involve asking standardized questions of large groups of people who represent a sample of the population of interest. Concerns include ...
... controlled situation, such as a laboratory. o Case studies are detailed investigations of one subject. One concern is the generalizability of the results. o Surveys involve asking standardized questions of large groups of people who represent a sample of the population of interest. Concerns include ...
Cognitive-Behavioral Approaches
... • Identify a 6 month goal; write it according to guidelines. • Counselor, facilitate a discussion of strategies your partner can use to achieve their goal. • Switch roles. ...
... • Identify a 6 month goal; write it according to guidelines. • Counselor, facilitate a discussion of strategies your partner can use to achieve their goal. • Switch roles. ...
Behavioral Theory rev 2012
... Stimulus discrimination – Identifying key elements of stimulus which differentiate it from other similar stimuli ...
... Stimulus discrimination – Identifying key elements of stimulus which differentiate it from other similar stimuli ...
Name two scientists famous for their studies of classical conditioning 2
... Bill’s aversion to green cars is an example of ___________. 7 – In Garcia and Koelling’s studies of taste-aversion learning, rats learned to associate taste with sickness, but not the shape of food. Why? 8 – Give an example of operant conditioning. 9 – What is one difference between classical condit ...
... Bill’s aversion to green cars is an example of ___________. 7 – In Garcia and Koelling’s studies of taste-aversion learning, rats learned to associate taste with sickness, but not the shape of food. Why? 8 – Give an example of operant conditioning. 9 – What is one difference between classical condit ...
Document
... 2. Classical _________________________ is a simple form of learning in which one stimulus comes to call forth the response that is usually associated with a different stimulus. 3. Russian physiologist Ivan ____________________ discovered that dogs can learn to associate one thing with another when f ...
... 2. Classical _________________________ is a simple form of learning in which one stimulus comes to call forth the response that is usually associated with a different stimulus. 3. Russian physiologist Ivan ____________________ discovered that dogs can learn to associate one thing with another when f ...
Chapter15
... For example, “ate because hungry” “ate because good price, 6 hours since last meal, etc.” Free Will vs. Determinism: -Free Will: We are free and spontaneous. We are responsible for what we did. -Determinism: Our behaviors are determined by Environmental control. For example, you bought a computer ...
... For example, “ate because hungry” “ate because good price, 6 hours since last meal, etc.” Free Will vs. Determinism: -Free Will: We are free and spontaneous. We are responsible for what we did. -Determinism: Our behaviors are determined by Environmental control. For example, you bought a computer ...
6AnimalBehavior
... Niko Tinbergen animal behavior Q’s: 1. What stimulus elicits the behavior, and what physiological mechanisms mediate the response? (proximate) 2. How does the animal’s experience during growth and development influence the response? (proximate) 3. How does the behavior aid survival and reproductio ...
... Niko Tinbergen animal behavior Q’s: 1. What stimulus elicits the behavior, and what physiological mechanisms mediate the response? (proximate) 2. How does the animal’s experience during growth and development influence the response? (proximate) 3. How does the behavior aid survival and reproductio ...
Term - Manhasset Schools
... implications -real life cases offer opportunity for insights one could never or would never attempt to gain through artificially designing an experiment -in-depth understanding of single cases will allow for general conclusions about other similar cases -Ex: Phineas Gage -research method involving q ...
... implications -real life cases offer opportunity for insights one could never or would never attempt to gain through artificially designing an experiment -in-depth understanding of single cases will allow for general conclusions about other similar cases -Ex: Phineas Gage -research method involving q ...
The Class
... • Selection Bias – Random Assignment • Experimenter Bias – Single Blind Technique Double Blind Technique ∙ Placebo Effect – Need to realize this can change results ...
... • Selection Bias – Random Assignment • Experimenter Bias – Single Blind Technique Double Blind Technique ∙ Placebo Effect – Need to realize this can change results ...
Theory of Reasoned Action and Theory of Planned Behavior
... What ISN’T in the Model Other factors such as the modifying factors in the HBM (demographics, etc.) are not directly addressed. They can have an indirect effect on the other components, but are not specifically incorporated into the model. ...
... What ISN’T in the Model Other factors such as the modifying factors in the HBM (demographics, etc.) are not directly addressed. They can have an indirect effect on the other components, but are not specifically incorporated into the model. ...