*Homeostasis is maintaining a stable internal environment
... *Bacteria are prokaryotes so they do not have a nucleus. *Homologous structures have a similar structure but different function (human hand and bat wing). *Darwin stated the theory of natural selection or “survival of the fittest”. *Natural selection leads to traits that allow an organism to survive ...
... *Bacteria are prokaryotes so they do not have a nucleus. *Homologous structures have a similar structure but different function (human hand and bat wing). *Darwin stated the theory of natural selection or “survival of the fittest”. *Natural selection leads to traits that allow an organism to survive ...
review_answers_ch._7__8
... chronologically, one could observe the changes in a particular group of organisms. In the same way, organisms could be traced back and their common ancestors identified. 5. Varied answers possible. Your answer should include something along the line of genetic change over time as a result of random ...
... chronologically, one could observe the changes in a particular group of organisms. In the same way, organisms could be traced back and their common ancestors identified. 5. Varied answers possible. Your answer should include something along the line of genetic change over time as a result of random ...
chapters_7__8_review_answers_0
... chronologically, one could observe the changes in a particular group of organisms. In the same way, organisms could be traced back and their common ancestors identified. 5. Varied answers possible. Your answer should include something along the line of genetic change over time as a result of random ...
... chronologically, one could observe the changes in a particular group of organisms. In the same way, organisms could be traced back and their common ancestors identified. 5. Varied answers possible. Your answer should include something along the line of genetic change over time as a result of random ...
Evolution, Ecology, and Biodiversity
... 1. Describe the fundamental processes that cause or prevent adaptive evolution, speciation and extinction 2. Describe the basic methods that are used to reconstruct the evolutionary histories of, and relationships among, groups of organisms 3. Based on evolutionary theory, predict how differences in ...
... 1. Describe the fundamental processes that cause or prevent adaptive evolution, speciation and extinction 2. Describe the basic methods that are used to reconstruct the evolutionary histories of, and relationships among, groups of organisms 3. Based on evolutionary theory, predict how differences in ...
File
... the most likely to survive and pass on their genes. Fossils help us because they show us remains or imprints of once-living organisms. A group of organisms that can mate with each other to produce fertile offspring are called species. Speciation can occur through reproductive isolation and then the ...
... the most likely to survive and pass on their genes. Fossils help us because they show us remains or imprints of once-living organisms. A group of organisms that can mate with each other to produce fertile offspring are called species. Speciation can occur through reproductive isolation and then the ...
evolution / taxonomy study guide
... it was instant, in that organisms lifetime 3. Changes in the organism’s structure or function was the result of use or disuse and those changes were passed on to its offspring a. mice do not use their tails so offspring would be born without tails B. Darwin – natural selection (survival of the fitte ...
... it was instant, in that organisms lifetime 3. Changes in the organism’s structure or function was the result of use or disuse and those changes were passed on to its offspring a. mice do not use their tails so offspring would be born without tails B. Darwin – natural selection (survival of the fitte ...
Darwin
... Struggle for existence: members of each species compete regularly to obtain food, living space, and other necessities. ◦ Predators that are faster or have a particular way of ensnaring other organisms, will catch more prey. ◦ Those prey that are faster, better camouflaged, or better protected can av ...
... Struggle for existence: members of each species compete regularly to obtain food, living space, and other necessities. ◦ Predators that are faster or have a particular way of ensnaring other organisms, will catch more prey. ◦ Those prey that are faster, better camouflaged, or better protected can av ...
Science Understandings - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... apparent when analyzing the internal structures of organisms Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing their common ancestry (fossil record) Diversity of species develops gradually over many generations as a result of heredity and environment Species ac ...
... apparent when analyzing the internal structures of organisms Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing their common ancestry (fossil record) Diversity of species develops gradually over many generations as a result of heredity and environment Species ac ...
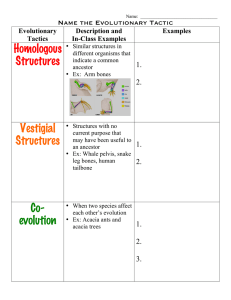
Homologous Structures Vestigial Structures Co
... • Similar structures in different organisms that indicate a common ancestor • Ex: Arm bones ...
... • Similar structures in different organisms that indicate a common ancestor • Ex: Arm bones ...
How Evolution Works: 1. Random mutations cause changes, or
... 1. Random mutations cause changes, or variation, in a population of organisms. 2. These different organisms then compete to survive and reproduce. 3. Those which are best able to survive and reproduce do so, and tend to leave the most offspring. This is called “natural selection.” 4. Over time, if s ...
... 1. Random mutations cause changes, or variation, in a population of organisms. 2. These different organisms then compete to survive and reproduce. 3. Those which are best able to survive and reproduce do so, and tend to leave the most offspring. This is called “natural selection.” 4. Over time, if s ...
Evolution1
... A process of change through time Existing forms have evolved from earlier forms Diversity leads to evolution ...
... A process of change through time Existing forms have evolved from earlier forms Diversity leads to evolution ...
Charles Darwin
... An English naturalist who, along with Alfred Russell Wallace, developed the theory of evolution through natural selection. It is this name that is most closely associated with the theory of evolution. Species ...
... An English naturalist who, along with Alfred Russell Wallace, developed the theory of evolution through natural selection. It is this name that is most closely associated with the theory of evolution. Species ...
Darwins Theory of Evolution
... continued to grow, sooner or later there would not be enough resources for everyone… What did Darwin think about that? ...
... continued to grow, sooner or later there would not be enough resources for everyone… What did Darwin think about that? ...
Changes Over Time - twpunionschools.org
... Natural Selection: The process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. ...
... Natural Selection: The process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. ...
Evolving digital ecological networks
Evolving digital ecological networks are webs of interacting, self-replicating, and evolving computer programs (i.e., digital organisms) that experience the same major ecological interactions as biological organisms (e.g., competition, predation, parasitism, and mutualism). Despite being computational, these programs evolve quickly in an open-ended way, and starting from only one or two ancestral organisms, the formation of ecological networks can be observed in real-time by tracking interactions between the constantly evolving organism phenotypes. These phenotypes may be defined by combinations of logical computations (hereafter tasks) that digital organisms perform and by expressed behaviors that have evolved. The types and outcomes of interactions between phenotypes are determined by task overlap for logic-defined phenotypes and by responses to encounters in the case of behavioral phenotypes. Biologists use these evolving networks to study active and fundamental topics within evolutionary ecology (e.g., the extent to which the architecture of multispecies networks shape coevolutionary outcomes, and the processes involved).