chapter8_PC - Wikispaces : gandell
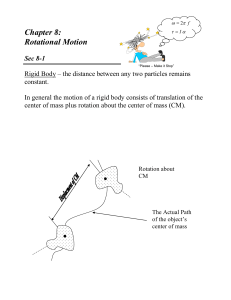
... must lie on the axis of symmetry. Often, the center of gravity of such an object is the geometric center of the object. ...
... must lie on the axis of symmetry. Often, the center of gravity of such an object is the geometric center of the object. ...
Notes in pdf format
... • Dynamics deals with the action of forces • We will discuss torques and Newton’s second law for rotational motion ...
... • Dynamics deals with the action of forces • We will discuss torques and Newton’s second law for rotational motion ...
Geneva mechanism
... of form and sizes increasing the number of slots in the mechanisms driven wheel decreases the angular displacement by each rotation of the driving wheel. The other characteristic of geneva mechanism is the “locking” feature. That is when the driven wheel is not being turned by the driving wheel ...
... of form and sizes increasing the number of slots in the mechanisms driven wheel decreases the angular displacement by each rotation of the driving wheel. The other characteristic of geneva mechanism is the “locking” feature. That is when the driven wheel is not being turned by the driving wheel ...
iES-2309Integrated Easy Servo Motor + Drive +
... The integrated 1,000-line encoder of the iES-2309 offers the real-time motor shaft position to the drive. Based on that position, the drive can then close the loop between the motor and drive, ensure no step is lost, and eliminate the possibility of stall or loss of movement synchronization which is ...
... The integrated 1,000-line encoder of the iES-2309 offers the real-time motor shaft position to the drive. Based on that position, the drive can then close the loop between the motor and drive, ensure no step is lost, and eliminate the possibility of stall or loss of movement synchronization which is ...
40 N m
... When using conservation of energy, both rotational and translational kinetic energy must be taken into account. All these objects have the same potential energy at the top, but the time it takes them to get down the incline depends on how much rotational inertia they have. ...
... When using conservation of energy, both rotational and translational kinetic energy must be taken into account. All these objects have the same potential energy at the top, but the time it takes them to get down the incline depends on how much rotational inertia they have. ...