File
... express the eternal ideas of reason, moderation, symmetry, balance, and harmony. In architecture, the most important form was the temple, and the classic example of this type of architecture is the Parthenon, built between 447 and 432 B.C. Located on the Acropolis in Athens, the Parthenon was dedica ...
... express the eternal ideas of reason, moderation, symmetry, balance, and harmony. In architecture, the most important form was the temple, and the classic example of this type of architecture is the Parthenon, built between 447 and 432 B.C. Located on the Acropolis in Athens, the Parthenon was dedica ...
Ancient World Ch. 6
... The Spread of Greek Culture –D. Hellenistic – describing Greek culture after the death of Alexander the Great; includes the 3 main kingdoms formed by the breakup of Alexander’s empire ...
... The Spread of Greek Culture –D. Hellenistic – describing Greek culture after the death of Alexander the Great; includes the 3 main kingdoms formed by the breakup of Alexander’s empire ...
File
... Historians have often credited Ancient Greece as “the first democracy”. As Thomas Jefferson and our Founding Fathers sat to draft our Constitution, they looked back upon the works of the Ancient Greeks for inspiration and guidance. Analyze the extent to which the ancient Athenian government was demo ...
... Historians have often credited Ancient Greece as “the first democracy”. As Thomas Jefferson and our Founding Fathers sat to draft our Constitution, they looked back upon the works of the Ancient Greeks for inspiration and guidance. Analyze the extent to which the ancient Athenian government was demo ...
Ancient Greece Review: Lessons 17-24
... 2. The main purpose of the lesson is to: a. detail the accomplishments of Greek citizens. b. detail the wars between Athens and Sparta. c. show how Alexander was a great warrior. d. show the accomplishments and impact of ancient Greece on modern culture. 3. Mark each statement T ...
... 2. The main purpose of the lesson is to: a. detail the accomplishments of Greek citizens. b. detail the wars between Athens and Sparta. c. show how Alexander was a great warrior. d. show the accomplishments and impact of ancient Greece on modern culture. 3. Mark each statement T ...
1 Classical and Hellenistic Greece The Golden Age of Athens I
... c. Created the first _______________________________________________________________________ d. Accurately calculated the distance from the __________________ to the ________________________ ...
... c. Created the first _______________________________________________________________________ d. Accurately calculated the distance from the __________________ to the ________________________ ...
Ancient Greece
... We have learned many things from the ancient Greeks, but perhaps the most important is the value of ideas. The Greeks believed in wisdom. Wisdom is the knowledge and the judgment needed to make good decisions. Ancient Greece was remembered for its many great philosophers. Philosophers were people wh ...
... We have learned many things from the ancient Greeks, but perhaps the most important is the value of ideas. The Greeks believed in wisdom. Wisdom is the knowledge and the judgment needed to make good decisions. Ancient Greece was remembered for its many great philosophers. Philosophers were people wh ...
Chapter 5 - HERE in Barrington
... (unfair rulers) who tried to gain power, but Draco was appointed to establish new rules and laws (even though he came up with unpopular and harsh laws). Death was a penalty for most crimes (even smaller ones). It was pretty much a military state (government where the police/military are in ...
... (unfair rulers) who tried to gain power, but Draco was appointed to establish new rules and laws (even though he came up with unpopular and harsh laws). Death was a penalty for most crimes (even smaller ones). It was pretty much a military state (government where the police/military are in ...
according to what facts - Santorini Lodging Rooms
... the portion of their divine nature still was strong. But with time it faded and was more and more diluted. "When the human nature got the upper hand" (Plato, Critias 121b), they became sinful and invaded by crimes. As a consequence, they were bound to loose their paradise. Towards the outer world, t ...
... the portion of their divine nature still was strong. But with time it faded and was more and more diluted. "When the human nature got the upper hand" (Plato, Critias 121b), they became sinful and invaded by crimes. As a consequence, they were bound to loose their paradise. Towards the outer world, t ...
Ancient Greek Theatre The Greek theatre history began with festiv
... due to the political and social conditions of Athens, it finally held up the mirror to all that was characteristic of Athenian life. By a consensus of authorities comedy has been arranged in three divisions, or rather should they be termed variations in form--the old, the middle and the new--and the ...
... due to the political and social conditions of Athens, it finally held up the mirror to all that was characteristic of Athenian life. By a consensus of authorities comedy has been arranged in three divisions, or rather should they be termed variations in form--the old, the middle and the new--and the ...
Greece and Rome
... many hated the Carthaginians especially because there seemed to be nothing that could force them on their knees. Many Romans wanted to gain glory, and no enemy was more attractive than Carthage, even if the city state now longer aspired to become an empire. ...
... many hated the Carthaginians especially because there seemed to be nothing that could force them on their knees. Many Romans wanted to gain glory, and no enemy was more attractive than Carthage, even if the city state now longer aspired to become an empire. ...
What is a myth? - Schoolhistory.co.nz
... • May have been a battle to eliminate trade competition or to get scarce metals • Troy fell 1250BC • Within a century all major sites on the mainland Greece fell • Except Athens ...
... • May have been a battle to eliminate trade competition or to get scarce metals • Troy fell 1250BC • Within a century all major sites on the mainland Greece fell • Except Athens ...
Minoan Society: Between 2000 – 1700 BCE Minoans built a brilliant
... Thus it is no surprise to learn that the Persians are important because they really worked hard to unify their empire. They not only standardized coinage, (so it was the same money was used in all parts of the empire) and then regularized taxes were collected instead of Tribute (which could be anyt ...
... Thus it is no surprise to learn that the Persians are important because they really worked hard to unify their empire. They not only standardized coinage, (so it was the same money was used in all parts of the empire) and then regularized taxes were collected instead of Tribute (which could be anyt ...
Greek Tragedy And Comedy
... humble form) and morality, and they were suffering along with the heroes. Its role (very important at first) was fading during the time. ...
... humble form) and morality, and they were suffering along with the heroes. Its role (very important at first) was fading during the time. ...
Guest Editor`s Preface Nomos despotes: Law and Legal Procedures
... carried out in the past century, on the problem of the sources and on current trends and future prospects. He suggests that important advances are to be ob6 ...
... carried out in the past century, on the problem of the sources and on current trends and future prospects. He suggests that important advances are to be ob6 ...
Chapter 5 Outline
... government - the city-state - against invaders from Asia. ii. Athens emerged from the war as the most powerful city-state in Greece. iii. To meet continued threats against Persia, the Delian League was organized in alliance with other Greek city-states. 2. Athens in the Age of Pericles a. Political ...
... government - the city-state - against invaders from Asia. ii. Athens emerged from the war as the most powerful city-state in Greece. iii. To meet continued threats against Persia, the Delian League was organized in alliance with other Greek city-states. 2. Athens in the Age of Pericles a. Political ...
Ancient Greece
... Greece’s Golden Age Philosophy Plato 1. Student of Socrates 2. Use reason to create the ideal society 3. State should regulate all aspects of a person’s life – did not trust democracy 4. Wrote The Republic (ideal state) a. Philosopher-king (rulers) ...
... Greece’s Golden Age Philosophy Plato 1. Student of Socrates 2. Use reason to create the ideal society 3. State should regulate all aspects of a person’s life – did not trust democracy 4. Wrote The Republic (ideal state) a. Philosopher-king (rulers) ...
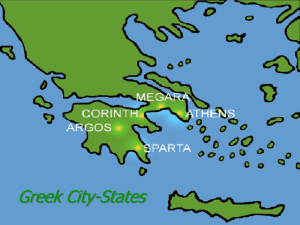
Greek City - States
... • Each city-state had its own form of government. • Some city-states, like Corinth, were ruled by kings. Some, like Sparta, were ruled by a small group of men. Others, like Athens, experimented with new forms of government. ...
... • Each city-state had its own form of government. • Some city-states, like Corinth, were ruled by kings. Some, like Sparta, were ruled by a small group of men. Others, like Athens, experimented with new forms of government. ...
Chapter 4 - Cloudfront.net
... – Try to find balance in the universe…try to explain everything – Theories…some wrong…about the motions of the planets, elemental principles of earth, fire, air, and water. – Impressive work in Geometry (Pythagoras’ theorem) ...
... – Try to find balance in the universe…try to explain everything – Theories…some wrong…about the motions of the planets, elemental principles of earth, fire, air, and water. – Impressive work in Geometry (Pythagoras’ theorem) ...
The Greek Verb System - Ch 2
... All others are variations of one of these 3, depending on how the writer/speaker wishes to communicate the kind of action ...
... All others are variations of one of these 3, depending on how the writer/speaker wishes to communicate the kind of action ...
War, Stasis, and Greek Political Thought
... on constitutional problems. Causes of war, external conflicts remained marginal issues rather than central problems. He finds this situation to be a paradox since, he notes, "war was an ever present reality in Greek life." And he further suspects that the reason for this emphasis is that “the Greeks ...
... on constitutional problems. Causes of war, external conflicts remained marginal issues rather than central problems. He finds this situation to be a paradox since, he notes, "war was an ever present reality in Greek life." And he further suspects that the reason for this emphasis is that “the Greeks ...
DUE: Thursday, Sept
... 5. placed great emphasis on literature and the arts 4. Alexander the Great’s conquests of Greece, Asia Minor, Egypt, and Persia led to the 1. spread of Hellenic culture 2. adoption of a feudal system 3. establishment of representative democracy 4. spread of Islamic culture throughout Europe 5. isola ...
... 5. placed great emphasis on literature and the arts 4. Alexander the Great’s conquests of Greece, Asia Minor, Egypt, and Persia led to the 1. spread of Hellenic culture 2. adoption of a feudal system 3. establishment of representative democracy 4. spread of Islamic culture throughout Europe 5. isola ...
Next: The Science of Astronomy Geocentric vs Heliocentric
... Why didn’t Copernicus's model accurately predict the positions of the planets? A. He had the order of the planets wrong. B. He had the distances to each of the planets ...
... Why didn’t Copernicus's model accurately predict the positions of the planets? A. He had the order of the planets wrong. B. He had the distances to each of the planets ...
ASTR 105 Intro Astronomy: The Solar System
... the real explanation for planetary motion? • Their inability to observe stellar parallax was the key. ...
... the real explanation for planetary motion? • Their inability to observe stellar parallax was the key. ...
Chapter 5-Section 3
... – 430 B.C. a _________ killed 1/3 of all • The Spartans attacked the Athenians Athenians and they fought for • 421 B.C. Both sides had became ___ more years worn down and called a truce – 404 B.C. Athens surrendered losing their _________, wealth and ________ ...
... – 430 B.C. a _________ killed 1/3 of all • The Spartans attacked the Athenians Athenians and they fought for • 421 B.C. Both sides had became ___ more years worn down and called a truce – 404 B.C. Athens surrendered losing their _________, wealth and ________ ...
the greco-persian wars
... Darius I leads Persians in invasion of mainland Greece; Athenians defeat Persians at Battle of Marathon Darius I dies, son Xerxes succeeds him Xerxes leads Persians in invasion of mainland Greece, defeats Spartans & their allies at Battle of Thermopylae; allied Greeks defeat Persians at Battle of Sa ...
... Darius I leads Persians in invasion of mainland Greece; Athenians defeat Persians at Battle of Marathon Darius I dies, son Xerxes succeeds him Xerxes leads Persians in invasion of mainland Greece, defeats Spartans & their allies at Battle of Thermopylae; allied Greeks defeat Persians at Battle of Sa ...
History of science in classical antiquity

The history of science in classical antiquity encompasses both those inquiries into the workings of the universe aimed at such practical goals as establishing a reliable calendar or determining how to cure a variety of illnesses and those abstract investigations known as natural philosophy. The ancient peoples who are considered the first scientists may have thought of themselves as natural philosophers, as practitioners of a skilled profession (for example, physicians), or as followers of a religious tradition (for example, temple healers). The encyclopedic works of Aristotle, Archimedes, Hippocrates, Galen, Ptolemy, Euclid, and others spread throughout the world. These works and the important commentaries on them were the wellspring of science.