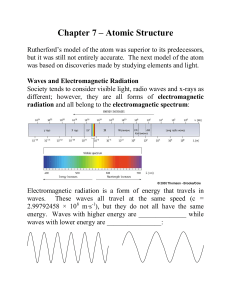
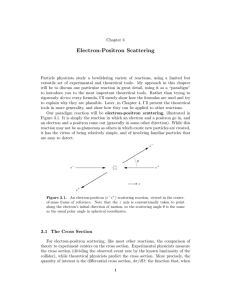
Many-body systems
... In other words, two particles that initially were in the states (~k, σ), (k~0 , σ 0 ) have interacted with one another, exchanged some momentum ~q (but with total momentum conserved, as it should be since this interaction is invariant to global translations), and end up in the states (~k + ~q, σ), ( ...
... In other words, two particles that initially were in the states (~k, σ), (k~0 , σ 0 ) have interacted with one another, exchanged some momentum ~q (but with total momentum conserved, as it should be since this interaction is invariant to global translations), and end up in the states (~k + ~q, σ), ( ...
CHM 110 - Equation Interpretation (r14)
... 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3 In fact, the chemical equation is easier, since it's more consistent! We don't have to worry about things like what exactly a "package" or a "cup" is. Interpretation From balancing equations, we already know one way to interpret the chemical formula, the "molecular" interpretation ...
... 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3 In fact, the chemical equation is easier, since it's more consistent! We don't have to worry about things like what exactly a "package" or a "cup" is. Interpretation From balancing equations, we already know one way to interpret the chemical formula, the "molecular" interpretation ...
Chapter 2 – Atoms and Elements - U of L Class Index
... equations: an operator acts on a function (Ψ), generating a scalar (i.e. a number) times the same function. These kind of equations always have an infinite number of solutions. Ψ is called the wavefunction of the electron. There is an infinite number of wavefunctions permitted by the Schrödinger equ ...
... equations: an operator acts on a function (Ψ), generating a scalar (i.e. a number) times the same function. These kind of equations always have an infinite number of solutions. Ψ is called the wavefunction of the electron. There is an infinite number of wavefunctions permitted by the Schrödinger equ ...
Atomic Orbitals Lab - North Carolina High School Computational
... “Hamiltonian” operator, calculates information about the electrons in an atom or molecule. There are four types of data that are determined by the Hamiltonian operator (NOTE: for purposes of this reading, this discussion is being presented very simplistically – the mathematics behind the Schrödinge ...
... “Hamiltonian” operator, calculates information about the electrons in an atom or molecule. There are four types of data that are determined by the Hamiltonian operator (NOTE: for purposes of this reading, this discussion is being presented very simplistically – the mathematics behind the Schrödinge ...
Lecture 14 Thermodynamic Properties
... where Q(N, V, T ) is the statistical mechanical partition function for the canonical ensemble is given by Q(N, V, T ) = ...
... where Q(N, V, T ) is the statistical mechanical partition function for the canonical ensemble is given by Q(N, V, T ) = ...
Publication : Relativistic Coupled Cluster Calculations with
... QED calculations using the Uehling and Källén–Sabry [25,56] terms (as implemented in GRASP) for the VP, and the effective nonlocal SE operator (ENLO) originally introduced by Ginges and Flambaum [23], and modified and implemented by our group into GRASP [24]. The two approaches (ENLO and MLSO) give ...
... QED calculations using the Uehling and Källén–Sabry [25,56] terms (as implemented in GRASP) for the VP, and the effective nonlocal SE operator (ENLO) originally introduced by Ginges and Flambaum [23], and modified and implemented by our group into GRASP [24]. The two approaches (ENLO and MLSO) give ...
Unbounded operators and the incompleteness of quantum mechanics
... At this point it may seem to the reader that there is a rather simple solution to the problem that we have given, namely weaken Postulate 1 so that the problem functions do not represent states. Unfortunately we have good reasons for accepting Postulate 1, which, though not completely compelling, su ...
... At this point it may seem to the reader that there is a rather simple solution to the problem that we have given, namely weaken Postulate 1 so that the problem functions do not represent states. Unfortunately we have good reasons for accepting Postulate 1, which, though not completely compelling, su ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 16 Which of the following elements is most likely to form compounds involving an expanded valence shell of electrons ? a) b) e) d) *e) ...
... 16 Which of the following elements is most likely to form compounds involving an expanded valence shell of electrons ? a) b) e) d) *e) ...
Lectures 6-7 - U of L Class Index
... Scientists often use ħ to stand for h/2, so this formula can also be written as: ...
... Scientists often use ħ to stand for h/2, so this formula can also be written as: ...
Reactions
... 2. A chemical reaction must account for every atom that is used. This is an application of the Law of Conservation of Matter which states that in a chemical reaction atoms are neither created nor destroyed. ...
... 2. A chemical reaction must account for every atom that is used. This is an application of the Law of Conservation of Matter which states that in a chemical reaction atoms are neither created nor destroyed. ...
Quantum Theory of Hydrogen
... equation for the electron in a hydrogen atom, aren't we. Nevertheless, we talk about solving the "hydrogen atom," because our solution will provide us with much of what we need to know about hydrogen. ...
... equation for the electron in a hydrogen atom, aren't we. Nevertheless, we talk about solving the "hydrogen atom," because our solution will provide us with much of what we need to know about hydrogen. ...