Mazuri® Primate High Fiber Sticks
... Mazuri® Primate High Fiber Sticks are designed to be an essential part of a total primate feeding system and may be used in conjunction with all other Mazuri ® primate products. Primates generally consume about 2% to 4% of their body weight in food each day on a dry matter basis (i.e., a 50 kg anima ...
... Mazuri® Primate High Fiber Sticks are designed to be an essential part of a total primate feeding system and may be used in conjunction with all other Mazuri ® primate products. Primates generally consume about 2% to 4% of their body weight in food each day on a dry matter basis (i.e., a 50 kg anima ...
Click here to view the full presentation.
... American Journal of Cardiology, December, 2008 This cross-sectional study examined the burden of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) using serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) and prevalence of hypovitaminosis D in adults with CVDs using data from NHANES 2001 to 2004. Serum 25(OH)D levels were divided int ...
... American Journal of Cardiology, December, 2008 This cross-sectional study examined the burden of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) using serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) and prevalence of hypovitaminosis D in adults with CVDs using data from NHANES 2001 to 2004. Serum 25(OH)D levels were divided int ...
Vitamin A
... – Animal foods generally are rich sources – Palm and coconut oil also are rich sources ...
... – Animal foods generally are rich sources – Palm and coconut oil also are rich sources ...
Vitamin A - E
... carboxylation of the amino acid, glutamic acid, resulting in its conversion to gammacarboxyglutamic acid (Gla). It is critical to the calcium-binding function of the proteins. ...
... carboxylation of the amino acid, glutamic acid, resulting in its conversion to gammacarboxyglutamic acid (Gla). It is critical to the calcium-binding function of the proteins. ...
Water soluble vitamins
... • sources: meats, mushrooms, eggs, whole grains, legumes, broccoli and avocados, liver • AI 5mg/day • Deficiency is rare: “Burning foot syndrome” -skin sensations exacerbated by warmth ...
... • sources: meats, mushrooms, eggs, whole grains, legumes, broccoli and avocados, liver • AI 5mg/day • Deficiency is rare: “Burning foot syndrome” -skin sensations exacerbated by warmth ...
The Vitamins - Central Washington University
... Of 253 women hospitalized with hip fracture 27% received treatment for osteoporosis 1 year mortality was 17% Average age 81 yrs ...
... Of 253 women hospitalized with hip fracture 27% received treatment for osteoporosis 1 year mortality was 17% Average age 81 yrs ...
LECTURE NOTES: Vitamin A and Carotenoids
... -stored in fat droplets in cells -body can accumulate > 1 year supply -absorption from diet much better if there is also fat in the diet -in the United States, both deficiency and toxicity occur -worldwide, there is a great deal of vitamin A deficiency: one of the world’s major nutrition problems ...
... -stored in fat droplets in cells -body can accumulate > 1 year supply -absorption from diet much better if there is also fat in the diet -in the United States, both deficiency and toxicity occur -worldwide, there is a great deal of vitamin A deficiency: one of the world’s major nutrition problems ...
Vitamins
... • Some women many require additional iron if menstrual losses are high. • The evidence for benefits from antioxidant supplementation for athletes is mixed. ...
... • Some women many require additional iron if menstrual losses are high. • The evidence for benefits from antioxidant supplementation for athletes is mixed. ...
Vitamins
... Smaller amounts from meat, poultry, fish, eggs, milk products, nuts, seeds Wheat germ is a good source Animal fats have almost no vitamin E ...
... Smaller amounts from meat, poultry, fish, eggs, milk products, nuts, seeds Wheat germ is a good source Animal fats have almost no vitamin E ...
Vitamin D deficiency, guideline for the diagnosis
... with pigmented skin, exposure time or frequency needs to be increased 2-fold to 10-fold. Note that from November–February in the UK there is no benefit from sun exposure. Patients with the following conditions or therapies should avoid unprotected sun exposure: skin cancer, porphyrias, ...
... with pigmented skin, exposure time or frequency needs to be increased 2-fold to 10-fold. Note that from November–February in the UK there is no benefit from sun exposure. Patients with the following conditions or therapies should avoid unprotected sun exposure: skin cancer, porphyrias, ...
Requirement of Human Nutrition Human Dietary Needs The human
... ions are incorporated along with calcium and phosphate ions in the crystalline structure of which both bones and teeth are constructed. But it may have other functions. In order to grow properly, a rat must consume 0.5 parts per million (ppm) of fluoride ions in its diet. The rat in the bottom photo ...
... ions are incorporated along with calcium and phosphate ions in the crystalline structure of which both bones and teeth are constructed. But it may have other functions. In order to grow properly, a rat must consume 0.5 parts per million (ppm) of fluoride ions in its diet. The rat in the bottom photo ...
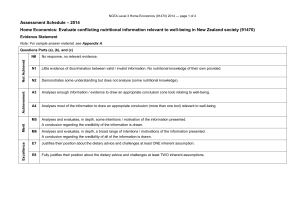
61KB - NZQA
... can’t be sure of his motives. The question needs to be asked: does he genuinely believe that children from 12 months of age need a vitamin supplement, or is this just an opportunity for him to sell his product? For this reason, Doctor Greene seems less credible than the other contributors in the res ...
... can’t be sure of his motives. The question needs to be asked: does he genuinely believe that children from 12 months of age need a vitamin supplement, or is this just an opportunity for him to sell his product? For this reason, Doctor Greene seems less credible than the other contributors in the res ...
Vitamin K
Vitamin K refers to a group of structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamins the human body needs for complete synthesis of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation, and also certain proteins that the body uses to control binding of calcium in bone and other tissues. The vitamin K-related modification of the proteins allows them to bind calcium ions, which they cannot do otherwise. Without vitamin K, blood coagulation is seriously impaired, and uncontrolled bleeding occurs. Low levels of vitamin K also weaken bones and promote calcification of arteries and other soft tissues.Chemically, the vitamin K family comprises 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone (3-) derivatives. Vitamin K includes two natural vitamers: vitamin K1 and vitamin K2. Vitamin K2, in turn, consists of a number of related chemical subtypes, with differing lengths of carbon side chains made of isoprenoid groups of atoms.Vitamin K1, also known as phylloquinone, phytomenadione, or phytonadione, is synthesized by plants, and is found in highest amounts in green leafy vegetables because it is directly involved in photosynthesis. It may be thought of as the ""plant"" form of vitamin K. It is active as a vitamin in animals and performs the classic functions of vitamin K, including its activity in the production of blood-clotting proteins. Animals may also convert it to vitamin K2.Vitamin K2, the main storage form in animals, has several subtypes, which differ in isoprenoid chain length. These vitamin K2 homologues are called menaquinones, and are characterized by the number of isoprenoid residues in their side chains. Menaquinones are abbreviated MK-n, where M stands for menaquinone, the K stands for vitamin K, and the n represents the number of isoprenoid side chain residues. For example, menaquinone-4 (abbreviated MK-4) has four isoprene residues in its side chain. Menaquinone-4 (also known as menatetrenone from its four isoprene residues) is the most common type of vitamin K2 in animal products since MK-4 is normally synthesized from vitamin K1 in certain animal tissues (arterial walls, pancreas, and testes) by replacement of the phytyl tail with an unsaturated geranylgeranyl tail containing four isoprene units, thus yielding menaquinone-4. This homolog of vitamin K2 may have enzyme functions distinct from those of vitamin K1.Bacteria in the colon (large intestine) can also convert K1 into vitamin K2. In addition, bacteria typically lengthen the isoprenoid side chain of vitamin K2 to produce a range of vitamin K2 forms, most notably the MK-7 to MK-11 homologues of vitamin K2. All forms of K2 other than MK-4 can only be produced by bacteria, which use these forms in anaerobic respiration. The MK-7 and other bacterially derived forms of vitamin K2 exhibit vitamin K activity in animals, but MK-7's extra utility over MK-4, if any, is unclear and is a matter of investigation.Three synthetic types of vitamin K are known: vitamins K3, K4, and K5. Although the natural K1 and all K2 homologues and synthetic K4 and K5 have proven nontoxic, the synthetic form K3 (menadione) has shown toxicity.