Powerpoint - John Provost, PhD
... very clear that both female and male energies are needed, & that it is a problem when they aren’t balanced. ...
... very clear that both female and male energies are needed, & that it is a problem when they aren’t balanced. ...
In this chapter, you will explore the origins of
... Vedas (VAYduhz) are a collection of sacred texts, including verses, hymns, prayers, and teachings composed in Sanskrit (SAN-skrit). (Veda is Sanskrit for “knowledge.”) The earliest of the Vedas grew out of traditions brought into India by the Aryans. These traditions expanded over centuries in India ...
... Vedas (VAYduhz) are a collection of sacred texts, including verses, hymns, prayers, and teachings composed in Sanskrit (SAN-skrit). (Veda is Sanskrit for “knowledge.”) The earliest of the Vedas grew out of traditions brought into India by the Aryans. These traditions expanded over centuries in India ...
Hinduism PowerPoint
... Hinduism is the name given in the 1800s to describe a broad range of religious in India. It comes from the Persian word hindu, in Sanskrit sindhu, which means “river” and refers to the people of the Indus valley. There are more than 1 billion followers of Hinduism in the world today. There a ...
... Hinduism is the name given in the 1800s to describe a broad range of religious in India. It comes from the Persian word hindu, in Sanskrit sindhu, which means “river” and refers to the people of the Indus valley. There are more than 1 billion followers of Hinduism in the world today. There a ...
Religions of India - Fulton County Schools
... Not founded on the teachings of one person. Religion of many deities. 800-400 BCE, a collection of writings and philosophies were reflected in a text known as the Upanishads. The Upanishads tell of a universal spirit present within all life. All living things have souls. All souls are part of one et ...
... Not founded on the teachings of one person. Religion of many deities. 800-400 BCE, a collection of writings and philosophies were reflected in a text known as the Upanishads. The Upanishads tell of a universal spirit present within all life. All living things have souls. All souls are part of one et ...
What is Hinduism?
... past (and among many Indians today) it is believed that they would contaminate others’ ritual purity if there was any personal contact between them. Untouchables lived in separate communities, had separate wells for water, and in the 19th century, were prohibited from using roads used by other caste ...
... past (and among many Indians today) it is believed that they would contaminate others’ ritual purity if there was any personal contact between them. Untouchables lived in separate communities, had separate wells for water, and in the 19th century, were prohibited from using roads used by other caste ...
Aryan Roots - Scarsdale Union Free School District
... Actually, we believe there is! The Ascetic Roots of Hinduism 1. Shramanas – “spiritual rebels” during the time the Upanishads were being written Modern day sadhu, ascetics that practice yoga -ascetics: practiced celibacy, poverty, fasting, exposing the body to hardships in an attempt to achieve moks ...
... Actually, we believe there is! The Ascetic Roots of Hinduism 1. Shramanas – “spiritual rebels” during the time the Upanishads were being written Modern day sadhu, ascetics that practice yoga -ascetics: practiced celibacy, poverty, fasting, exposing the body to hardships in an attempt to achieve moks ...
Chp. 1.2 “Origins of Hinduism” pgs. 22
... Because of these strict rules, people spent almost all of their time with others in their same class. ...
... Because of these strict rules, people spent almost all of their time with others in their same class. ...
Aim: What does it mean to be Hindu?
... “The Dalits, also known as the “untouchables” make up nearly one quarter of India’s 1.2 billion society.. In 70% of India’s villages, for example, non-Dalits will not eat or drink with Dalits. After drinking their tea, they are expected to crush the cup on the ground so that no other person risks be ...
... “The Dalits, also known as the “untouchables” make up nearly one quarter of India’s 1.2 billion society.. In 70% of India’s villages, for example, non-Dalits will not eat or drink with Dalits. After drinking their tea, they are expected to crush the cup on the ground so that no other person risks be ...
Hinduism Reading
... texts. The Vedas (VAYduhz) are a collection of sacred texts, including verses, hymns, prayers, and teachings composed in Sanskrit (SAN-skrit). (Veda is Sanskrit for “knowledge.”) The earliest of the Vedas grew out of traditions brought into India by the Aryans. These traditions expanded over centuri ...
... texts. The Vedas (VAYduhz) are a collection of sacred texts, including verses, hymns, prayers, and teachings composed in Sanskrit (SAN-skrit). (Veda is Sanskrit for “knowledge.”) The earliest of the Vedas grew out of traditions brought into India by the Aryans. These traditions expanded over centuri ...
hinduism- essential questions
... HINDUISM- ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. Define 5 Hindu theological terms. 2. Explain Hinduism’s founding/beginning. 3. Identify and describe the 3 key developments of Vedic religious practice. 4. Explain the doctrines of Hinduism (Brahman and Atman, reincarnation, karma, samsara, moksha and bhakti). 5. Des ...
... HINDUISM- ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. Define 5 Hindu theological terms. 2. Explain Hinduism’s founding/beginning. 3. Identify and describe the 3 key developments of Vedic religious practice. 4. Explain the doctrines of Hinduism (Brahman and Atman, reincarnation, karma, samsara, moksha and bhakti). 5. Des ...
Hinduism - Hindu Temple of Greater Cincinnati
... The word Hindu is derived from the ancient Persians who called people living on the other side of the river Indus (then called Sindhu in Sanskrit) and called them Sindhus, and the word Sindhu became Hindu and the people living in India came to be known as Hindus. Hinduism with more than a billion fo ...
... The word Hindu is derived from the ancient Persians who called people living on the other side of the river Indus (then called Sindhu in Sanskrit) and called them Sindhus, and the word Sindhu became Hindu and the people living in India came to be known as Hindus. Hinduism with more than a billion fo ...
Intro to Hinduism
... The earliest evidence of prehistoric religion in India date to the late Neolithic Era, (5500-2600 BCE). Millennia later, during the period of 1500-500 BCE, the Vedas, understood as sacred texts, appear. The Vedas were four canonical collections of hymns, prayers, and liturgical formulas. As early a ...
... The earliest evidence of prehistoric religion in India date to the late Neolithic Era, (5500-2600 BCE). Millennia later, during the period of 1500-500 BCE, the Vedas, understood as sacred texts, appear. The Vedas were four canonical collections of hymns, prayers, and liturgical formulas. As early a ...
Hinduism
... one last time close to the end of the world. Associated with light, especially the sun. Represented with a human body, with blue skin and four arms. Each hand holds an object he is ...
... one last time close to the end of the world. Associated with light, especially the sun. Represented with a human body, with blue skin and four arms. Each hand holds an object he is ...
Hinduism - Boise State University
... does this belief hinge? The immortal soul is essential to the teaching of Karma, and Karma is what makes the Hindu view of the soul differ from that of Christendom. The Hindu believes that each personal soul passes through many reincarnations and possibly “hell”. It must strive to unite with the “Su ...
... does this belief hinge? The immortal soul is essential to the teaching of Karma, and Karma is what makes the Hindu view of the soul differ from that of Christendom. The Hindu believes that each personal soul passes through many reincarnations and possibly “hell”. It must strive to unite with the “Su ...
Slide 1
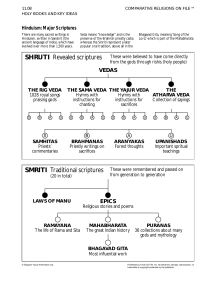
... • The basic scriptures of Hinduism, are the Vedas (sometimes called the Rig Veda). • Two types of sacred writings comprise the Hindu scriptures: "Shruti" (heard) and "Smriti" (memorized). They were passed on from generation to generation orally for centuries before they were written down mostly in t ...
... • The basic scriptures of Hinduism, are the Vedas (sometimes called the Rig Veda). • Two types of sacred writings comprise the Hindu scriptures: "Shruti" (heard) and "Smriti" (memorized). They were passed on from generation to generation orally for centuries before they were written down mostly in t ...
Chapter 19 section 2 Origins of Hinduism Power Point Notes
... varnas, or social divisions, in Aryan society. These varnas were: • Brahmins-priests • Kshatriyas – rulers and warriors • Vaisyas – farmers, craftspeople and traders • Sudras – laborers and non-Aryans • The Brahmins were at the highest rank because they performed rituals for the gods. ...
... varnas, or social divisions, in Aryan society. These varnas were: • Brahmins-priests • Kshatriyas – rulers and warriors • Vaisyas – farmers, craftspeople and traders • Sudras – laborers and non-Aryans • The Brahmins were at the highest rank because they performed rituals for the gods. ...
Hinduism honors JDR (KAF modified 4-25-07).
... Chief Religion of India • Hinduism has its roots in Aryan beliefs and practices ...
... Chief Religion of India • Hinduism has its roots in Aryan beliefs and practices ...
Seeing the Divine: Music‟s Role in Hinduism
... encompassed in this sound. The syllable Om is comprised of three separate Sanskrit letters aa, au, and ma, and for this reason, the syllable has been used to represent a vast number of trios3. The Om can bring to mind the Hindu Trinity (Brahma, Visnu, and Shiva) and the creation, the maintaining of, ...
... encompassed in this sound. The syllable Om is comprised of three separate Sanskrit letters aa, au, and ma, and for this reason, the syllable has been used to represent a vast number of trios3. The Om can bring to mind the Hindu Trinity (Brahma, Visnu, and Shiva) and the creation, the maintaining of, ...
Chapter 3: Ancient Indian Civilizations
... a long time in India, giving rise to a variety of beliefs and practices and to other religions, including Jainism. Focus • What basic teachings do most Hindus share? ...
... a long time in India, giving rise to a variety of beliefs and practices and to other religions, including Jainism. Focus • What basic teachings do most Hindus share? ...
Soma in Indian Religion
... an agriculturist, 'digging stick in hand', came from Siberia, not by invasion, and not in 1500 BCE, but by a process of diffusion, as described by the famous archaeologist Colin Renfrew,18 around 7000 BCE. The first Aryans settled in what is called the Saraswati Valley. However, there is eviden ...
... an agriculturist, 'digging stick in hand', came from Siberia, not by invasion, and not in 1500 BCE, but by a process of diffusion, as described by the famous archaeologist Colin Renfrew,18 around 7000 BCE. The first Aryans settled in what is called the Saraswati Valley. However, there is eviden ...
Introduction to Hinduism by Dr. James L Rowell Founders, Texts
... A) Pensive & Philosophical: “There was neither non-existence nor existence then; there was neither the realm of space nor the sky which is beyond. What stirred? Where? In whose protection? Was there water, bottomlessly deep? There was neither death nor immortality then. There was no distinguishing s ...
... A) Pensive & Philosophical: “There was neither non-existence nor existence then; there was neither the realm of space nor the sky which is beyond. What stirred? Where? In whose protection? Was there water, bottomlessly deep? There was neither death nor immortality then. There was no distinguishing s ...
vedic tradition and the buddha
... chants or melodies; the Yajur Veda of ritual and sacrificial formulas; and the Atharva Veda, which is sometimes treated as a different kind of collection,10 of spells and incantations. These four subcollections have in common an insistence on the foundational importance of sacrifice (yajna), describ ...
... chants or melodies; the Yajur Veda of ritual and sacrificial formulas; and the Atharva Veda, which is sometimes treated as a different kind of collection,10 of spells and incantations. These four subcollections have in common an insistence on the foundational importance of sacrifice (yajna), describ ...