Indian Empires and Religions
... civilization; include the rise and fall of the Maurya Empire, the “Golden Age” under Gupta, and the emperor Ashoka. Explain the development and impact of Hinduism and Buddhism on India and subsequent diffusion of Buddhism. ...
... civilization; include the rise and fall of the Maurya Empire, the “Golden Age” under Gupta, and the emperor Ashoka. Explain the development and impact of Hinduism and Buddhism on India and subsequent diffusion of Buddhism. ...
CHRISTIANITY ISLAM JUDAISM HINDUISM BUDDHISM
... MANY GODS (Polytheists) Belief in a universal life force called Brahman Gods take different forms Brahma (Creator Vishnu (Protector) Shiva (Destroyer) Hindus believe in reincarnation; a cycle of birth, life, death, rebirth. Doing good deeds allows for the spirit to be reincarnated to a higher ...
... MANY GODS (Polytheists) Belief in a universal life force called Brahman Gods take different forms Brahma (Creator Vishnu (Protector) Shiva (Destroyer) Hindus believe in reincarnation; a cycle of birth, life, death, rebirth. Doing good deeds allows for the spirit to be reincarnated to a higher ...
Global I – Test #3 Review – Part II
... How do the two compare? (see chart in notes) How did Buddhism eventually spread? Did it stay in India? Where can one read Buddha’s teachings? What are the two schools of Buddhist beliefs? How did Hinduism eventually incorporate Buddha into their religion? Why did Buddha reject some of the rituals an ...
... How do the two compare? (see chart in notes) How did Buddhism eventually spread? Did it stay in India? Where can one read Buddha’s teachings? What are the two schools of Buddhist beliefs? How did Hinduism eventually incorporate Buddha into their religion? Why did Buddha reject some of the rituals an ...
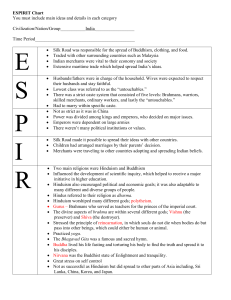
SPRITE Chart - BMcFeeleyAPWHP4
... Hinduism also encouraged political and economic goals; it was also adaptable to many different and diverse groups of people. Hindus referred to their religion as dharma. Hinduism worshiped many different gods; polytheism. Gurus – Brahmans who served as teachers for the princes of the imperia ...
... Hinduism also encouraged political and economic goals; it was also adaptable to many different and diverse groups of people. Hindus referred to their religion as dharma. Hinduism worshiped many different gods; polytheism. Gurus – Brahmans who served as teachers for the princes of the imperia ...
India and Hinduism
... There are four main class levels or Varna’s in the caste system, Brahmans, Kshatrias, Vaishias, and Sundras. According to the religious aspect of the ancient creation myth, each level of class was created from each body part of Purush. In reference to the ancient Hindu book, Purush was the primal ma ...
... There are four main class levels or Varna’s in the caste system, Brahmans, Kshatrias, Vaishias, and Sundras. According to the religious aspect of the ancient creation myth, each level of class was created from each body part of Purush. In reference to the ancient Hindu book, Purush was the primal ma ...
Cultural Geography B Mr. Ehlke
... Sudra’s (Servants & Peasants) Position is based on birth Can not move up or down Can not inter-marry 5th group not considered a class (UNTOUCHABLES) ...
... Sudra’s (Servants & Peasants) Position is based on birth Can not move up or down Can not inter-marry 5th group not considered a class (UNTOUCHABLES) ...
Hinduism - Lecture - Helena High School
... Important to spread ashes of deceased family members in the river Highly polluted – human and industrial waste – endangered species ...
... Important to spread ashes of deceased family members in the river Highly polluted – human and industrial waste – endangered species ...
Pastor`s Class October 21, 2009 World Religions
... Sanatana Dharma – eternal religion Vaidika Dharma – religion of the Vedas Hinduism -- the most commonly used name in North America Multiple Expressions and Variations of Hinduism The word "Hindu" is derived from the name of River Indus, which flows through northwestern India. In ancient times the ri ...
... Sanatana Dharma – eternal religion Vaidika Dharma – religion of the Vedas Hinduism -- the most commonly used name in North America Multiple Expressions and Variations of Hinduism The word "Hindu" is derived from the name of River Indus, which flows through northwestern India. In ancient times the ri ...
chapter 4, Hinduism
... Modern Bhakti Dualistic devotionalism There is a people in southern India who developed a variant of Hinduism that emphasized love and that de-emphasized works. Who are they? Which of the Hindu trinity was their god? What was his local manifestation? In west-central India another devotional movement ...
... Modern Bhakti Dualistic devotionalism There is a people in southern India who developed a variant of Hinduism that emphasized love and that de-emphasized works. Who are they? Which of the Hindu trinity was their god? What was his local manifestation? In west-central India another devotional movement ...
EarlyIndiaandChina2015.doc
... 2. Later converted and spread Buddhism across India 3. Indians developed a caste system with little social mobility B. Gupta Empire (320-550 AD) 1. India reunited in a “Golden Age”; became a center of trade and culture 2. New leader makes Hinduism main religion of India, Buddhism goes to China 3. Kn ...
... 2. Later converted and spread Buddhism across India 3. Indians developed a caste system with little social mobility B. Gupta Empire (320-550 AD) 1. India reunited in a “Golden Age”; became a center of trade and culture 2. New leader makes Hinduism main religion of India, Buddhism goes to China 3. Kn ...
atman
... prakriti - nature/natural order puja - daily prayer or offering Ramayana – Indian epic about Ram and his allies rescuing Sita from the cluthes of Ravana (a demon) samsara – the lifecycle the atman is trapped in of birth, death, and reincarnation before achieving moksha shakti – cosmic energy, found ...
... prakriti - nature/natural order puja - daily prayer or offering Ramayana – Indian epic about Ram and his allies rescuing Sita from the cluthes of Ravana (a demon) samsara – the lifecycle the atman is trapped in of birth, death, and reincarnation before achieving moksha shakti – cosmic energy, found ...
Ch 5 - TeacherWeb
... modern cities. There was a large public bath and even garbage collection. e. Harappan civilization vanished suddenly around 1700 BC possibly because of some type of natural disaster such as a monsoon, flood, or earthquake. B. The Aryans Arrive and Culture Spreads 1. A group of people called the Arya ...
... modern cities. There was a large public bath and even garbage collection. e. Harappan civilization vanished suddenly around 1700 BC possibly because of some type of natural disaster such as a monsoon, flood, or earthquake. B. The Aryans Arrive and Culture Spreads 1. A group of people called the Arya ...
IV. Hinduism
... I. Hinduism A. General Characteristics 1. mix of Aryan & Dravidian beliefs 2. no single founder 3. monotheistic (brahman) or polytheistic? ...
... I. Hinduism A. General Characteristics 1. mix of Aryan & Dravidian beliefs 2. no single founder 3. monotheistic (brahman) or polytheistic? ...
Hinduism
... common beliefs. Can have different languages, cultures, and race. They may be spread over many countries. • Ethnic Group – group made up of people with similar language and culture. They may or may not share religious beliefs or values. Usually of the same race with common ancestors. ...
... common beliefs. Can have different languages, cultures, and race. They may be spread over many countries. • Ethnic Group – group made up of people with similar language and culture. They may or may not share religious beliefs or values. Usually of the same race with common ancestors. ...
Hinduism Notes
... A. Leave behind the harsh material world and be united with the god, Brahman. - There is no purpose towards which the whole world appears to be working. There is only the endless repetition of life. Within this repetition, individuals make progress towards Brahman. ...
... A. Leave behind the harsh material world and be united with the god, Brahman. - There is no purpose towards which the whole world appears to be working. There is only the endless repetition of life. Within this repetition, individuals make progress towards Brahman. ...
India - Home - Archer Lodge Middle School
... outsiders to describe the people of South Asia, now it has come to describe their religion A “Hindu” is someone who accepts the authority of the Vedas Hinduism is the largest religion in India today ...
... outsiders to describe the people of South Asia, now it has come to describe their religion A “Hindu” is someone who accepts the authority of the Vedas Hinduism is the largest religion in India today ...
File
... The Vedas are a collection of ancient hymns and poems The Vedas are important because they tell us information about early Aryan culture The Vedas explain about Aryan beliefs, rituals, and cultural practices The Indian social system is divided into four groups called castes The most powerful caste c ...
... The Vedas are a collection of ancient hymns and poems The Vedas are important because they tell us information about early Aryan culture The Vedas explain about Aryan beliefs, rituals, and cultural practices The Indian social system is divided into four groups called castes The most powerful caste c ...
Religions of South Asia
... Today, 13%of world’s population Oldest organized major religion Originated in Indus River Valley – Between 2500-1500 BCE – Ca. 900 BCE hymns and prayers were recorded in the Rig Veda, the oldest and most sacred of the Vedas. ...
... Today, 13%of world’s population Oldest organized major religion Originated in Indus River Valley – Between 2500-1500 BCE – Ca. 900 BCE hymns and prayers were recorded in the Rig Veda, the oldest and most sacred of the Vedas. ...
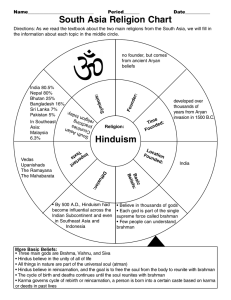
HinduismChart
... Directions: As we read the textbook about the two main religions from the South Asia, we will fill in the information about each topic in the middle circle. ...
... Directions: As we read the textbook about the two main religions from the South Asia, we will fill in the information about each topic in the middle circle. ...
TCI Chapter 15: Learning About Hindu Beliefs
... DIRECTIONS: As you read the chapter, thoroughly answer the questions below. You’re answers must be in your own words (do not simply copy down the words in the text) and in complete sentences. 15.1 Introduction 1. How has Hinduism shaped Indian life? 2. What is dharma? ...
... DIRECTIONS: As you read the chapter, thoroughly answer the questions below. You’re answers must be in your own words (do not simply copy down the words in the text) and in complete sentences. 15.1 Introduction 1. How has Hinduism shaped Indian life? 2. What is dharma? ...
Eastern Religions
... on one divine and omnipotent being called Brahman, a god who is unknowable. All living reality one day dies and is then absorbed back into Brahman. Hinduism accepts the different gods as the many faces of Brahman. India is full of shrines and temples, which are inhabited by one or more of the Hindu ...
... on one divine and omnipotent being called Brahman, a god who is unknowable. All living reality one day dies and is then absorbed back into Brahman. Hinduism accepts the different gods as the many faces of Brahman. India is full of shrines and temples, which are inhabited by one or more of the Hindu ...