Chapter_13__1940s_files/War in Europe
... invasion of France Operation Overlord. • On June 6, 1944 - D-Day American, Canadian, and British shores hit the beaches of Normandy. • American General Dwight D. Eisenhower led the invasion. ...
... invasion of France Operation Overlord. • On June 6, 1944 - D-Day American, Canadian, and British shores hit the beaches of Normandy. • American General Dwight D. Eisenhower led the invasion. ...
World War II Notes
... other countries. They included Germany, Italy, and Japan. The Soviet Union had a treaty (agreement) with Germany, but did not officially join the war. ...
... other countries. They included Germany, Italy, and Japan. The Soviet Union had a treaty (agreement) with Germany, but did not officially join the war. ...
Classwork WW2 Powerpoint
... Hitler and Stalin 5-paragraph Essay • Similar to Mao/Gandhi, just in writing! • “Compare and contrast the lives of Germans under Hitler’s rule to those of Russians under Stalin’s rule. What did each ruler do to gain and keep his power, and how were the lives of the people changed in each country?” ...
... Hitler and Stalin 5-paragraph Essay • Similar to Mao/Gandhi, just in writing! • “Compare and contrast the lives of Germans under Hitler’s rule to those of Russians under Stalin’s rule. What did each ruler do to gain and keep his power, and how were the lives of the people changed in each country?” ...
World War II - Supplemental 1 - Multi-flow map
... August 1939 – German-Soviet Non-aggression pact (Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact) ...
... August 1939 – German-Soviet Non-aggression pact (Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact) ...
The allies turn the tide - Brunswick City Schools / Homepage
... prepare, Allied bombers targeted and destroyed railroads and bridges. • Why did the Allies have to invade France if it was an Ally? • The invasion, known as D-Day, occurred on June 6, ...
... prepare, Allied bombers targeted and destroyed railroads and bridges. • Why did the Allies have to invade France if it was an Ally? • The invasion, known as D-Day, occurred on June 6, ...
GEOWWIIEnd - WordPress.com
... most others were sent to prison • Important because it established the idea that individuals are responsible for their own actions, even in times of war – (Could not use “I was following orders” as a ...
... most others were sent to prison • Important because it established the idea that individuals are responsible for their own actions, even in times of war – (Could not use “I was following orders” as a ...
World War II Scavenger Hunt
... 12. In 1944, a huge Allied army liberated (freed) France and then invaded Germany. By May of _____________, the war was over. 13. How did the Pacific war finally end? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ...
... 12. In 1944, a huge Allied army liberated (freed) France and then invaded Germany. By May of _____________, the war was over. 13. How did the Pacific war finally end? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ...
WWII in a nutshell
... Hitler uses air attacks to prepare for amphibious invasion (needs control of air to destroy British navy) – also wants to destroy fighter planes, factories, British morale British (although outnumbered) had superior fighter planes & use of radar Had the German cipher machine (Enigma) Germans acciden ...
... Hitler uses air attacks to prepare for amphibious invasion (needs control of air to destroy British navy) – also wants to destroy fighter planes, factories, British morale British (although outnumbered) had superior fighter planes & use of radar Had the German cipher machine (Enigma) Germans acciden ...
Axis Powers - Endeavor Charter School
... Austrian) will rise to power in the German Reichstag (government) the same time the US is going through the roaring 20’s and the Great Depression. ...
... Austrian) will rise to power in the German Reichstag (government) the same time the US is going through the roaring 20’s and the Great Depression. ...
Allies Strike Back” - Center Joint Unified School District
... • The German Blitzkrieg stalled in Stalingrad • German troops were prepared for Summer fighting, not the harsh Russian winters • The Germans lost 147,000 men and 91,000 ...
... • The German Blitzkrieg stalled in Stalingrad • German troops were prepared for Summer fighting, not the harsh Russian winters • The Germans lost 147,000 men and 91,000 ...
“Allies Strike Back”
... • The German Blitzkrieg stalled in Stalingrad • German troops were prepared for Summer fighting, not the harsh Russian winters • The Germans lost 147,000 men and 91,000 ...
... • The German Blitzkrieg stalled in Stalingrad • German troops were prepared for Summer fighting, not the harsh Russian winters • The Germans lost 147,000 men and 91,000 ...
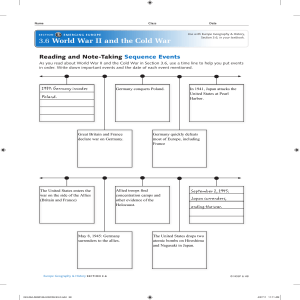
3.6 World War II and the Cold War
... As you read about World War II and the Cold War in Section 3.6, use a time line to help you put events in order. Write down important events and the date of each event mentioned. ...
... As you read about World War II and the Cold War in Section 3.6, use a time line to help you put events in order. Write down important events and the date of each event mentioned. ...
World War II When Germany invaded Poland in 1939 and Britain
... States, as it had in World War I, stood poised to remain neutral but supply Britain and France with weapons and other material. This would create jobs for American workers and profits for American companies, bringing an end to the Great Depression. And again, this involvement would lead us into war ...
... States, as it had in World War I, stood poised to remain neutral but supply Britain and France with weapons and other material. This would create jobs for American workers and profits for American companies, bringing an end to the Great Depression. And again, this involvement would lead us into war ...
World War 2 - HCC Learning Web
... set up a Polish Provisional Government of National Unity 'pledged to the holding of free and unfettered elections as soon as possible'. help the freed peoples of Europe set up democratic and self-governing countries by helping them to (a) maintain law and order; (b) carry out emergency relief measur ...
... set up a Polish Provisional Government of National Unity 'pledged to the holding of free and unfettered elections as soon as possible'. help the freed peoples of Europe set up democratic and self-governing countries by helping them to (a) maintain law and order; (b) carry out emergency relief measur ...
world war ii
... ___________________. This decimated the Nazi troops. Stalin pleaded with England to open up a second front in Europe. England had its own battles to fight. Hitler wanted to invade England, but knew there would need to be an extensive bombing campaign first. This campaign is known as the Battle of __ ...
... ___________________. This decimated the Nazi troops. Stalin pleaded with England to open up a second front in Europe. England had its own battles to fight. Hitler wanted to invade England, but knew there would need to be an extensive bombing campaign first. This campaign is known as the Battle of __ ...
Chapter 25
... • Many small units were forced to fight against overwhelming odds • Allies sent troops & in a few weeks under General Omar Bradley knocked the Germans back • After the battle, most Nazi leaders recognized that the war was lost ...
... • Many small units were forced to fight against overwhelming odds • Allies sent troops & in a few weeks under General Omar Bradley knocked the Germans back • After the battle, most Nazi leaders recognized that the war was lost ...
File
... noticed so on Aug. 9 a second bomber, ________________ dropped a second (and our last) bomb on ______________ Again, the city was destroyed and tens of thousands died. This time, the Japanese got the message and agreed to surrender on August 14, 1945. That day became known as __________ or Victory i ...
... noticed so on Aug. 9 a second bomber, ________________ dropped a second (and our last) bomb on ______________ Again, the city was destroyed and tens of thousands died. This time, the Japanese got the message and agreed to surrender on August 14, 1945. That day became known as __________ or Victory i ...
World War II Vocab List
... 30. “Rosie the Riveter” – The symbol of the Patriotic American Woman who worked in the factories during the war 31. Rationing – the practice of limiting the supply of products on the Home Front in order to use in the Military 32. Holocaust – The period from the late 1930’s to the end of the war when ...
... 30. “Rosie the Riveter” – The symbol of the Patriotic American Woman who worked in the factories during the war 31. Rationing – the practice of limiting the supply of products on the Home Front in order to use in the Military 32. Holocaust – The period from the late 1930’s to the end of the war when ...
Overview: The War in Europe In 1918, the Central Powers and Allies
... forces and materiel helped start to turn the tide of the war, and also provided resources for the D-Day invasion. More than 150,000 troops along with 4,000 landing craft, 600 warships, and 11,000 planes participated in the largest land-sea-air operation in world history. Within weeks of the landing ...
... forces and materiel helped start to turn the tide of the war, and also provided resources for the D-Day invasion. More than 150,000 troops along with 4,000 landing craft, 600 warships, and 11,000 planes participated in the largest land-sea-air operation in world history. Within weeks of the landing ...
World War II (1939
... • Separate peace was signed with new Italian government in September, 1943 ...
... • Separate peace was signed with new Italian government in September, 1943 ...
Allied Control Council

The Allied Control Council or Allied Control Authority, known in the German language as the Alliierter Kontrollrat and also referred to as the Four Powers (German: Vier Mächte), was a military occupation governing body of the Allied Occupation Zones in Germany after the end of World War II in Europe. The members were the Soviet Union, the United States, and the United Kingdom; France was later added with a vote, but had no duties. The organization was based in Berlin-Schöneberg.