Nuclear Weapon Facts
... $27,000,000,000 – amount the U.S. spends annually on nuclear war preparations $2,200,000,000 – cost of one B-2 bomber (the U.S. has more than 20 of them) At the peak of the Cold War, the U.S. and the Soviet Union each possessed about 25,000 strategic warheads. Most have since been decommissioned, bu ...
... $27,000,000,000 – amount the U.S. spends annually on nuclear war preparations $2,200,000,000 – cost of one B-2 bomber (the U.S. has more than 20 of them) At the peak of the Cold War, the U.S. and the Soviet Union each possessed about 25,000 strategic warheads. Most have since been decommissioned, bu ...
Name: Period
... D-Day Invasion: On ________ _____, _________ (date) a fleet of _______ (#) Allied ships carried an invasion force to France. Allied troops scrambled ashore at _____________. Despite intense German gunfire and heavy losses, __________ forces pushed on. On August 25, 1944, the Allies entered _________ ...
... D-Day Invasion: On ________ _____, _________ (date) a fleet of _______ (#) Allied ships carried an invasion force to France. Allied troops scrambled ashore at _____________. Despite intense German gunfire and heavy losses, __________ forces pushed on. On August 25, 1944, the Allies entered _________ ...
Chapter 14 Study Guide - Madison County Schools
... Vocab List: D-Day, V-E Day, Battle of Iwo Jima, Battle of Okinawa, Harry S. Truman, Hirohito, V-J Day, Yalta Conference, United Nations, Potsdam Conference ...
... Vocab List: D-Day, V-E Day, Battle of Iwo Jima, Battle of Okinawa, Harry S. Truman, Hirohito, V-J Day, Yalta Conference, United Nations, Potsdam Conference ...
The End of World War Two
... knockout blow, the Allies launched the invasion of France known as ‘D-Day’. This landing of several hundred thousand Allies troops drew German strength away from the Eastern Front, enabling the Russians to rapidly advance. It also enabled the liberation of France after four years of Nazi occupation. ...
... knockout blow, the Allies launched the invasion of France known as ‘D-Day’. This landing of several hundred thousand Allies troops drew German strength away from the Eastern Front, enabling the Russians to rapidly advance. It also enabled the liberation of France after four years of Nazi occupation. ...
World War II
... other American forces joined the English and Free French fighting in Europe and North Africa o However, within six months of the attack on Pearl Harbor, the American forces were beginning to push the Japanese out of the territory they had conquered as the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere o N ...
... other American forces joined the English and Free French fighting in Europe and North Africa o However, within six months of the attack on Pearl Harbor, the American forces were beginning to push the Japanese out of the territory they had conquered as the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere o N ...
The US at War
... “We shall not flag nor fail. We shall go on to the end. We shall fight in France and on the seas and oceans; we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air. We shall defend our island whatever the cost may be; we shall fight on beaches, landing grounds, in streets and on hi ...
... “We shall not flag nor fail. We shall go on to the end. We shall fight in France and on the seas and oceans; we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air. We shall defend our island whatever the cost may be; we shall fight on beaches, landing grounds, in streets and on hi ...
WWII Faces
... (1900-45), German National Socialist (Nazi) official, notorious as the head of the Nazi police forces. He joined the party in 1925, and from 1926 to 1930 he was its director of propaganda. In 1929 he became chief of the Schutzstaffel (known as the SS, or Black Shirts), an elite military force of the ...
... (1900-45), German National Socialist (Nazi) official, notorious as the head of the Nazi police forces. He joined the party in 1925, and from 1926 to 1930 he was its director of propaganda. In 1929 he became chief of the Schutzstaffel (known as the SS, or Black Shirts), an elite military force of the ...
World War II
... Japan – over 1.5 combat deaths; 900,000 civilians dead Soviet Union - 13 million combat deaths U.S. – 300,000 combat deaths, over 100,000 other deaths When you include all combat and civilian deaths, World War II becomes the most destructive war in history with estimates as high as 60 million, inclu ...
... Japan – over 1.5 combat deaths; 900,000 civilians dead Soviet Union - 13 million combat deaths U.S. – 300,000 combat deaths, over 100,000 other deaths When you include all combat and civilian deaths, World War II becomes the most destructive war in history with estimates as high as 60 million, inclu ...
WWII Study Guide - Answers
... The government is in the hands of the military dictator, and individuals’ rights are subordinate to the state. ...
... The government is in the hands of the military dictator, and individuals’ rights are subordinate to the state. ...
Notes
... constitutional power’ and falls into the ugly abyss of racism.” • “The judicial test of whether the Government, on a plea of military necessity, can validly deprive and individual of any of his constitutional rights is whether the deprivation is reasonably related to a public danger that is so ‘imme ...
... constitutional power’ and falls into the ugly abyss of racism.” • “The judicial test of whether the Government, on a plea of military necessity, can validly deprive and individual of any of his constitutional rights is whether the deprivation is reasonably related to a public danger that is so ‘imme ...
NS2-M1C8_-_World_War_II_-_The_Atlantic_War,_1939
... Provisional capital of unoccupied France (1940 - 1942) Actually controlled by the Germans. Forces aligned with the Axis Powers. Established by Hitler in 1940. Never recognized by the Axis Powers. ...
... Provisional capital of unoccupied France (1940 - 1942) Actually controlled by the Germans. Forces aligned with the Axis Powers. Established by Hitler in 1940. Never recognized by the Axis Powers. ...
American History Chapter 14 Section 5 The War Ends
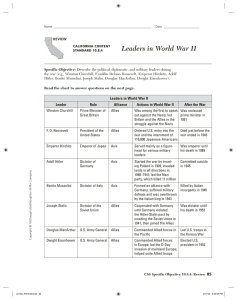
... • In 1945, representatives from 50 countries came to San Francisco to officially organize the United Nations. • They designed its charter, or constitution. • The General Assembly would vote on resolutions and choose the nonpermanent security group’s members. • The Security Council attended to intern ...
... • In 1945, representatives from 50 countries came to San Francisco to officially organize the United Nations. • They designed its charter, or constitution. • The General Assembly would vote on resolutions and choose the nonpermanent security group’s members. • The Security Council attended to intern ...
WW2 Vocab answer
... promised to not allow any further acts of aggression by Nazi Germany First step in Hitler’s plan to destroy the Treaty of Versailles Term referring to the Nazi takeover of Austria Policy of the United State prior to World War 2 to stay out of European affairs Failure of the League of Nations to act ...
... promised to not allow any further acts of aggression by Nazi Germany First step in Hitler’s plan to destroy the Treaty of Versailles Term referring to the Nazi takeover of Austria Policy of the United State prior to World War 2 to stay out of European affairs Failure of the League of Nations to act ...
WW2-Europe
... • Stalin then ordered Soviet Red Army to use “scorched earth” tactics- Soviets destroyed crops, factories, RRs, etc. so Nazis could not control them and get supplies. ...
... • Stalin then ordered Soviet Red Army to use “scorched earth” tactics- Soviets destroyed crops, factories, RRs, etc. so Nazis could not control them and get supplies. ...
The Beginning of the War The policy which sought to prevent
... On the first day of September in 1939, Germany declared war on Poland; the British and French responded by declaring war on Germany two days later. The Germans used the tactic of blitzkrieg (lightning war) in Poland, defeating the Polish Army at lightning speed. By the end of the first week of Octob ...
... On the first day of September in 1939, Germany declared war on Poland; the British and French responded by declaring war on Germany two days later. The Germans used the tactic of blitzkrieg (lightning war) in Poland, defeating the Polish Army at lightning speed. By the end of the first week of Octob ...
Dealing with the Defeated Axis Powers
... lesser sentences. Seven were sentenced to death by hanging, including Hideki Tojo, Japan’s leader for much of the war. ...
... lesser sentences. Seven were sentenced to death by hanging, including Hideki Tojo, Japan’s leader for much of the war. ...
An Overview of the Nuremberg Trials
... War II. Before Germany surrendered, leaders of the Allied nations began to discuss what should be done to punish Germany. After World War I, the Germans had trade restrictions imposed on them. Land they had taken was restored to the citizens of the original country. Many believed that the punishment ...
... War II. Before Germany surrendered, leaders of the Allied nations began to discuss what should be done to punish Germany. After World War I, the Germans had trade restrictions imposed on them. Land they had taken was restored to the citizens of the original country. Many believed that the punishment ...
World War II - EHS Faculty Pages
... As a prelude to a partition of Poland, the Nazis and Soviets sign an agreement not to attack each other ...
... As a prelude to a partition of Poland, the Nazis and Soviets sign an agreement not to attack each other ...
Notes-16-End-of-WWII
... to decide whether Germany was to be divided into several nations, and if so, what borders and interrelationships the new German states were to have. • The eventual partition of Germany into Allied Occupation Zones: British zone, French zone (two exclaves), American zone, Soviet zone, and Allied-admi ...
... to decide whether Germany was to be divided into several nations, and if so, what borders and interrelationships the new German states were to have. • The eventual partition of Germany into Allied Occupation Zones: British zone, French zone (two exclaves), American zone, Soviet zone, and Allied-admi ...
united states holocaust memorial museum
... German troops stationed in Italy seized control of the northern half of the peninsula, and continued to resist. Mussolini, who had been arrested by Italian military authorities, was rescued by SS commandos in September and established (under German supervision) a neoFascist puppet regime in northern ...
... German troops stationed in Italy seized control of the northern half of the peninsula, and continued to resist. Mussolini, who had been arrested by Italian military authorities, was rescued by SS commandos in September and established (under German supervision) a neoFascist puppet regime in northern ...
Study guide for Unit 5 Test 1) What is the difference between Lenin`s
... 6) Hitler passed the First Decree to the German Reich Citizenship Law in 1935 which said, “A Jew cannot be a Reich citizen. He has no voting rights in political matters; he cannot occupy public office.” What did policies like this lead to before and during the war? The Holocaust 7) What results came ...
... 6) Hitler passed the First Decree to the German Reich Citizenship Law in 1935 which said, “A Jew cannot be a Reich citizen. He has no voting rights in political matters; he cannot occupy public office.” What did policies like this lead to before and during the war? The Holocaust 7) What results came ...
Allied Control Council

The Allied Control Council or Allied Control Authority, known in the German language as the Alliierter Kontrollrat and also referred to as the Four Powers (German: Vier Mächte), was a military occupation governing body of the Allied Occupation Zones in Germany after the end of World War II in Europe. The members were the Soviet Union, the United States, and the United Kingdom; France was later added with a vote, but had no duties. The organization was based in Berlin-Schöneberg.