File - miss king`s world
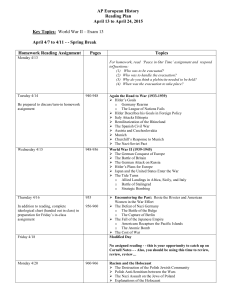
... 1. A major goal of France and Great Britain at the Conference of Versailles following World War I was to do what? 2. After World War I, Japan attempted to solve some of its economic problems by doing what? 3. Between the Meiji Restoration and World War II, Japan tried to solve the problem of its sca ...
... 1. A major goal of France and Great Britain at the Conference of Versailles following World War I was to do what? 2. After World War I, Japan attempted to solve some of its economic problems by doing what? 3. Between the Meiji Restoration and World War II, Japan tried to solve the problem of its sca ...
Timeline of WWII
... • WW I ends with an Allied victory. • The Treaty of Versailles is imposed on the defeated Germans. • Its conditions are harsh, leading to years of German resentment, political chaos, and economic disaster – fueling the desire for revenge. • In 1918, it is called the “Great War” or the “War to End Al ...
... • WW I ends with an Allied victory. • The Treaty of Versailles is imposed on the defeated Germans. • Its conditions are harsh, leading to years of German resentment, political chaos, and economic disaster – fueling the desire for revenge. • In 1918, it is called the “Great War” or the “War to End Al ...
Megan Blash
... (1) Who was to be evacuated? (2) Who was to handle the evacuation? (3) Why do you think a plebiscite needed to be held? (4) When was the evacuation to take place? Tuesday 4/14 ...
... (1) Who was to be evacuated? (2) Who was to handle the evacuation? (3) Why do you think a plebiscite needed to be held? (4) When was the evacuation to take place? Tuesday 4/14 ...
D-Day & Battle of the Bulge
... – Allies create fictional army under Gen. Patton (fake HQ, tanks, radio, etc.) – Convince Germans attack will come from Calais…not Normandy • Worked: Hitler order top divisions to Calais – Germans still on beaches of Normandy • Fire from trenches, mined beaches (bombs), anti-landing obstructions • S ...
... – Allies create fictional army under Gen. Patton (fake HQ, tanks, radio, etc.) – Convince Germans attack will come from Calais…not Normandy • Worked: Hitler order top divisions to Calais – Germans still on beaches of Normandy • Fire from trenches, mined beaches (bombs), anti-landing obstructions • S ...
6 Young People hand out
... parents). Boys would be made to be brave and fit so that they could become soldiers. Girls would be taught to be fit and obedient to become mothers. In order to do this the Nazi party set out to control all aspects of young people’s lives including their time at school and their leisure time. ...
... parents). Boys would be made to be brave and fit so that they could become soldiers. Girls would be taught to be fit and obedient to become mothers. In order to do this the Nazi party set out to control all aspects of young people’s lives including their time at school and their leisure time. ...
World War 2 – Things I Know
... enacted the Enabling Act that gave Hitler power to make new laws. One of his actions was to ban other political parties. ...
... enacted the Enabling Act that gave Hitler power to make new laws. One of his actions was to ban other political parties. ...
File
... the German form of fascism. Hitler was imprisoned after taking part in a failed coup (overthrowing the government through force) against the Weimar Republic in 1923. While in jail, Hitler wrote Mein Kampf in which he stated his belief that Germans were superior, democracy had many faults and the cou ...
... the German form of fascism. Hitler was imprisoned after taking part in a failed coup (overthrowing the government through force) against the Weimar Republic in 1923. While in jail, Hitler wrote Mein Kampf in which he stated his belief that Germans were superior, democracy had many faults and the cou ...
`Origins and Beginnings of WWII Dictator Chart (Who was the worst
... declared that any further attacks by Germany on small states would trigger war France and Britain followed through with their original announcement and declared war on Germany ...
... declared that any further attacks by Germany on small states would trigger war France and Britain followed through with their original announcement and declared war on Germany ...
WWII
... Hitler then violated the Munich Conference by seizing all of Czechoslovakia and then begins an attack on Poland. Britain and France would come to the aid of Poland. Hitler and Stalin (Soviet Union) agreed to a Non-aggressive Pact. The Nazi- Soviet Pact shocked the world ( communism and nazism wer ...
... Hitler then violated the Munich Conference by seizing all of Czechoslovakia and then begins an attack on Poland. Britain and France would come to the aid of Poland. Hitler and Stalin (Soviet Union) agreed to a Non-aggressive Pact. The Nazi- Soviet Pact shocked the world ( communism and nazism wer ...
WWII - PHS-Test-Bank
... Which of the following was NOT a reason France and England followed this policy ? A) to avoid war; B) didn’t know about it; C) thought Stalin in Russia was a greater threat; D) many French & English people thought Hitler’s actions were okay. At the Munich Conference, what did Hitler Promise Chamberl ...
... Which of the following was NOT a reason France and England followed this policy ? A) to avoid war; B) didn’t know about it; C) thought Stalin in Russia was a greater threat; D) many French & English people thought Hitler’s actions were okay. At the Munich Conference, what did Hitler Promise Chamberl ...
The USSR in World War II
... But the Axis powers were also challenging other Great Powers in Europe and Asia – the continuing conflict between empires In the 1920s-early 1930s, before Hitler’s coming to power in Germany, USSR cooperated with Germany against Britain and France When Germany became a radical anticommunist force, U ...
... But the Axis powers were also challenging other Great Powers in Europe and Asia – the continuing conflict between empires In the 1920s-early 1930s, before Hitler’s coming to power in Germany, USSR cooperated with Germany against Britain and France When Germany became a radical anticommunist force, U ...
World War II
... solved only by means of force, and this is never without risk.” Hitler met with Austria’s chancellor Kurt von Schuschnigg in February 1938 and demanded Austrian Nazis enter the government; although von Schuschnigg changed his mind, German troops marched into Austria unopposed on March 12, 1938 ...
... solved only by means of force, and this is never without risk.” Hitler met with Austria’s chancellor Kurt von Schuschnigg in February 1938 and demanded Austrian Nazis enter the government; although von Schuschnigg changed his mind, German troops marched into Austria unopposed on March 12, 1938 ...
Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial
... Hitler’s policy of Nazi racism targeted Jewish people and fed on European antisemitism Hitler viewed Jews as a national enemy and began implementing his Final Solution—elimination of Jewish people by sending them to concentration camps as slave laborers and then executing them in gas chambers The ex ...
... Hitler’s policy of Nazi racism targeted Jewish people and fed on European antisemitism Hitler viewed Jews as a national enemy and began implementing his Final Solution—elimination of Jewish people by sending them to concentration camps as slave laborers and then executing them in gas chambers The ex ...
The Holocaust - Livingston Public Schools
... following World War I made Germany an easy target to take over. In his book, Mein Kampf (1925), Hitler wrote about restoring Germany to glory. He said in order to this, Germany had to eliminate ...
... following World War I made Germany an easy target to take over. In his book, Mein Kampf (1925), Hitler wrote about restoring Germany to glory. He said in order to this, Germany had to eliminate ...
Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial World History from
... Hitler’s policy of Nazi racism targeted Jewish people and fed on European antisemitism Hitler viewed Jews as a national enemy and began implementing his Final Solution—elimination of Jewish people by sending them to concentration camps as slave laborers and then executing them in gas chambers The ex ...
... Hitler’s policy of Nazi racism targeted Jewish people and fed on European antisemitism Hitler viewed Jews as a national enemy and began implementing his Final Solution—elimination of Jewish people by sending them to concentration camps as slave laborers and then executing them in gas chambers The ex ...
World History from World War I to World War II
... Hitler’s policy of Nazi racism targeted Jewish people and fed on European antisemitism Hitler viewed Jews as a national enemy and began implementing his Final Solution—elimination of Jewish people by sending them to concentration camps as slave laborers and then executing them in gas chambers The ex ...
... Hitler’s policy of Nazi racism targeted Jewish people and fed on European antisemitism Hitler viewed Jews as a national enemy and began implementing his Final Solution—elimination of Jewish people by sending them to concentration camps as slave laborers and then executing them in gas chambers The ex ...
The Holocaust - Livingston Public Schools
... following World War I made Germany an easy target to take over. In his book, Mein Kampf (1925), Hitler wrote about restoring Germany to glory. He said in order to this, Germany had to eliminate ...
... following World War I made Germany an easy target to take over. In his book, Mein Kampf (1925), Hitler wrote about restoring Germany to glory. He said in order to this, Germany had to eliminate ...
2/24/2016
... 1933-Hitler Becomes Supreme Nazi Leader 1934 August 2 - German President Hindenburg dies. August 19 - Adolf Hitler becomes Führer (Supreme Chancellor) of Germany. 1935 1936 March 16 - Hitler violates the Treaty of Versailles by introducing military requirement for all Germans. September 15 - German ...
... 1933-Hitler Becomes Supreme Nazi Leader 1934 August 2 - German President Hindenburg dies. August 19 - Adolf Hitler becomes Führer (Supreme Chancellor) of Germany. 1935 1936 March 16 - Hitler violates the Treaty of Versailles by introducing military requirement for all Germans. September 15 - German ...
World War II
... through the Polish Corridor, which had been created after World War I. This corridor was a strip of land that separated East Prussia from the rest of Germany, giving Poland access to the sea. ...
... through the Polish Corridor, which had been created after World War I. This corridor was a strip of land that separated East Prussia from the rest of Germany, giving Poland access to the sea. ...
WWII L2 - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... Axis, followed by the Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis (also known as the Anti-Comintern [Com-intern stands for “Communist International”] Pact against the Soviet Union) ...
... Axis, followed by the Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis (also known as the Anti-Comintern [Com-intern stands for “Communist International”] Pact against the Soviet Union) ...
WARRING NATIONS - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... Axis, followed by the Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis (also known as the Anti-Comintern [Com-intern stands for “Communist International”] Pact against the Soviet Union) ...
... Axis, followed by the Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis (also known as the Anti-Comintern [Com-intern stands for “Communist International”] Pact against the Soviet Union) ...
9B-Chapter 24 Review Worksheet—ANSWERS
... action; 887 ships of all sizes (mostly private), sometimes dangerously, crossed the English Channel to rescue 338,226 men by bringing them to England. Allied forces were battered, but they were in tact enough to fight another day. ...
... action; 887 ships of all sizes (mostly private), sometimes dangerously, crossed the English Channel to rescue 338,226 men by bringing them to England. Allied forces were battered, but they were in tact enough to fight another day. ...
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany or the Third Reich (German: Drittes Reich) are common English names for the period of history in Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a dictatorship under the control of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Under Hitler's rule, Germany was transformed into a fascist totalitarian state which controlled nearly all aspects of life. The official name of the state was the Deutsches Reich (German Reich) from 1933 to 1943 and Großdeutsches Reich (Greater German Reich) from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany ceased to exist after the Allied Forces defeated Germany in May 1945, ending World War II in Europe.Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany by the President of the Weimar Republic Paul von Hindenburg on 30 January 1933. The Nazi Party then began to eliminate all political opposition and consolidate its power. Hindenburg died on 2 August 1934, and Hitler became dictator of Germany by merging the powers and offices of the Chancellery and Presidency. A national referendum held 19 August 1934 confirmed Hitler as sole Führer (leader) of Germany. All power was centralised in Hitler's hands, and his word became above all laws. The government was not a coordinated, co-operating body, but a collection of factions struggling for power and Hitler's favour. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Nazis restored economic stability and ended mass unemployment using heavy military spending and a mixed economy. Extensive public works were undertaken, including the construction of Autobahns (high speed highways). The return to economic stability boosted the regime's popularity.Racism, especially antisemitism, was a central feature of the regime. The Germanic peoples (the Nordic race) were considered the purest of the Aryan race, and were therefore the master race. Millions of Jews and others deemed undesirable were persecuted and murdered in the Holocaust. Opposition to Hitler's rule was ruthlessly suppressed. Members of the liberal, socialist, and communist opposition were killed, imprisoned, or exiled. The Christian churches were also oppressed, with many leaders imprisoned. Education focused on racial biology, population policy, and fitness for military service. Career and educational opportunities for women were curtailed. Recreation and tourism were organised via the Strength Through Joy program, and the 1936 Summer Olympics showcased the Third Reich on the international stage. Propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels made effective use of film, mass rallies, and Hitler's hypnotising oratory to control public opinion. The government controlled artistic expression, promoting specific art forms and banning or discouraging others.Nazi Germany made increasingly aggressive territorial demands, threatening war if they were not met. It seized Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938 and 1939. Hitler made a pact with Joseph Stalin and invaded Poland in September 1939, launching World War II in Europe. In alliance with Italy and smaller Axis powers, Germany conquered most of Europe by 1940 and threatened Great Britain. Reichskommissariats took control of conquered areas, and a German administration was established in what was left of Poland. Jews and others deemed undesirable were imprisoned and murdered in Nazi concentration camps and extermination camps. The implementation of the regime's racial policies culminated in the mass murder of Jews and other minorities in the Holocaust. Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, the tide turned against the Nazis, who suffered major military defeats in 1943. Large-scale aerial bombing of Germany escalated in 1944, and the Nazis retreated from Eastern and Southern Europe. Following the Allied invasion of France, Germany was conquered by the Soviets from the east and the other Allied powers from the west and surrendered within a year. Hitler's refusal to admit defeat led to massive destruction of German infrastructure and additional war-related deaths in the closing months of the war. The victorious Allies initiated a policy of denazification and put many of the surviving Nazi leadership on trial for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.