Ch. 17 – World War II
... in December 1941: – Growth of dictatorships in Europe & Japan (and their invasion of other countries). – Japanese attack on U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor (December 7th 1941). World War II would be a fight between the: – Allies – United States, Great Britain, Soviet Union (and France, China) – Ax ...
... in December 1941: – Growth of dictatorships in Europe & Japan (and their invasion of other countries). – Japanese attack on U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor (December 7th 1941). World War II would be a fight between the: – Allies – United States, Great Britain, Soviet Union (and France, China) – Ax ...
America in WWII
... to the Allies, there was a new problem: German U-Boats, sinking the supply ships, and British vessels. • Roosevelt could not order the U.S. Navy to protect British ships. The USA was still technically neutral. -> Instead, FDR developed the idea of a hemispheric defense zone. -> Roosevelt declared th ...
... to the Allies, there was a new problem: German U-Boats, sinking the supply ships, and British vessels. • Roosevelt could not order the U.S. Navy to protect British ships. The USA was still technically neutral. -> Instead, FDR developed the idea of a hemispheric defense zone. -> Roosevelt declared th ...
Chapter 17 Worksheets
... France, and the United States remained neutral, although individuals from these countries fought with the Loyalists. By 1939, Franco had triumphed. German aggression continued. In 1938, Hitler forced the Anschluss, or union with Austria. Next, Hitler set his sights on the Sudentenland. This was a pa ...
... France, and the United States remained neutral, although individuals from these countries fought with the Loyalists. By 1939, Franco had triumphed. German aggression continued. In 1938, Hitler forced the Anschluss, or union with Austria. Next, Hitler set his sights on the Sudentenland. This was a pa ...
Name
... 8. What was the rest of the world’s response to Jewish refugees? 9. What was Nazis want to accomplish by creating ghettos? 10. Why might Hitler have chosen Poland to put his ghetto policy for “the Jewish problem” into effect? 11. How were some Jews able to hang on in the ghetto? 12. What is the “Fin ...
... 8. What was the rest of the world’s response to Jewish refugees? 9. What was Nazis want to accomplish by creating ghettos? 10. Why might Hitler have chosen Poland to put his ghetto policy for “the Jewish problem” into effect? 11. How were some Jews able to hang on in the ghetto? 12. What is the “Fin ...
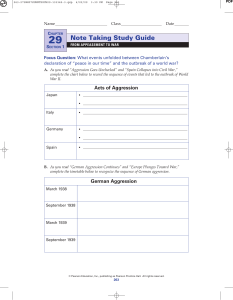
Aggression, Appeasement, and War
... Aggression, Appeasement, and War A. Main ideas The charts below show the main events in Europe of the years 1935 to 1939. Complete the charts as you read Section 1. ...
... Aggression, Appeasement, and War A. Main ideas The charts below show the main events in Europe of the years 1935 to 1939. Complete the charts as you read Section 1. ...
Hitler`s Lightning War Close Read
... Hitler’s Lightning War Germany Sparks a New War in Europe What caused Britain and France to declare war? In 1939, Adolf Hitler decided to move on Poland. He had already conquered Austria and Czechoslovakia. When Hitler signed a nonaggression pact with Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union, they agreed ...
... Hitler’s Lightning War Germany Sparks a New War in Europe What caused Britain and France to declare war? In 1939, Adolf Hitler decided to move on Poland. He had already conquered Austria and Czechoslovakia. When Hitler signed a nonaggression pact with Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union, they agreed ...
United States Foreign Policy in the 1920s and 1930s Road to WW II
... rise in various European and Asian nations – these leaders work to rebuild their nations than to begin a series of imperialistic actions that will eventually take the world into WW II Rise of Dictators • Italy -- Mussolini (1922) fascism: glorified the state and sought to expand • Japanese military ...
... rise in various European and Asian nations – these leaders work to rebuild their nations than to begin a series of imperialistic actions that will eventually take the world into WW II Rise of Dictators • Italy -- Mussolini (1922) fascism: glorified the state and sought to expand • Japanese military ...
Chapter 25: World War II
... Most Jews left Germany out of fear for their lives. Hitler’s expansionism Hitler thought European countries would not stop Germany’s expansion because they were led by cowards. Appeasement Appeasement: tolerating illegal actions by a person/group out of fear that punishing them might lead to even l ...
... Most Jews left Germany out of fear for their lives. Hitler’s expansionism Hitler thought European countries would not stop Germany’s expansion because they were led by cowards. Appeasement Appeasement: tolerating illegal actions by a person/group out of fear that punishing them might lead to even l ...
questions about the “varying viewpoints” - apush11
... “We shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight in the fields and streets, we shall fight in the hills, we shall never surrender.” Winston Churchill (1874–1965) (Speech, 1940) “It may be asked how could the Soviet government have consented to conclude a non-aggression pact with such perfidious…fiends ...
... “We shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight in the fields and streets, we shall fight in the hills, we shall never surrender.” Winston Churchill (1874–1965) (Speech, 1940) “It may be asked how could the Soviet government have consented to conclude a non-aggression pact with such perfidious…fiends ...
Introduction
... new things about history. I became very interested in wars after I read about it in a book. The vastness of World War II made me more curious about it. It is very interesting to learn about who started the war and why it happened. Because we’ll be learning about world history in middle school, doing ...
... new things about history. I became very interested in wars after I read about it in a book. The vastness of World War II made me more curious about it. It is very interesting to learn about who started the war and why it happened. Because we’ll be learning about world history in middle school, doing ...
The School Document Pack
... 1943, he was wounded in the face by fire from a low flying Allied plane. He feared that he might lose his eyesight completely, but he kept one eye and lost his right hand, half of the left hand, and part of his leg. He was saved by the surgery performed by one of Germany’s most famous doctors. Repor ...
... 1943, he was wounded in the face by fire from a low flying Allied plane. He feared that he might lose his eyesight completely, but he kept one eye and lost his right hand, half of the left hand, and part of his leg. He was saved by the surgery performed by one of Germany’s most famous doctors. Repor ...
Beginning of WWII and Main Events
... Conference Sept. 28, 1938 • Appeasement (making compromises to an aggressor to keep peace) by letting Germany occupy Sudetenland • Agreement between Germany and Britain, France, Italy (called the Munich Pact) said Germany could occupy Sudetenland if it was their last territorial demand in Europe • ( ...
... Conference Sept. 28, 1938 • Appeasement (making compromises to an aggressor to keep peace) by letting Germany occupy Sudetenland • Agreement between Germany and Britain, France, Italy (called the Munich Pact) said Germany could occupy Sudetenland if it was their last territorial demand in Europe • ( ...
Study Guide for - Pascack Valley Regional High School District
... i. The war had to be fought on several fronts 51. This battle was most well known for being one of the first “all air” battles. It was because of Britain’s excellent technology and strategic placement of weapons on its planes that that Britain won this battle. a. Battle of Britain 52. This battle to ...
... i. The war had to be fought on several fronts 51. This battle was most well known for being one of the first “all air” battles. It was because of Britain’s excellent technology and strategic placement of weapons on its planes that that Britain won this battle. a. Battle of Britain 52. This battle to ...
World War II unit test
... Axis or Allies? Place the country under the correct alliance. ½ point each Germany ...
... Axis or Allies? Place the country under the correct alliance. ½ point each Germany ...
File
... 14. What advantages might a weaker army fighting on its home soil have over a stronger invading army? 15. What did the conquest of Sicily do? 16. Trace the events January 1943 to April 1945 in Italy: 15. What happened to Mussolini at the end of the war? 17. How did Americans make contributions to th ...
... 14. What advantages might a weaker army fighting on its home soil have over a stronger invading army? 15. What did the conquest of Sicily do? 16. Trace the events January 1943 to April 1945 in Italy: 15. What happened to Mussolini at the end of the war? 17. How did Americans make contributions to th ...
Canadians in Action
... The Canadian Army single handedly drove the Nazis out of Holland and saved the country from oppression and starvation Canada and Holland still have a special relationship and our there are parades and festivities hold every year in honor of Canadian veterans. In Holland, the grave of every fallen Ca ...
... The Canadian Army single handedly drove the Nazis out of Holland and saved the country from oppression and starvation Canada and Holland still have a special relationship and our there are parades and festivities hold every year in honor of Canadian veterans. In Holland, the grave of every fallen Ca ...
Ch. 35-36 Review Packet File
... a. After a period of inaction over the winter of 1939–1940, called the “_____________ war,” Hitler invaded and conquered _______________ (through Scandinavia, Netherlands, and Belgium). The British successfully evacuated their troops from the French port of _______________. Prime Minister Winston __ ...
... a. After a period of inaction over the winter of 1939–1940, called the “_____________ war,” Hitler invaded and conquered _______________ (through Scandinavia, Netherlands, and Belgium). The British successfully evacuated their troops from the French port of _______________. Prime Minister Winston __ ...
Note Taking Study Guide
... France, and the United States remained neutral, although individuals from these countries fought with the Loyalists. By 1939, Franco had triumphed. German aggression continued. In 1938, Hitler forced the Anschluss, or union with Austria. Next, Hitler set his sights on the Sudentenland. This was a pa ...
... France, and the United States remained neutral, although individuals from these countries fought with the Loyalists. By 1939, Franco had triumphed. German aggression continued. In 1938, Hitler forced the Anschluss, or union with Austria. Next, Hitler set his sights on the Sudentenland. This was a pa ...
Slide 1
... Western Europe’s Policy of Appeasement Policy of Appeasement = is an approach to foreign relations which tries to maintain peace by making concessions to the aggressor to prevent war. It was practiced by many Western nations facing Hitler, but the two main appeasing countries were Britain and Franc ...
... Western Europe’s Policy of Appeasement Policy of Appeasement = is an approach to foreign relations which tries to maintain peace by making concessions to the aggressor to prevent war. It was practiced by many Western nations facing Hitler, but the two main appeasing countries were Britain and Franc ...
Chapter 10 The Weimar Republic: an Experiment in Democracy
... 31. Write a short note on the Munich Putsch. Mention why it happened; what was attempted; what happened; what happened to the leaders. 32. What valuable lessons did Hitler learn from the Putsch? 33. How did Hitler and the Nazis undermine the new republic? Think Point! – Jot down your thoughts on the ...
... 31. Write a short note on the Munich Putsch. Mention why it happened; what was attempted; what happened; what happened to the leaders. 32. What valuable lessons did Hitler learn from the Putsch? 33. How did Hitler and the Nazis undermine the new republic? Think Point! – Jot down your thoughts on the ...
Key Events of WWII File
... • Operation Barbarossa ultimately led to Hitler’s downfall • At the time though the decision was not so foolish • Hitler needed another victory to keep Nazi momentum ...
... • Operation Barbarossa ultimately led to Hitler’s downfall • At the time though the decision was not so foolish • Hitler needed another victory to keep Nazi momentum ...
Unit 4 Selfcheck #1 Answers
... plans, including the executions of enemies of the state. 11. Why did Stalin sign a Nazi-Soviet Pact in August of 1939? Stalin was worried that the Soviet Union would one day be one of Hitler’s targets, and Britain and France had rejected his attempt at establishing collective security. ...
... plans, including the executions of enemies of the state. 11. Why did Stalin sign a Nazi-Soviet Pact in August of 1939? Stalin was worried that the Soviet Union would one day be one of Hitler’s targets, and Britain and France had rejected his attempt at establishing collective security. ...
File wwii holocaust
... the troops, they didn’t have to leave any behind! It seemed like a victory getting the troops back – to fight another day. It captured the minds & hearts of the British at a time when it looked probable they, too, would soon be invaded. ...
... the troops, they didn’t have to leave any behind! It seemed like a victory getting the troops back – to fight another day. It captured the minds & hearts of the British at a time when it looked probable they, too, would soon be invaded. ...
Appeasement

Appeasement in a political context is a diplomatic policy of making political or material concessions to an enemy power in order to avoid conflict.The term is most often applied to the foreign policy of the British Prime Ministers Ramsay Macdonald, Stanley Baldwin and Neville Chamberlain towards Nazi Germany between 1933 and 1939. Their policies of avoiding war with Germany have been the subject of intense debate for more than seventy years among academics, politicians and diplomats. The historians' assessments have ranged from condemnation for allowing Adolf Hitler's Germany to grow too strong, to the judgment that they had no alternative and acted in Britain's best interests. At the time, these concessions were widely seen as positive, and the Munich Pact concluded on 30 September 1938 among Germany, Britain, France, and Italy prompted Chamberlain to announce that he had secured ""peace for our time.""