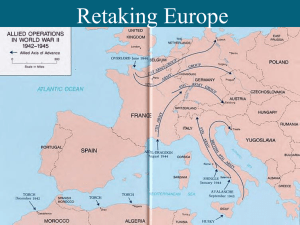
How did America turn the tide in Europe and North Africa?
... How did America turn the tide in Europe and North Africa? ...
... How did America turn the tide in Europe and North Africa? ...
No Slide Title
... United States’ General Patton used blitzkrieg techniques to burst out of Normandy. He and his troops swept across ...
... United States’ General Patton used blitzkrieg techniques to burst out of Normandy. He and his troops swept across ...
Unit 7: World War II and its Aftermath
... people by having the state own and control the means of production of major industries; government determines the needs of the people and then provides these for them. ...
... people by having the state own and control the means of production of major industries; government determines the needs of the people and then provides these for them. ...
Germany
... Scapegoat- a person or group blamed for the mistakes and problems of others; Hitler hated the Jews because he blamed them for all that Germany had lost. They were Germany’s scapegoat. Concentration Camp- a prison camp for people thought to be dangerous to a ruling group Genocide- an attempt to kill ...
... Scapegoat- a person or group blamed for the mistakes and problems of others; Hitler hated the Jews because he blamed them for all that Germany had lost. They were Germany’s scapegoat. Concentration Camp- a prison camp for people thought to be dangerous to a ruling group Genocide- an attempt to kill ...
Mr O`Sullivan: Terza Media History - Mr. O`Sullivan`s World of History
... The 33rd U.S. president, who succeeded Franklin D. Roosevelt upon Roosevelt’s death in April 1945. Truman, who led the country through the last few months of World War II, is best known for making the controversial decision to use two atomic bombs against Japan in August 1945. After the war, Truman ...
... The 33rd U.S. president, who succeeded Franklin D. Roosevelt upon Roosevelt’s death in April 1945. Truman, who led the country through the last few months of World War II, is best known for making the controversial decision to use two atomic bombs against Japan in August 1945. After the war, Truman ...
Allied Turning Points in WWII
... • Great Britain & US send troops into Italy • Italians overthrow Mussolini but Hitler sends troops to Italy to restore his power ...
... • Great Britain & US send troops into Italy • Italians overthrow Mussolini but Hitler sends troops to Italy to restore his power ...
WorldWarIIPowerPointPresentation
... 2. Britain and France said, “You better not, or else…” 3. Germany ignored the treat and did it anyway. 4. Britain and France declared war on Germany. 5. Unfortunately, Germany quickly conquered France and Poland. ...
... 2. Britain and France said, “You better not, or else…” 3. Germany ignored the treat and did it anyway. 4. Britain and France declared war on Germany. 5. Unfortunately, Germany quickly conquered France and Poland. ...
The End of World War Two
... knockout blow, the Allies launched the invasion of France known as ‘D-Day’. This landing of several hundred thousand Allies troops drew German strength away from the Eastern Front, enabling the Russians to rapidly advance. It also enabled the liberation of France after four years of Nazi occupation. ...
... knockout blow, the Allies launched the invasion of France known as ‘D-Day’. This landing of several hundred thousand Allies troops drew German strength away from the Eastern Front, enabling the Russians to rapidly advance. It also enabled the liberation of France after four years of Nazi occupation. ...
World War II - Issaquah Connect
... – Because of the horrors of World War I – They were not ready to fight another war ...
... – Because of the horrors of World War I – They were not ready to fight another war ...
WW2 Europe
... • US wanted to go straight into France • Africa was the first fight for 2 reasons 1. Only place Allies could win • Control Mediterranean Sea (Suez Canal) 2. Would pull forces away from Russia ...
... • US wanted to go straight into France • Africa was the first fight for 2 reasons 1. Only place Allies could win • Control Mediterranean Sea (Suez Canal) 2. Would pull forces away from Russia ...
Princeton Paper 10-11 (pdf)
... Before World War II, Germany intended Italy to be the main organizing power in the Middle East, replacing British and French rule. A Greater Arabia was to be set up under the influence of the Axis powers of Germany, Italy, and Japan. But initial German victories in the war, particularly the fall of ...
... Before World War II, Germany intended Italy to be the main organizing power in the Middle East, replacing British and French rule. A Greater Arabia was to be set up under the influence of the Axis powers of Germany, Italy, and Japan. But initial German victories in the war, particularly the fall of ...
Chapter 17
... d. The British air force rebuilt its strength. 26. Citizens of the Soviet Union experienced severe food and housing shortages because a. industry could not produce enough for the growing population. b. all resources went into the war economy. c. the German army destroyed everything. d. the Allied fo ...
... d. The British air force rebuilt its strength. 26. Citizens of the Soviet Union experienced severe food and housing shortages because a. industry could not produce enough for the growing population. b. all resources went into the war economy. c. the German army destroyed everything. d. the Allied fo ...
The US at War
... shall defend our island whatever the cost may be; we shall fight on beaches, landing grounds, in streets and on hills. We shall never surrender…” ...
... shall defend our island whatever the cost may be; we shall fight on beaches, landing grounds, in streets and on hills. We shall never surrender…” ...
WORLD WAR TWO
... minister. He was strongly against any negotiation with Hitler. o Operation Sea Lion – a German plan of an invasion to Britain, with a preceding air assault performed by the Luftwaffe o RAF (Royal Air Force) - British air force which stood up against Luftwaffe, the RAF was also assisted by Canadian, ...
... minister. He was strongly against any negotiation with Hitler. o Operation Sea Lion – a German plan of an invasion to Britain, with a preceding air assault performed by the Luftwaffe o RAF (Royal Air Force) - British air force which stood up against Luftwaffe, the RAF was also assisted by Canadian, ...
Document
... • Events in Asia drew the US into war (not Europe) • In response, Roosevelt banned American exports of iron/steel/oil to Japan • Because of this, Japanese leaders decided on war and to attack the US ...
... • Events in Asia drew the US into war (not Europe) • In response, Roosevelt banned American exports of iron/steel/oil to Japan • Because of this, Japanese leaders decided on war and to attack the US ...
WWII Study Guide
... 1. How did the following led to WWII a. Aggression of Totalitarian Powers-Dictators built up their armies b. Nationalism-Countries formed alliances and demanded obedience c. Treaty of Versailles-Extremely harsh to the Axis Powers d. League of Nations-Couldn’t enforce its rules e. Appeasements-France ...
... 1. How did the following led to WWII a. Aggression of Totalitarian Powers-Dictators built up their armies b. Nationalism-Countries formed alliances and demanded obedience c. Treaty of Versailles-Extremely harsh to the Axis Powers d. League of Nations-Couldn’t enforce its rules e. Appeasements-France ...
World War II Unit Test Study Guide
... 15. What style of warfare did German use? Describe it. Blitzkrieg; Overwhelm the enemy with speed and force usually combining air and ground forces 16. Describe Germany’s actions in the early years of World War II (1939-1941). Germany was successful in taking over neighboring nations including Czech ...
... 15. What style of warfare did German use? Describe it. Blitzkrieg; Overwhelm the enemy with speed and force usually combining air and ground forces 16. Describe Germany’s actions in the early years of World War II (1939-1941). Germany was successful in taking over neighboring nations including Czech ...
World History Semester 2 Study Guide
... 13. Under the Treaty of Versailles, to whom did the Allies give Chinese territories to that had previously been controlled by Germany? 14. Who was the leader responsible for the Great Purge and who was the main group that was victimized by it? ...
... 13. Under the Treaty of Versailles, to whom did the Allies give Chinese territories to that had previously been controlled by Germany? 14. Who was the leader responsible for the Great Purge and who was the main group that was victimized by it? ...
Causes of World War I
... and unsanitary conditions. In the trenches men stood for hours on end in waterlogged trenches without being able to remove wet socks or boots. ...
... and unsanitary conditions. In the trenches men stood for hours on end in waterlogged trenches without being able to remove wet socks or boots. ...
MARCH 5TH: The Spitfire, the iconic British fighter of World War Two
... SEPTEMBER 25TH : With XXX Corps on the other side of the Rhine river but unable to cross due to German artillery controlling the river the British 1ST Airborne division withdraws across the Rhine during the night under Operation Berlin. By the morning of the 26th some 2,500 eventually had made the ...
... SEPTEMBER 25TH : With XXX Corps on the other side of the Rhine river but unable to cross due to German artillery controlling the river the British 1ST Airborne division withdraws across the Rhine during the night under Operation Berlin. By the morning of the 26th some 2,500 eventually had made the ...