The Road to US Involvement in World War II
... • U.S. would not trade weapons or grant loans to belligerent nations at war • No travel on vessels of nations at war (no Lusitania this time) • Cash and Carry Policy for non-military goods • U.S. navy loses relative strength (idea that strong navies cause war) ...
... • U.S. would not trade weapons or grant loans to belligerent nations at war • No travel on vessels of nations at war (no Lusitania this time) • Cash and Carry Policy for non-military goods • U.S. navy loses relative strength (idea that strong navies cause war) ...
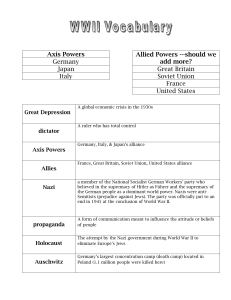
World War II Terms
... World War II Terms Chapter 11 1. Appeasement- satisfying the demands of dissatisfied powers in an effort to maintain peace and stability. 2. Axis Powers- the nations of Germany, Italy and Japan during World War II who opposed the Allies. 3. Allies- in World War II the nations of Great Britain, the S ...
... World War II Terms Chapter 11 1. Appeasement- satisfying the demands of dissatisfied powers in an effort to maintain peace and stability. 2. Axis Powers- the nations of Germany, Italy and Japan during World War II who opposed the Allies. 3. Allies- in World War II the nations of Great Britain, the S ...
10.8 Students analyze the causes and consequences of
... socialists, Jews, and foreigners. • Hitler was Austrian born, WWI veteran, who became the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party (Nazi’s). • 1925 he is put in jail where he writes Mein Kamph (My Struggle) • Nazis gain support during the depression from the unemployed. • 1933 Hitler as ...
... socialists, Jews, and foreigners. • Hitler was Austrian born, WWI veteran, who became the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party (Nazi’s). • 1925 he is put in jail where he writes Mein Kamph (My Struggle) • Nazis gain support during the depression from the unemployed. • 1933 Hitler as ...
WWII Causes - World history
... Sudetenland- An area of Czechoslovakia on the border with Germany with a large ...
... Sudetenland- An area of Czechoslovakia on the border with Germany with a large ...
Great Britain - Teacher Pages
... paved the way for the outbreak of World War II. Focus Question: How did German and Japanese actions lead to World War II? ...
... paved the way for the outbreak of World War II. Focus Question: How did German and Japanese actions lead to World War II? ...
Social Impact of World War II
... Another question is how such an event could occur at all. The long term Anti-Semitism throughout Europe. German culture teaches to obey authority even though you may disapproved of what was happening Trained to follow orders. ...
... Another question is how such an event could occur at all. The long term Anti-Semitism throughout Europe. German culture teaches to obey authority even though you may disapproved of what was happening Trained to follow orders. ...
First phase of World War II
... capacities of technologically most advanced industry, GDP more than doubled from 1940 to 1945) modernization also in transport (improved infrastructure) & agriculture (rise of demand after decade of depression, mechanization enhanced by conscription of labour surplus) internal demand kept under cont ...
... capacities of technologically most advanced industry, GDP more than doubled from 1940 to 1945) modernization also in transport (improved infrastructure) & agriculture (rise of demand after decade of depression, mechanization enhanced by conscription of labour surplus) internal demand kept under cont ...
World War II: The Road to War
... - Attention shifts to Poland. Avoid a two front War! - Hitler and Joseph Stalin astonish the world by signing the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact in Aug.1939. - On September 1, 1939 Blitzkrieg is unleashed on Poland. WW II in Europe had begun! America was alarmed! Yet Neutral for the moment I. From ...
... - Attention shifts to Poland. Avoid a two front War! - Hitler and Joseph Stalin astonish the world by signing the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact in Aug.1939. - On September 1, 1939 Blitzkrieg is unleashed on Poland. WW II in Europe had begun! America was alarmed! Yet Neutral for the moment I. From ...
US Hisory
... 44. What long tradition did FDR break in the election of 1940? 45. What was the quarantine speech and how did the American public react to it? 46. What belief was held by those who make up the American First Committee? 47. What was the “over-age destroyer” deal with England? 48. What was the Lend-Le ...
... 44. What long tradition did FDR break in the election of 1940? 45. What was the quarantine speech and how did the American public react to it? 46. What belief was held by those who make up the American First Committee? 47. What was the “over-age destroyer” deal with England? 48. What was the Lend-Le ...
flashcards_ww2
... World War II Who was president during World War II? What event started World War II in Europe? What were the Axis nations during World War II? What was the Battle of Britain? What country did Hitler invade in mid-1941? What was the position of the U.S. during the first two years of World War II? Wha ...
... World War II Who was president during World War II? What event started World War II in Europe? What were the Axis nations during World War II? What was the Battle of Britain? What country did Hitler invade in mid-1941? What was the position of the U.S. during the first two years of World War II? Wha ...
WORLD WAR II
... Battle of the Bulge – Dec 1944 to Jan 1945 Heavy Bombardment of Berlin begins Adolf Hitler moves underground March 1945 – Allies Crossed the Rhine Adolf Hitler commits suicide on April 30. Germany surrenders May 7, 1945 – V-E Day ...
... Battle of the Bulge – Dec 1944 to Jan 1945 Heavy Bombardment of Berlin begins Adolf Hitler moves underground March 1945 – Allies Crossed the Rhine Adolf Hitler commits suicide on April 30. Germany surrenders May 7, 1945 – V-E Day ...
key - San Leandro Unified School District
... 10. With the help of Italy’s Mussolini, the Germans controlled most of North Africa by April of 1940. British General Montgomery faced German Field Marshall Rommel, whose nickname was the Desert Fox. THE WAR IN WESTERN EUROPE: 11. FRANCE: In May of 1940 the Nazis invade France. France surrenders in ...
... 10. With the help of Italy’s Mussolini, the Germans controlled most of North Africa by April of 1940. British General Montgomery faced German Field Marshall Rommel, whose nickname was the Desert Fox. THE WAR IN WESTERN EUROPE: 11. FRANCE: In May of 1940 the Nazis invade France. France surrenders in ...
HI136 The History of Germany Lecture 14
... The question of whether the interests of both parties make desirable the maintenance of an independent Polish States and how such a state should be bounded can only be definitely determined in the course of further political developments. In any event both Governments will resolve this question by m ...
... The question of whether the interests of both parties make desirable the maintenance of an independent Polish States and how such a state should be bounded can only be definitely determined in the course of further political developments. In any event both Governments will resolve this question by m ...
Goal 10: WWII and the Beginning of the Cold War (1930
... was now authorized to lend and lease “defense articles” to those necessary in the interest of the defense of the U.S. • Atlantic Charter- FDR and Winston Churchill met on a battleship to agree on certain principles for building a lasting peace and establishing free governments in the world. Germany ...
... was now authorized to lend and lease “defense articles” to those necessary in the interest of the defense of the U.S. • Atlantic Charter- FDR and Winston Churchill met on a battleship to agree on certain principles for building a lasting peace and establishing free governments in the world. Germany ...
Following the Civil War, a plan for Reconstruction was
... 35. Many women took jobs that fell outside the traditional realm of woman’s work ...
... 35. Many women took jobs that fell outside the traditional realm of woman’s work ...
World War II
... ► 2 Failures of the Treaty of Versailles Caused anger and resentment Democracies that were created collapsed ...
... ► 2 Failures of the Treaty of Versailles Caused anger and resentment Democracies that were created collapsed ...
Causes of WWII
... wish to see sovereign rights and self government restored to those who have been forcibly deprived of them; Fourth, they will endeavor, with due respect for their existing obligations, to further the enjoyment by all States, great or small, victor or vanquished, of access, on equal terms, to the tra ...
... wish to see sovereign rights and self government restored to those who have been forcibly deprived of them; Fourth, they will endeavor, with due respect for their existing obligations, to further the enjoyment by all States, great or small, victor or vanquished, of access, on equal terms, to the tra ...
Chapter VI America Before and During the Second World War Outline
... group collective mindset. They differentiated themselves from other Germans. 7. Some say Hitler and the Nazis were simply opportunistic demagogues. Inciting hatred of the Jews was the means to an end. The Nazis used hatred of the Jews to unify the German people and create a new German empire. Antise ...
... group collective mindset. They differentiated themselves from other Germans. 7. Some say Hitler and the Nazis were simply opportunistic demagogues. Inciting hatred of the Jews was the means to an end. The Nazis used hatred of the Jews to unify the German people and create a new German empire. Antise ...
Economy of Nazi Germany

World War I caused economic and manpower losses on Germany led to a decade of economic woes, including hyperinflation in the mid-1920s. Following the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the German economy, like those of many other western nations, suffered the effects of the Great Depression, with unemployment soaring. When Hitler became Chancellor in 1933, he introduced new efforts to improve Germany's economy, including autarky and the development of the German agricultural economy by placing tariffs on agricultural imports.However, these changes—including autarky and nationalization of key industries—had a mixed record. By 1938, unemployment was practically extinct. Wages increased by 10.9% in real terms during this period. However, nationalization and a cutting off of trade meant rationing in key resources like poultry, fruit, and clothing for many Germans.In 1934 Hjalmar Schacht, the Reich Minister of Economics, introduced the Mefo bills, allowing Germany to rearm without spending Reichmarks but instead pay industry with Reichmarks and Mefo bills (Government IOU's) which they could trade with each other. Between 1933 and 1939, the total revenue was 62 billion marks, whereas expenditure (at times made up to 60% by rearmament costs) exceeded 101 billion, thus creating a huge deficit and national debt (reaching 38 billion marks in 1939) coinciding with the Kristallnacht and intensified persecutions of Jews and the outbreak of the war.