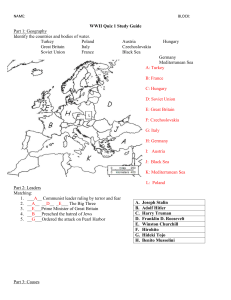
NAME: BLOCK: WWII Quiz 1 Study Guide Part 1: Geography Identify
... Define and explain each of the four causes of World War II. Fascism (Name 2 fascist leaders) – a political philosophy in which total power is given to a dictator. The two fascist leaders were Hitler and Mussolini ...
... Define and explain each of the four causes of World War II. Fascism (Name 2 fascist leaders) – a political philosophy in which total power is given to a dictator. The two fascist leaders were Hitler and Mussolini ...
Standard 5-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of
... a democracy in occupied Japan. Germany was divided into four zones and occupied by the four Allied powers. Soon the United States, Great Britain, and France united their zones and helped to create a democratic government in what later became known as West Germany. The Soviet Union established a comm ...
... a democracy in occupied Japan. Germany was divided into four zones and occupied by the four Allied powers. Soon the United States, Great Britain, and France united their zones and helped to create a democratic government in what later became known as West Germany. The Soviet Union established a comm ...
WORD
... had Pan-German dream of bringing all Germans ‘home to the Reich’ - Hitler said that “Germany’s problem could only be solved by means of force and this was never without attendant risk” ...
... had Pan-German dream of bringing all Germans ‘home to the Reich’ - Hitler said that “Germany’s problem could only be solved by means of force and this was never without attendant risk” ...
Japan Italy Germany Spain
... 29-5: The World After the War IV. New Conflicts Developed (cont.) B. The Marshall Plan 1. United States gave food and economic assistance to Europe 2. Helped war-shattered Europe to recover very quickly 3. Stalin declined aid and forbade Eastern Europe from accepting it ...
... 29-5: The World After the War IV. New Conflicts Developed (cont.) B. The Marshall Plan 1. United States gave food and economic assistance to Europe 2. Helped war-shattered Europe to recover very quickly 3. Stalin declined aid and forbade Eastern Europe from accepting it ...
Hitler and the Rise of Germany
... fate of the Eastern European lands that it occupied. Stalin wanted communist governments installed in these countries as a protection against Germany. The U.S. and Britain were against the idea and wanted free elections in Eastern Europe. ...
... fate of the Eastern European lands that it occupied. Stalin wanted communist governments installed in these countries as a protection against Germany. The U.S. and Britain were against the idea and wanted free elections in Eastern Europe. ...
World War II
... World wide Depression Germany’s high World War I debt (remember Treaty of Versailles and reparations) High inflation – the value of money goes down over time. Massive unemployment ...
... World wide Depression Germany’s high World War I debt (remember Treaty of Versailles and reparations) High inflation – the value of money goes down over time. Massive unemployment ...
HARRISON BETH JACKO 4
... 1935- Italy invades and conqueres Ethiopia 1938- Germany marches into Austria and takes over. Germany fighters and bombers. 1940- first bombing on Birmingham. Battle for the Rhine has become achase. ...
... 1935- Italy invades and conqueres Ethiopia 1938- Germany marches into Austria and takes over. Germany fighters and bombers. 1940- first bombing on Birmingham. Battle for the Rhine has become achase. ...
unit 8b World War II
... Existence of only the leader’s political party No individual rights The state was supreme ...
... Existence of only the leader’s political party No individual rights The state was supreme ...
Chapter 8 Lesson 4 World War II Begins
... Allies had expected Germany to pay for damages during World War I Didn’t have enough money to do this Adolph Hitler, leader of Germany during the 20’s, said Germany had been treated unfairly. Believed only Germans with blond hair and blue eyes were “true Germans” Blamed Jews for many of the problems ...
... Allies had expected Germany to pay for damages during World War I Didn’t have enough money to do this Adolph Hitler, leader of Germany during the 20’s, said Germany had been treated unfairly. Believed only Germans with blond hair and blue eyes were “true Germans” Blamed Jews for many of the problems ...
Section 2 Soviet Union Joseph stalin Italy Benito Mussolini Germany
... • blamed Jews for Germany’s problems ...
... • blamed Jews for Germany’s problems ...
World War II Section 1
... Germany Expands After World War I • Treaty of Versailles seriously damaged German economy • Adolf Hitler came to power – Promised to restore Germany’s greatness – Lebensraum, or “living room” • Hitler wanted more territory – Neighbors aware of threat – Memories of World War I still fresh – No one wi ...
... Germany Expands After World War I • Treaty of Versailles seriously damaged German economy • Adolf Hitler came to power – Promised to restore Germany’s greatness – Lebensraum, or “living room” • Hitler wanted more territory – Neighbors aware of threat – Memories of World War I still fresh – No one wi ...
Lecture 01 December
... ambitions of imperial powers, who could easily flaunt their threats and sanctions (Germany was never a member; Japan withdrew in 1933) • In reality, the old balance of power system prevailed – forging an alliance between Britain, France and the Soviet Union to check German and Japanese aggression ...
... ambitions of imperial powers, who could easily flaunt their threats and sanctions (Germany was never a member; Japan withdrew in 1933) • In reality, the old balance of power system prevailed – forging an alliance between Britain, France and the Soviet Union to check German and Japanese aggression ...
Global Struggles
... – Thought most of Hitler’s demands were reasonable – People ASSUMED the Nazi’s would be interested in ...
... – Thought most of Hitler’s demands were reasonable – People ASSUMED the Nazi’s would be interested in ...
find the important word
... FIND THE IMPORTANT WORD Political system in which the government controls every aspect of the citizens’ lives. ...
... FIND THE IMPORTANT WORD Political system in which the government controls every aspect of the citizens’ lives. ...
World H - WWII Need to Know - HFAWorldHistory-Kos
... The Early Stages • September 1, 1939: Germany invades Poland, Great Britain and France declare war on Germany • Summer, 1940 – Nazi Germany captures France • Mid-late 1940 – Nazi Germany bombs but does not capture Great Britain • Summer, 1941 – Operation Barbarossa: Nazi Germany invades the Soviet ...
... The Early Stages • September 1, 1939: Germany invades Poland, Great Britain and France declare war on Germany • Summer, 1940 – Nazi Germany captures France • Mid-late 1940 – Nazi Germany bombs but does not capture Great Britain • Summer, 1941 – Operation Barbarossa: Nazi Germany invades the Soviet ...
WWII Timeline PowerPoint
... April 1945: As German troops started getting captured in large numbers and surrendering in the different areas that they occupied, defeat seemed inevitable. ...
... April 1945: As German troops started getting captured in large numbers and surrendering in the different areas that they occupied, defeat seemed inevitable. ...
Study Guide for Short Answer Chapter 21 section 2: Explain how
... What role did Great Britain and France play? They accept Hitler’s demands, sent written protests. Preparations for War: What preparations did Great Britain and France make for war when Hitler's plans became clear? They begin to rearm themselves and also to draft soldiers into the military Why did Hi ...
... What role did Great Britain and France play? They accept Hitler’s demands, sent written protests. Preparations for War: What preparations did Great Britain and France make for war when Hitler's plans became clear? They begin to rearm themselves and also to draft soldiers into the military Why did Hi ...
World War II (Visuals)
... Europeans were fearful of another war, so they supported Hitler’s actions in return for his promise that he would not invade any more countries ...
... Europeans were fearful of another war, so they supported Hitler’s actions in return for his promise that he would not invade any more countries ...
KEYActiveReadChpt5
... By end of war, 4th lgst. In World. 373 warships, 100 000 personnel Can plays major part with defence (first) German uboats (28) had sunk 6 million tonnes of supplies Corvettes rushed into service – escorts for convoys 1941 – USA joins war and joins Canada in the Battle of the Atlantic Can forc ...
... By end of war, 4th lgst. In World. 373 warships, 100 000 personnel Can plays major part with defence (first) German uboats (28) had sunk 6 million tonnes of supplies Corvettes rushed into service – escorts for convoys 1941 – USA joins war and joins Canada in the Battle of the Atlantic Can forc ...
Economy of Nazi Germany

World War I caused economic and manpower losses on Germany led to a decade of economic woes, including hyperinflation in the mid-1920s. Following the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the German economy, like those of many other western nations, suffered the effects of the Great Depression, with unemployment soaring. When Hitler became Chancellor in 1933, he introduced new efforts to improve Germany's economy, including autarky and the development of the German agricultural economy by placing tariffs on agricultural imports.However, these changes—including autarky and nationalization of key industries—had a mixed record. By 1938, unemployment was practically extinct. Wages increased by 10.9% in real terms during this period. However, nationalization and a cutting off of trade meant rationing in key resources like poultry, fruit, and clothing for many Germans.In 1934 Hjalmar Schacht, the Reich Minister of Economics, introduced the Mefo bills, allowing Germany to rearm without spending Reichmarks but instead pay industry with Reichmarks and Mefo bills (Government IOU's) which they could trade with each other. Between 1933 and 1939, the total revenue was 62 billion marks, whereas expenditure (at times made up to 60% by rearmament costs) exceeded 101 billion, thus creating a huge deficit and national debt (reaching 38 billion marks in 1939) coinciding with the Kristallnacht and intensified persecutions of Jews and the outbreak of the war.