World War II Chapter 17 Section 1 Where did we leave off?
... The Axis Powers Form an Alliance Germany, Italy, and Japan make an alliance called the Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis. The three nations agree to fight Communism but more importantly they will not interfere if any of the other countries try to expand. This agreement made it easier for these countries ...
... The Axis Powers Form an Alliance Germany, Italy, and Japan make an alliance called the Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis. The three nations agree to fight Communism but more importantly they will not interfere if any of the other countries try to expand. This agreement made it easier for these countries ...
The Coming of the Second World War
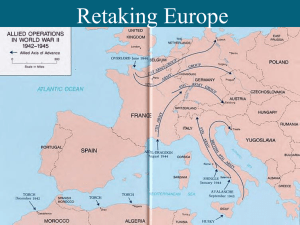
... used by Germany to quickly defeat an enemy by poking a hole in enemy line and cutting off front lines from the rear thus surrounding enemy. • Used coordinated attack on one part of enemy line with airforce, tanks, and artillery • Poland defeated in about a month; partition occurred when USSR attacke ...
... used by Germany to quickly defeat an enemy by poking a hole in enemy line and cutting off front lines from the rear thus surrounding enemy. • Used coordinated attack on one part of enemy line with airforce, tanks, and artillery • Poland defeated in about a month; partition occurred when USSR attacke ...
No Slide Title
... FDR, Churchill and Stalin fair elections in E. European countries meet to plan the final defeat and participation in of Hilter and decide the shape of the post-war world. the Pacific theater. ...
... FDR, Churchill and Stalin fair elections in E. European countries meet to plan the final defeat and participation in of Hilter and decide the shape of the post-war world. the Pacific theater. ...
World War II - OCPS TeacherPress
... • Soviet Union dismantled 1500 factories and rebuilt them in Ural Mountains • Russian women took over 50% of industrial jobs and 75% of agricultural jobs • German women were encouraged to stay home and have children – Imported 7 million “guest workers” ...
... • Soviet Union dismantled 1500 factories and rebuilt them in Ural Mountains • Russian women took over 50% of industrial jobs and 75% of agricultural jobs • German women were encouraged to stay home and have children – Imported 7 million “guest workers” ...
battle of iwo jima
... that does not want them to have peace ... It is the people who are at home both nowhere and everywhere, who do not have anywhere a soil on which they have grown up, but who live in Berlin today, in Brussels tomorrow, Paris the day after that, and then again in Prague or Vienna or London, and who fee ...
... that does not want them to have peace ... It is the people who are at home both nowhere and everywhere, who do not have anywhere a soil on which they have grown up, but who live in Berlin today, in Brussels tomorrow, Paris the day after that, and then again in Prague or Vienna or London, and who fee ...
Chapter 17 Section 2 The War for Europe and North Africa
... was killed in 1945 (p. 573) – Germany would continue to try to regain Italy until their own surrender years later Q# 9 Hitler and his wife killed themselves in Berlin in April of 1945 rather than witnessing the “disgrace of capitulation (surrender).” Eisenhower accepted unconditional surrender calle ...
... was killed in 1945 (p. 573) – Germany would continue to try to regain Italy until their own surrender years later Q# 9 Hitler and his wife killed themselves in Berlin in April of 1945 rather than witnessing the “disgrace of capitulation (surrender).” Eisenhower accepted unconditional surrender calle ...
FinalSolution11
... Extermination 6 million Jews were exterminated during the whole Holocaust by Nazis and Germans. The Holocaust took place between 1932 – 1945. During the Holocaust there were a lot of events, decisions, motivations, and realities which permits almost a historical understanding. To a large exte ...
... Extermination 6 million Jews were exterminated during the whole Holocaust by Nazis and Germans. The Holocaust took place between 1932 – 1945. During the Holocaust there were a lot of events, decisions, motivations, and realities which permits almost a historical understanding. To a large exte ...
Civilians at War Video Key
... * On August 15, 1945, Japan surrendered unconditionally. WWII was finally officially over. * At Nuremburg, war crimes trials now made it clear to the world what Hitler had tried to accomplish. For the first time ever, national leaders were held responsible for their aggressions; the murder and ensl ...
... * On August 15, 1945, Japan surrendered unconditionally. WWII was finally officially over. * At Nuremburg, war crimes trials now made it clear to the world what Hitler had tried to accomplish. For the first time ever, national leaders were held responsible for their aggressions; the murder and ensl ...
World War II: The Road to War - Miami Beach Senior High School
... other but want to secure their border first. Hitler knows he will someday attack the he Soviet Union but does not wish to yet. Stalin knows he will be attacked & is just buying time as he attempts to rebuild Russia & prepare for war. ...
... other but want to secure their border first. Hitler knows he will someday attack the he Soviet Union but does not wish to yet. Stalin knows he will be attacked & is just buying time as he attempts to rebuild Russia & prepare for war. ...
chapter 27 the european crisis: world war ii
... 6. How did the Nazis attempt to establish a new Order in Europe after their military victories? What were the results of their efforts? 7. Discuss the “Final Solution.” What was it? Who was responsible for it? How did it work? How committed was the entire German war machine to this murderous campaig ...
... 6. How did the Nazis attempt to establish a new Order in Europe after their military victories? What were the results of their efforts? 7. Discuss the “Final Solution.” What was it? Who was responsible for it? How did it work? How committed was the entire German war machine to this murderous campaig ...
WWII ppt
... in the East and the Occupation of Europe • Hitler’s ultimate goal • Nazi-Soviet pact as a matter of convenience for Hitler • On June 22, 1941, Hitler authorized Operation Barbarossa—the invasion of the Soviet Union • Stalin’s purges had gotten rid of Russia’s most capable commanders ...
... in the East and the Occupation of Europe • Hitler’s ultimate goal • Nazi-Soviet pact as a matter of convenience for Hitler • On June 22, 1941, Hitler authorized Operation Barbarossa—the invasion of the Soviet Union • Stalin’s purges had gotten rid of Russia’s most capable commanders ...
Propaganda Analysis of Capra
... and invade Poland. Appeasement attempts are made, but it is soon evident that the curtain is about to rise on World War II. USA, 1943, B&W, 41 minutes. ...
... and invade Poland. Appeasement attempts are made, but it is soon evident that the curtain is about to rise on World War II. USA, 1943, B&W, 41 minutes. ...
Dictators Threaten World Peace
... grew out of ancient and ordinary human emotions- anger and arrogance and bigotry, victimhood and the lust for power. • And it ended because other human qualitiescourage and perseverance and selflessness, faith, leadership, and the hunger for freedomcombined with unimaginable brutality to change the ...
... grew out of ancient and ordinary human emotions- anger and arrogance and bigotry, victimhood and the lust for power. • And it ended because other human qualitiescourage and perseverance and selflessness, faith, leadership, and the hunger for freedomcombined with unimaginable brutality to change the ...
World_War_II_noteshrink_and_images
... agreement which promised “peace in our times.” Historians now agree that by signing this document Chamberlain was merely appeasing Hitler. ...
... agreement which promised “peace in our times.” Historians now agree that by signing this document Chamberlain was merely appeasing Hitler. ...
World War II and the Post
... Adolf Hitler promised to make Germany a strong nation again. He declared that there would be jobs and food for everyone. He told the people that they were superior to other Europeans, and that other countries shouldn’t tell them what to do. Many Germans liked what he had to say because he placed bla ...
... Adolf Hitler promised to make Germany a strong nation again. He declared that there would be jobs and food for everyone. He told the people that they were superior to other Europeans, and that other countries shouldn’t tell them what to do. Many Germans liked what he had to say because he placed bla ...
File
... the decade, the United States was on the brink of war. Japan’s decision to bomb Pearl Harbor pushed us over the brink and dragged the U.S. into the conflict. During World War II, America experienced changes that reached into virtually every corner of the country. The conflict revamped the economy an ...
... the decade, the United States was on the brink of war. Japan’s decision to bomb Pearl Harbor pushed us over the brink and dragged the U.S. into the conflict. During World War II, America experienced changes that reached into virtually every corner of the country. The conflict revamped the economy an ...
Barrington 220
... wounded or went missing during the Battle of Normandy. This figure includes over 209,000 Allied casualties, with nearly 37,000 dead amongst the ground forces and a further 16,714 deaths amongst the Allied air forces. Of the Allied casualties, 83,045 were from 21st Army Group (British, Canadian and P ...
... wounded or went missing during the Battle of Normandy. This figure includes over 209,000 Allied casualties, with nearly 37,000 dead amongst the ground forces and a further 16,714 deaths amongst the Allied air forces. Of the Allied casualties, 83,045 were from 21st Army Group (British, Canadian and P ...
Chapter 11 Test
... The act of assembling and preparing for war. _____ 1.5 million people died when this city was under siege for 900 days. ____ The man who became president of the U.S. after Roosevelt’s death. _____ Where 110 thousand Japanese-Americans were resettled and held captive. ____ Men who flew suicide missio ...
... The act of assembling and preparing for war. _____ 1.5 million people died when this city was under siege for 900 days. ____ The man who became president of the U.S. after Roosevelt’s death. _____ Where 110 thousand Japanese-Americans were resettled and held captive. ____ Men who flew suicide missio ...
Name: :___________Class:_____ APWH Notes| WWII and
... Jews and a corrupt governing system. During his early Nazi party origins he wrote Mein Kampf in which he details his rhetoric. During this time there was also global discrimination against Jews; even in the US Jews faced discrimination as immigrants and members of a mostly Protestant country. Hitler ...
... Jews and a corrupt governing system. During his early Nazi party origins he wrote Mein Kampf in which he details his rhetoric. During this time there was also global discrimination against Jews; even in the US Jews faced discrimination as immigrants and members of a mostly Protestant country. Hitler ...
The End of World War Two
... Germany had just suffered its worst-ever defeat at Stalingrad, and for the first time was on the defensive in Russia. The fighting culminated in a gigantic tank battle that summer in Kursk. Meanwhile, on the home front, the British were inflicting terrible damage on German industrial cities such as ...
... Germany had just suffered its worst-ever defeat at Stalingrad, and for the first time was on the defensive in Russia. The fighting culminated in a gigantic tank battle that summer in Kursk. Meanwhile, on the home front, the British were inflicting terrible damage on German industrial cities such as ...
Economy of Nazi Germany

World War I caused economic and manpower losses on Germany led to a decade of economic woes, including hyperinflation in the mid-1920s. Following the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the German economy, like those of many other western nations, suffered the effects of the Great Depression, with unemployment soaring. When Hitler became Chancellor in 1933, he introduced new efforts to improve Germany's economy, including autarky and the development of the German agricultural economy by placing tariffs on agricultural imports.However, these changes—including autarky and nationalization of key industries—had a mixed record. By 1938, unemployment was practically extinct. Wages increased by 10.9% in real terms during this period. However, nationalization and a cutting off of trade meant rationing in key resources like poultry, fruit, and clothing for many Germans.In 1934 Hjalmar Schacht, the Reich Minister of Economics, introduced the Mefo bills, allowing Germany to rearm without spending Reichmarks but instead pay industry with Reichmarks and Mefo bills (Government IOU's) which they could trade with each other. Between 1933 and 1939, the total revenue was 62 billion marks, whereas expenditure (at times made up to 60% by rearmament costs) exceeded 101 billion, thus creating a huge deficit and national debt (reaching 38 billion marks in 1939) coinciding with the Kristallnacht and intensified persecutions of Jews and the outbreak of the war.