Economics
... France ended their policy of appeasement. They warned Hitler that an invasion of Poland would mean war. Hitler, however, had stopped believing Britain and France. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Britain and France declared war on Germany two days later. Germany quickly overran Poland u ...
... France ended their policy of appeasement. They warned Hitler that an invasion of Poland would mean war. Hitler, however, had stopped believing Britain and France. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Britain and France declared war on Germany two days later. Germany quickly overran Poland u ...
Economics
... France ended their policy of appeasement. They warned Hitler that an invasion of Poland would mean war. Hitler, however, had stopped believing Britain and France. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Britain and France declared war on Germany two days later. Germany quickly overran Poland u ...
... France ended their policy of appeasement. They warned Hitler that an invasion of Poland would mean war. Hitler, however, had stopped believing Britain and France. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Britain and France declared war on Germany two days later. Germany quickly overran Poland u ...
Economics - Schoolwires
... France ended their policy of appeasement. They warned Hitler that an invasion of Poland would mean war. Hitler, however, had stopped believing Britain and France. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Britain and France declared war on Germany two days later. Germany quickly overran Poland u ...
... France ended their policy of appeasement. They warned Hitler that an invasion of Poland would mean war. Hitler, however, had stopped believing Britain and France. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Britain and France declared war on Germany two days later. Germany quickly overran Poland u ...
AKS 47: World War II - Brookwood High School
... violent attack on Jewish communities all over Germany ...
... violent attack on Jewish communities all over Germany ...
World War II Timeline 1. 1931 Japan Seizes the
... rebuild Germany as a military power. France and Great Britain waffled uncertainly as Germany pulled out of the League of Nations 6. *1934 German begins to rearm 7. 1936 Rhineland 8. 1935-1937 Neutrality Acts 9. 1938 Anschluss 10. September 1938 Munich Conference 11. March 1939 Czechoslovakia 12. *Ma ...
... rebuild Germany as a military power. France and Great Britain waffled uncertainly as Germany pulled out of the League of Nations 6. *1934 German begins to rearm 7. 1936 Rhineland 8. 1935-1937 Neutrality Acts 9. 1938 Anschluss 10. September 1938 Munich Conference 11. March 1939 Czechoslovakia 12. *Ma ...
Class Notes_PDF - Jessamine County Schools
... easy annexation of Austria, Hitler set his eyes on uniting some 3 million Germanspeaking people living in the resource rich, mountainous western region of Czechoslovakia, called the Sudetenland. Hitler charged that the Czechs were abusing Germans in the Sudetenland, and began putting troops on the ...
... easy annexation of Austria, Hitler set his eyes on uniting some 3 million Germanspeaking people living in the resource rich, mountainous western region of Czechoslovakia, called the Sudetenland. Hitler charged that the Czechs were abusing Germans in the Sudetenland, and began putting troops on the ...
22_The Consequences of World War II
... ensure a future invasion from the west would not happen again. Russia had been invaded three times from the west through Poland – Napoleon, World War I, and World War II. Communist influence was also spreading into Southeast Asia and the Chinese Communists, led by Mao, were fighting a Civil War agai ...
... ensure a future invasion from the west would not happen again. Russia had been invaded three times from the west through Poland – Napoleon, World War I, and World War II. Communist influence was also spreading into Southeast Asia and the Chinese Communists, led by Mao, were fighting a Civil War agai ...
whsem2studyguide
... 13.) Why wasn’t Russia at the Versailles Conference? 14.)Who were the Big Four? 15.)What land did Russia lose? 16.)Why were some Americans against the Treaty and the League? 17.)What did people in Africa and Asia think? 18.) How was the mandate system like European colonialism? 19) Be able to identi ...
... 13.) Why wasn’t Russia at the Versailles Conference? 14.)Who were the Big Four? 15.)What land did Russia lose? 16.)Why were some Americans against the Treaty and the League? 17.)What did people in Africa and Asia think? 18.) How was the mandate system like European colonialism? 19) Be able to identi ...
The Coming of World War II. 1937-1939
... of the war against Japan. Agreement was reached to divide Germany into four zones, separately occupied by Russia, the United States, Britain, and France. It was assumed that a permanently divided, disarmed, and de-industrialized Germany could never again wage aggressive war. (21) Stalin also agreed ...
... of the war against Japan. Agreement was reached to divide Germany into four zones, separately occupied by Russia, the United States, Britain, and France. It was assumed that a permanently divided, disarmed, and de-industrialized Germany could never again wage aggressive war. (21) Stalin also agreed ...
Section 2
... 17. What was Truman’s motivating factor in making the decision to using nuclear bomb? ...
... 17. What was Truman’s motivating factor in making the decision to using nuclear bomb? ...
The aim of this gigantic new labour mobilization is to use the rich and
... 6. The labor mobilization of the German women is of very great importance. Examining their very difficult problem and after getting thoroughly acquainted with the fundamental opinion of the Fuehrer as well as of the Reichsmarshal of the Greater German Reich and my own most careful inquiries and thei ...
... 6. The labor mobilization of the German women is of very great importance. Examining their very difficult problem and after getting thoroughly acquainted with the fundamental opinion of the Fuehrer as well as of the Reichsmarshal of the Greater German Reich and my own most careful inquiries and thei ...
rise-of-dictators-2010 - Jackson County Faculty Sites!
... “master race” that was destined to rule the world. • “Inferior races,” such as Jews, Slavs, and all nonwhites, were deemed fit only to serve the Aryans. ...
... “master race” that was destined to rule the world. • “Inferior races,” such as Jews, Slavs, and all nonwhites, were deemed fit only to serve the Aryans. ...
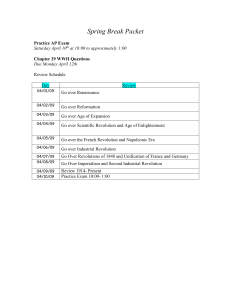
Spring Break Packet Chapter 29 WWI Questions
... What were some of the problems/inconveniences that the British and Americans on the home front had to cope with during the war? What were the similarities in how the Allied governments coped with the war at home during World War I and World War II? How was German slave labor, particularly in Eastern ...
... What were some of the problems/inconveniences that the British and Americans on the home front had to cope with during the war? What were the similarities in how the Allied governments coped with the war at home during World War I and World War II? How was German slave labor, particularly in Eastern ...
Germany Pre-World War II
... Treaty of Versailles. How did Great Britain react to this violation? How was this inaction an example of appeasement? What justification does Hitler give for world expansion? What country finally stood up to Hitler’s expansion? What demand by Hitler caused this stand? ...
... Treaty of Versailles. How did Great Britain react to this violation? How was this inaction an example of appeasement? What justification does Hitler give for world expansion? What country finally stood up to Hitler’s expansion? What demand by Hitler caused this stand? ...
World History - 20th Century - Teacher Copy
... Europe across the globe searching for new regions to colonize. It resulted in the colonizing of most of Africa and Asia. It also increased the rivalries between the nations of Europe. ...
... Europe across the globe searching for new regions to colonize. It resulted in the colonizing of most of Africa and Asia. It also increased the rivalries between the nations of Europe. ...
questions about the “varying viewpoints” - apush11
... Civil War. Other historians challenge this interpretation and cite the numerous cases of US intervention in the postWWI era as well as the economic and political agreements and treaties made with foreign governments. ...
... Civil War. Other historians challenge this interpretation and cite the numerous cases of US intervention in the postWWI era as well as the economic and political agreements and treaties made with foreign governments. ...
3rd Quarter Review
... a. By adopting a series of neutrality laws b. By constructing the Panama Canal c. By joining other democracies in a system of collective security d. By signing non-aggression pacts with totalitarian nations 61. The Munich Pact, which, according to Neville Chamberlain, meant “peace in our time,” was ...
... a. By adopting a series of neutrality laws b. By constructing the Panama Canal c. By joining other democracies in a system of collective security d. By signing non-aggression pacts with totalitarian nations 61. The Munich Pact, which, according to Neville Chamberlain, meant “peace in our time,” was ...
PART II: Checking Your Progress
... successfully prevented the fall of democratic Spain to Franco? Or might it have drawn them even earlier into a Europe-wide war? ...
... successfully prevented the fall of democratic Spain to Franco? Or might it have drawn them even earlier into a Europe-wide war? ...
Chapter 16 WORLD WAR LOOMS & Chapter 17
... Joseph Stalin came to power in 1924. He was a ruthless leader who let nothing stand in his way. Stalin focused on creating a model communist state. He wanted to stamp out private enterprise. He did away with private farms and created collectives or huge state-owned farms. The state also took over in ...
... Joseph Stalin came to power in 1924. He was a ruthless leader who let nothing stand in his way. Stalin focused on creating a model communist state. He wanted to stamp out private enterprise. He did away with private farms and created collectives or huge state-owned farms. The state also took over in ...
WW2 Notes 2015 - Boone County Schools
... during the war and many who returned came back broken men. This caused the WWI generation to gain the nickname “The Lost Generation.” This weariness of war continued into the 1930’s as it appeared that once again the European continent would erupt into warfare as a result of Hitler’s desire to invad ...
... during the war and many who returned came back broken men. This caused the WWI generation to gain the nickname “The Lost Generation.” This weariness of war continued into the 1930’s as it appeared that once again the European continent would erupt into warfare as a result of Hitler’s desire to invad ...
WW2 Packet
... over 12 million people in Europe, 6 million of which were targeted above all others, the Jewish race of Europe. So why did the German people elect Adolf Hitler in 1933 as Reich Chancellor? Because when the human race becomes so desperate for change, they are willing to try anything thinking that som ...
... over 12 million people in Europe, 6 million of which were targeted above all others, the Jewish race of Europe. So why did the German people elect Adolf Hitler in 1933 as Reich Chancellor? Because when the human race becomes so desperate for change, they are willing to try anything thinking that som ...
Hitler`s Lightning War Close Read
... struggle. However, Finland fought back. In March 1940, Finland was forced to surrender. For seven months after Poland fell to the Germans, Europe was calm. France and Britain got their armies ready. They waited for Hitler’s next move. The Fall of France; The Battle of Britain What happened when Fran ...
... struggle. However, Finland fought back. In March 1940, Finland was forced to surrender. For seven months after Poland fell to the Germans, Europe was calm. France and Britain got their armies ready. They waited for Hitler’s next move. The Fall of France; The Battle of Britain What happened when Fran ...
Ch 25 - wueschner.org
... America's task was far more complex and backbreaking than during World War I. We had to feed, clothe, and arm ourselves, as well as transport our forces to regions as far separated as Britain and Burma. More than that, we had to send a vast amount of food and munitions to our hardpressed allies, wh ...
... America's task was far more complex and backbreaking than during World War I. We had to feed, clothe, and arm ourselves, as well as transport our forces to regions as far separated as Britain and Burma. More than that, we had to send a vast amount of food and munitions to our hardpressed allies, wh ...
America: A Concise History 3e
... America's task was far more complex and backbreaking than during World War I. We had to feed, clothe, and arm ourselves, as well as transport our forces to regions as far separated as Britain and Burma. More than that, we had to send a vast amount of food and munitions to our hardpressed allies, wh ...
... America's task was far more complex and backbreaking than during World War I. We had to feed, clothe, and arm ourselves, as well as transport our forces to regions as far separated as Britain and Burma. More than that, we had to send a vast amount of food and munitions to our hardpressed allies, wh ...
New Order (Nazism)
The New Order (German: Neuordnung) or the New Order of Europe (German: Neuordnung Europas) was the political order which Nazi Germany wanted to impose on the conquered areas under its dominion. The establishment of the New Order had already begun long before the start of World War II, but was publicly proclaimed by Adolf Hitler in 1941:The year 1941 will be, I am convinced, the historical year of a great European New Order.Among other things, it entailed the creation of a pan-German racial state structured according to Nazi ideology to ensure the supremacy of an Aryan-Nordic master race, massive territorial expansion into Eastern Europe through its colonization with German settlers, the physical annihilation of the Jews and others considered to be ""unworthy of life"", and the extermination, expulsion, or enslavement of most of the Slavic peoples and others regarded as ""racially inferior"". Nazi Germany’s desire for aggressive territorial expansionism was one of the most important causes of World War II.Historians are still divided as to its ultimate goals, some believing that it was to be limited to Nazi German domination of Europe, while others maintain that it was a springboard for eventual world conquest and the establishment of a world government under German control.The Führer gave expression to his unshakable conviction that the Reich will be the master of all Europe. We shall yet have to engage in many fights, but these will undoubtedly lead to most wonderful victories. From there on the way to world domination is practically certain. Whoever dominates Europe will thereby assume the leadership of the world.