AP European History
... 1936 Rome-Berlin Axis 1936 Spanish Civil War March 1938 Annexation of Austria September 1938 Munich Conference March 1939 German occupation of Czechoslovakia August 1939 Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression Pact September 1, 1939 – German Invasion of Poland 2. Describe the Battle of Britain and analyze its imp ...
... 1936 Rome-Berlin Axis 1936 Spanish Civil War March 1938 Annexation of Austria September 1938 Munich Conference March 1939 German occupation of Czechoslovakia August 1939 Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression Pact September 1, 1939 – German Invasion of Poland 2. Describe the Battle of Britain and analyze its imp ...
The Deepening of the European Crisis: World War II
... of the Treaty of Versailles without serious British and French opposition. Hitler had come to believe, based on their responses to his early actions, that both states wanted to maintain the international status quo, but without using force. Consequently, he decided to announce publicly what had been ...
... of the Treaty of Versailles without serious British and French opposition. Hitler had come to believe, based on their responses to his early actions, that both states wanted to maintain the international status quo, but without using force. Consequently, he decided to announce publicly what had been ...
World War II - Teacher Pages
... – Reached city in Sept., but Soviets refused to give up – By Nov. Germans were in trouble • Running short on supplies and unable to deal with harsh winter ...
... – Reached city in Sept., but Soviets refused to give up – By Nov. Germans were in trouble • Running short on supplies and unable to deal with harsh winter ...
World War II - Union High School
... merciless bombing of Poland’s capital, Warsaw. France and Great Britain declared war on Germany on September 3. But Poland fell some time before those nations could make any military response. After his victory, Hitler annexed the western half of Poland. That region had a large German population. Th ...
... merciless bombing of Poland’s capital, Warsaw. France and Great Britain declared war on Germany on September 3. But Poland fell some time before those nations could make any military response. After his victory, Hitler annexed the western half of Poland. That region had a large German population. Th ...
From Appeasement to War 16sect 1
... Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain into believing that he only wanted peace. ...
... Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain into believing that he only wanted peace. ...
Why ex-Kings are Dangerous Text : Why ex
... even among the deprived as someone who was concerned about them (he never actually did anything) who asked only for their devotion. Hitler had to work hard to get comparable status. It is understandable Edward liked what he saw in Germany but had no desire to be a stooge like the King of Italy under ...
... even among the deprived as someone who was concerned about them (he never actually did anything) who asked only for their devotion. Hitler had to work hard to get comparable status. It is understandable Edward liked what he saw in Germany but had no desire to be a stooge like the King of Italy under ...
Newsletter 454 - Adelaide Institute
... context. If England would have been serious about protecting the territorial integrity of Poland, they would not only have declared war on Germany, but also on Stalin’s Soviet Union. Both countries divided Poland between themselves as a result of the Hitler-Stalin Pact. At the end of World War Two, ...
... context. If England would have been serious about protecting the territorial integrity of Poland, they would not only have declared war on Germany, but also on Stalin’s Soviet Union. Both countries divided Poland between themselves as a result of the Hitler-Stalin Pact. At the end of World War Two, ...
here
... Nazi policies towards the Jews, including boycotts, removal from jobs, concentration camps from 1933 to 1939, Nuremberg Laws of 1935 and the Night of Broken Glass (Kristallnacht) in 1938 The impact of these Nazi policies on the lives of Jews QUESTION 3 Nazi Policies and Actions in Europe, 1933–1941 ...
... Nazi policies towards the Jews, including boycotts, removal from jobs, concentration camps from 1933 to 1939, Nuremberg Laws of 1935 and the Night of Broken Glass (Kristallnacht) in 1938 The impact of these Nazi policies on the lives of Jews QUESTION 3 Nazi Policies and Actions in Europe, 1933–1941 ...
World War II, 1939–1945 Previewing Main Ideas
... merciless bombing of Poland’s capital, Warsaw. France and Great Britain declared war on Germany on September 3. But Poland fell some time before those nations could make any military response. After his victory, Hitler annexed the western half of Poland. That region had a large German population. Th ...
... merciless bombing of Poland’s capital, Warsaw. France and Great Britain declared war on Germany on September 3. But Poland fell some time before those nations could make any military response. After his victory, Hitler annexed the western half of Poland. That region had a large German population. Th ...
Chapter 14
... According to Hossbach’s notes, Hitler believed there was just one possible answer. “Germany’s problem,” Hossbach wrote, “could only be solved by means of force.” Germany needed to act quickly. Within a few years, the powerful German military, newly rebuilt after its post–World War I destruction, wou ...
... According to Hossbach’s notes, Hitler believed there was just one possible answer. “Germany’s problem,” Hossbach wrote, “could only be solved by means of force.” Germany needed to act quickly. Within a few years, the powerful German military, newly rebuilt after its post–World War I destruction, wou ...
World at War- Defensive-Offensive Wk1 st. ed.
... The Allies invaded the coast of Normandy on June 6, 1944, and after a costly battle headed toward Paris. The Germans retreated and France was soon free. An intensive bombing campaign crippled Germany’s industries and devastated many of its cities. Because Churchill and Roosevelt needed Stalin’s help ...
... The Allies invaded the coast of Normandy on June 6, 1944, and after a costly battle headed toward Paris. The Germans retreated and France was soon free. An intensive bombing campaign crippled Germany’s industries and devastated many of its cities. Because Churchill and Roosevelt needed Stalin’s help ...
01 The March to War
... Chamberlain returns to Britain with the agreement and says he has secured "peace in our time." This is the high point of the policy of "appeasement." Churchill rightly pointed out that it made a great deal more sense militarily to fight for Czechoslovakia than it did for Poland. The conditions for w ...
... Chamberlain returns to Britain with the agreement and says he has secured "peace in our time." This is the high point of the policy of "appeasement." Churchill rightly pointed out that it made a great deal more sense militarily to fight for Czechoslovakia than it did for Poland. The conditions for w ...
document
... -Britain wanted to attack up from North Africa through Italy while America wanted to go through France -The Allies agreed to follow Britain's plan; General Eisenhower led the attack -Germany was pushed out of Africa by May 1943 -Roosevelt and Churchill met at the Casablanca Conference -They decided ...
... -Britain wanted to attack up from North Africa through Italy while America wanted to go through France -The Allies agreed to follow Britain's plan; General Eisenhower led the attack -Germany was pushed out of Africa by May 1943 -Roosevelt and Churchill met at the Casablanca Conference -They decided ...
File
... According to Hossbach’s notes, Hitler believed there was just one possible answer. “Germany’s problem,” Hossbach wrote, “could only be solved by means of force.” Germany needed to act quickly. Within a few years, the powerful German military, newly rebuilt after its post–World War I destruction, wou ...
... According to Hossbach’s notes, Hitler believed there was just one possible answer. “Germany’s problem,” Hossbach wrote, “could only be solved by means of force.” Germany needed to act quickly. Within a few years, the powerful German military, newly rebuilt after its post–World War I destruction, wou ...
Chapter 11: World War II, 1939-1945
... leadership,” and forge a new domestic unity. All Germans would need to realize that “only a struggle can save us and that everything else must be subordinated to this idea.” The youth especially would have to be trained and their wills strengthened “to fight with all means.” Hitler went on to say th ...
... leadership,” and forge a new domestic unity. All Germans would need to realize that “only a struggle can save us and that everything else must be subordinated to this idea.” The youth especially would have to be trained and their wills strengthened “to fight with all means.” Hitler went on to say th ...
End in Europe
... German armies defeated France in 6 weeks and forced the British to evacuate their troops from Belgium. The U.S. feared Britain would quickly sign a treaty that gave Hitler control of Europe. ...
... German armies defeated France in 6 weeks and forced the British to evacuate their troops from Belgium. The U.S. feared Britain would quickly sign a treaty that gave Hitler control of Europe. ...
WORLD WAR II
... •US warns Japan that economic SANCTIONS (economic restrictions to enforce laws) will be used unless Japan w/draws to old borders ...
... •US warns Japan that economic SANCTIONS (economic restrictions to enforce laws) will be used unless Japan w/draws to old borders ...
World War II Lecture Slides
... concentration camps throughout Europe -extermination camps were built in many concentration camps, mostly in Poland -thousands killed everyday in these camps ...
... concentration camps throughout Europe -extermination camps were built in many concentration camps, mostly in Poland -thousands killed everyday in these camps ...
World War II Section 1 - Geneva Area City Schools
... -Stalin worried about Germany military expansion -1939 British and French officials discussed a possible alliance with the Soviets, but Stalin had lost faith in their ability to protect his country from the Germans. He was secretly negotiating with the Germans. -NONAGGRESSION PACT: signed between U. ...
... -Stalin worried about Germany military expansion -1939 British and French officials discussed a possible alliance with the Soviets, but Stalin had lost faith in their ability to protect his country from the Germans. He was secretly negotiating with the Germans. -NONAGGRESSION PACT: signed between U. ...
Chapter 17 Section 1
... • The democracies accepted that appeasement had failed. They pledged to protect Poland. • In August 1939, Hitler and Stalin announced the Nazi-Soviet Pact. This was a shaky alliance, since neither Hitler nor Stalin trusted the other. ...
... • The democracies accepted that appeasement had failed. They pledged to protect Poland. • In August 1939, Hitler and Stalin announced the Nazi-Soviet Pact. This was a shaky alliance, since neither Hitler nor Stalin trusted the other. ...
Outreach Educator Resource Guide
... a. Pearl Harbor – On December 7, 1941, Japanese naval and air forces attacked Pearl Harbor, an American naval base in Hawaii, along with other Allied bases in the Pacific and Asia. United States declared war on Japan on December 8, 1941. Three days later Germany and Italy declared war on the United ...
... a. Pearl Harbor – On December 7, 1941, Japanese naval and air forces attacked Pearl Harbor, an American naval base in Hawaii, along with other Allied bases in the Pacific and Asia. United States declared war on Japan on December 8, 1941. Three days later Germany and Italy declared war on the United ...
The Treaty of Versailles
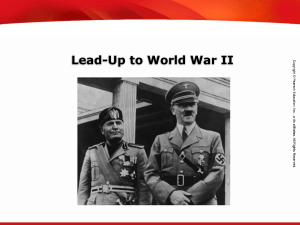
... it was clear that Germany was carving out its own empire and Italy was not. To compensate for this, Mussolini took over Albania on Good Friday 1939. To him, this was a sign of Italy’s expanding power in Europe. King Victor Emmanuel was offered the title of King of Albania. Italian propaganda made a ...
... it was clear that Germany was carving out its own empire and Italy was not. To compensate for this, Mussolini took over Albania on Good Friday 1939. To him, this was a sign of Italy’s expanding power in Europe. King Victor Emmanuel was offered the title of King of Albania. Italian propaganda made a ...
New Order (Nazism)
The New Order (German: Neuordnung) or the New Order of Europe (German: Neuordnung Europas) was the political order which Nazi Germany wanted to impose on the conquered areas under its dominion. The establishment of the New Order had already begun long before the start of World War II, but was publicly proclaimed by Adolf Hitler in 1941:The year 1941 will be, I am convinced, the historical year of a great European New Order.Among other things, it entailed the creation of a pan-German racial state structured according to Nazi ideology to ensure the supremacy of an Aryan-Nordic master race, massive territorial expansion into Eastern Europe through its colonization with German settlers, the physical annihilation of the Jews and others considered to be ""unworthy of life"", and the extermination, expulsion, or enslavement of most of the Slavic peoples and others regarded as ""racially inferior"". Nazi Germany’s desire for aggressive territorial expansionism was one of the most important causes of World War II.Historians are still divided as to its ultimate goals, some believing that it was to be limited to Nazi German domination of Europe, while others maintain that it was a springboard for eventual world conquest and the establishment of a world government under German control.The Führer gave expression to his unshakable conviction that the Reich will be the master of all Europe. We shall yet have to engage in many fights, but these will undoubtedly lead to most wonderful victories. From there on the way to world domination is practically certain. Whoever dominates Europe will thereby assume the leadership of the world.