* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II Section 1 - Geneva Area City Schools
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
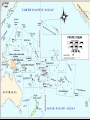
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
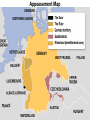
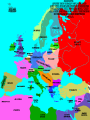
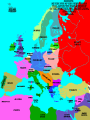
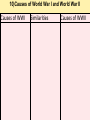
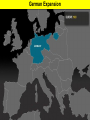
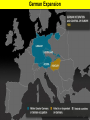
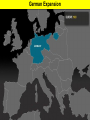
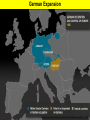
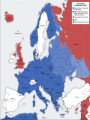
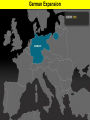
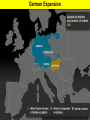
World War II Section 1 14-1 WorldCh War II Learning Goal/Content Statement Section 1 • Explain how the consequences of World War I and the worldwide depression set the stage for the rise of totalitarianism, aggressive Axis expansion and the policy of appeasement which in turn led to World War II. World War II • • • • • • • • • Ch 14-1 Vocabulary Appeasement Winston Churchill: Axis Powers:. nonaggression pact: blitzkrieg Allies Battle of Britain: (1940) Hideki Tojo Isolationism: Section 1 World War II Ch 14-1 vocabulary Section 1 • Appeasement : giving in to aggressive demands in order to avoid war. • -Italy/Ethiopia • -Japan/Manchuria, China • -Germany/Rhineland, Austria, Sudetenland, Czechoslovakia, Poland p.438 • Winston Churchill: (1874-1965) British prime minister; he opposed the policy of appeasement and led Great Britain through WWII. • Axis Powers: the alliance of Germany, Italy, and Japan in WWII. • nonaggression pact: an agreement between nations to not attack one another. • World War II Ch 14-1 vocabulary Section 1 • blitzkrieg: a German “lightning war”; a fast, forceful style of fighting used by Germans in WWII • Allies: the alliance of Britain, France, and Russia in WWII; joined by the United States after the Japanese bombing of Pearl Harbor in 1941. • Battle of Britain: (1940) three month air battle between Germany and Great Britain fought over Great Britain during WWII; Britain’s victory forestalled a German invasion. • Hideki Tojo: (1884-1948) Japanese nationalist and general; he took control of Japan during WWII. He was later tried and executed for war crimes. • Isolationism: staying out of the affairs and wars of other nations; the position initially held by the United States at the Beginning of WWII. Still supported the Allied forces. World War II Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Section 1 World War II Section 1 1)World How did feel? Warthe II Treaty of Versailles make Germans Section 1 What was lebensraum? Who was unwilling to do what? • -severely damaged the German economy • -terms of the treaty left Germans feeling humiliated • -Lebensraum (LAY-buhnz-rowm): Hitler wanted nation to have lebensraum or, “living space” in which the German people could grow and prosper. • -Hitler wanted Germany to have more territory. • Wanted to unite all German-speaking people(Nationalism). • -Germany’s neighbors were aware of the threat of German expansion. • -no one was willing to fight over Hitler’s words. 2) What What World Wardid II Hitler begin to do in secret? Section 1 did this violate? • -Hitler realized nobody wanted to fight over his words or actions • -became chancellor in 1933 • -Began to secretly rebuild the German military which had been greatly weakened post WWI • -violations of Treaty of Versailles RESENTMENT!!! • -Hitler signed treaty in 1935 allowing to build submarines and warships in the name of stopping the spread of communism; actually planning to build a mighty German empire. 3)What World does War IIHitler do in 1936? What did this violate? Section 1How do Britain and France react? Hitler grows what? • -he was ready to take more direct action • -March: sent a small armed force into the Rhineland this was territory that bordered France. • -Hitler claimed to be reacting to a recent French-Soviet military agreement , which he said threatened Germany. • -violates Treaty of Versailles!!!; which required Germany to stay out of that zone. • -Britain and France complained about Germany violating the treaty • -Britain and France took no direct action German troops remained in the Rhineland and Hitler grew bolder. World War II 4.Annexing Austria Aggressive moves Section 1 Hitler’s demands • Europeans eager to avoid war • Hitler demanded Austrian officials accept annexation • Hitler plotted his moves (Anschluss): officially join another country • Target-Austria • German-speaking country • Initial Austrian resistance • Hitler’s birthplace • Britain and France did nothing • Nazi supporters in Austria • March 1938-unopposed German forces take over Austria • Austria agreed to annexation because they knew Germany could take over forcefully if needed. World War II 5.Threats to Czechoslovakia Section 1 Another German-speaking population • Sudetenland eager to be a part of Germany. German speaking. • Hitler threatened the Czech government. Encouraged Czech citizens to revolt. • Czechs prepared for war Avoiding conflict: Munich Conference • September 1938—meeting in Munich: Munich Agreement: Hitler says no more territorial demands. March 1939 Hitler takes over rest of Czechoslovakia. • Chamberlain (British) and Daladier (French) agreed not to block Hitler. • Czechs had no representatives at the Munich Conference. • British and French were more interested in avoiding conflict. Don’t block Hitler. • Czechs had no support: would fight Germany alone. Accept Germany’s terms. Policy of appeasement • Appeasement—giving in to aggressive demands in order to avoid war • Winston Churchill opposed the policy • “We have achieved peace for our time” according to Chamberlain. Resigns PM 5/1940 • Churchill blasts Chamberlain. “Why not make a stand (against Hitler) while there is still a good company of united, very powerful countries?” World War II Appeasement Map Section 1 World War II Section 1 World War II Section 1 6)Where else World War II did totalitarian regimes emerge? Section 1 They showed a disregard for what? • -Italy and Japan • -Showed disregard for the opinions of other nations NATIONALISM World War II Section 1 7) What did Germany, Italy, and Japan form? • -formed a series of military alliances • -Anti-Comintern Pact (1936): vs communists • -AXIS POWERS (1939) World War II October 25, 1936 Section 1 8) Why War were II Germany and Italy seen as natural enemies to the1Soviet World Section Union? What happens that is surprising? • • • • • • • • • -1930’s Fascist Germany and Italy strongly opposed the Communist Soviet Union. Anti-Comintern Pact 1936. -fascism and communism were very different although both totalitarian. -fascism was based in extreme nationalism and loyalty to the state. -communism sought international change and a classless society. State would wither away. -Stalin worried about Germany military expansion -1939 British and French officials discussed a possible alliance with the Soviets, but Stalin had lost faith in their ability to protect his country from the Germans. He was secretly negotiating with the Germans. -NONAGGRESSION PACT: signed between U.S.S.R. and Germany -allowed further German aggression in Europe. Signed 8/1939. (Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact) -secret section of the pact recognized each side’s right to take territory in Eastern Europe, including dividing Poland into Soviet and German areas -News of the pact shocked Britain and France, hoped the Soviets would support themWWI Russia on the side of The Allies. 9)What happens on September 1, 1939? How was Poland World War II Section 1 defenseless? What happens on Sept. 3, 1939? • -Germany launches an attack on Poland; wants their land APPEASEMENT FAILS! • -*blitzkrieg : “lightning war”, it emphasized speed and close coordination between planes in the air and fast-moving forces on the ground • -Polish air force destroyed quickly. • -Poland countryside offered few natural barriers to slow the blitzkrieg. Taken over within a month. • -Sept. 3, 1939: Great Britain and France declare war on Germany in response to attack on Poland. • Two weeks later U.S.S.R invades eastern Poland. World War II Section 1 World War II Blitzkrieg Section 1 World War II Section 1 World War II WWI Tanks Section 1 World War II WWI Tanks Section 1 10)Causes of World War I and World War1II World War II Section Causes of WWI Similarities Causes of WWII 10)Causes of World War I and World War1II World War II Section Causes of WWI Similarities Causes of WWII -Rivalries due to Militarism imperialism Alliances: Axis Powers and -military alliances Central Powers vs Triple Alliance Allied Powers and Triple Imperialism: Entente Imperialism vs. Appeasement -assassination of Nationalism Franz Ferdinand Serbia vs “Greater Germany” -Treaty of Versailles -Rise of Dictators -Era of Appeasement *Japan and Manchuria *Italy and Ethiopia, and Albania *Germany and Rhineland, Sudetenland, Austria Czechoslovakia, and finally Poland 14-1 WorldCh War II Learning Goal/Content Statement Section 1 • Explain how the consequences of World War I and the worldwide depression set the stage for the rise of totalitarianism, aggressive Axis expansion and the policy of appeasement which in turn led to World War II. World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 11) What happens during combat in France and Britain? List 2 facts for each. World War II Section 1 Sept.1939-March 1940 *Sitzkrieg: phony war. Nothing happens Winter 1939-40. April 1940 Hitler invaded Denmark and Norway. Lightly defended. » This improved Germany’s access to the Atlantic. » Both countries fell with little resistance. May 1940 Germans invaded France. » Germans conquered the Netherlands and stormed into Belgium. » Belgian, British, and French troops tried to stop the Germans in Belgium. » By early June the Germans had trapped hundreds of thousands of Allied soldiers at the French port of Dunkirk. » Meanwhile, German forces attacked France through the Ardennes. The Maginot Line had been bypassed. June 1940 France surrendered to Germany and Italy. » The unoccupied part of France was known as Vichy France. » Many French leaders, including Charles de Gaulle, fled to Great Britain to organize resistance to German and Vichy control of France. **Battle of Britain**: Hitler attempts to invade Britain with Luftwaffe from June-Sept. 1940. Invasion unsuccessful. World War II Section 1 World War II Maginot Line Section 1 World War II Section 1 World War II Section 1 12)What in June of 1941? Who does World Warhappens II Section 1 this bring into the war? • • • • • • • -Hitler broke the non-aggression pact with Stalin and sent 3 million troops into the Soviet Union. -Brings Russia into the war. -at first blitzkrieg was very effective -Soviet Army was large in numbers but ill prepared for war -Germans had pushed deep into Soviet territory, but had not managed to reach Russia’s capital of Leningrad by autumn of 1941. -Germans had not prepared for the extremely harsh temperatures of the Soviet winter. -Germans lacked warm clothing and their vehicles and equipment worked poorly in the cold. -Soviets begin to fight back in winter of 1941-1942 Germany’s great blunder. World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 UNDER AXIS CONTROL World WarEUROPE II Section 1 World War II Section 1 World War II Section 1 13)What Japan? World War II had Americans banned to Section 1 • -Japan continued territorial expansion moved into French Indochina (Vietnam). • -area was rich in oil, rubber, and other natural resources. • -WHY WAS U.S. NERVOUS ABOUT PACIFIC?Hawaii and the Philippines. Worried about U.S. and British territories in the Pacific. • -Nervous American officials banned the sale of oil to Japan; move was designed to slow the Japanese war machine. • -Peace talks continued between Japan and U.S. but Japan planned for war World War II Section 1 World War II Section 1 13)What happens on December 7, 1941? List at World War II Section 1 least 3 facts. • • • • • • • • -U.S. saw treaty between Germany and Japan as cause for concern Japan initiates surprise attack on U.S. Navy Pacific Fleet Attack lasted two hours December 7, 1941 Fighters and bombers launched from carriers Raid a success Major destruction Heavy casualties – 2,400 dead – 200 planes gone – Eight battleships sunk – Pacific fleet decimated could have pushed further inland • Three carriers survived • -APPEASEMENT Japan thought all would be forgiven and they would get their oil back. 14) What America’s Response to Pearl Harbor? World Warwas II Section 1 • -had a profound impact • -prior to that point most Americans believed U.S. should stay out of the war *Isolationism • Prior to this point, provided financial support to Allies • -Isolationism common because many questioned what Allied victory in WWI had actually accomplishedMERCHANTS OF DEATH • -Did WWI accomplish anything??? • -On December 8, 1941 U.S. declares war on Japan. Three days later Germany and Italy declare war on U.S. World War II Section 1 World War II Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1 World War II German Expansion Section 1