The Underlying Causes of the Cold War
... they viewed each other. The western ideology was based on free market capitalism, individualism and personal rights. The United States, Britain, France, Canada, and most western European countries practiced capitalism’s free market ideal which called for as little government intervention as possible ...
... they viewed each other. The western ideology was based on free market capitalism, individualism and personal rights. The United States, Britain, France, Canada, and most western European countries practiced capitalism’s free market ideal which called for as little government intervention as possible ...
Chapter 16
... • Following Hitler’s invasion of the Sudetenland, four world leaders met to discuss German aggression • Neville Chamberlain (Great Britain) • Edward Daladier (France) • Benito Mussolini (Italy) • Adolf Hitler (Germany) ...
... • Following Hitler’s invasion of the Sudetenland, four world leaders met to discuss German aggression • Neville Chamberlain (Great Britain) • Edward Daladier (France) • Benito Mussolini (Italy) • Adolf Hitler (Germany) ...
10.8 Lecture – Steps Toward Another World War
... Czechoslovakia’s new borders. 2. Less than six months after the Munich meeting, Hitler took Czechoslovakia. 3. Soon after, Mussolini seized Albania. 4. Hitler demanded that Poland return the former German port of Danzig. a. The Poles refused and turned to Britain and France for aid. 1. Appeasement h ...
... Czechoslovakia’s new borders. 2. Less than six months after the Munich meeting, Hitler took Czechoslovakia. 3. Soon after, Mussolini seized Albania. 4. Hitler demanded that Poland return the former German port of Danzig. a. The Poles refused and turned to Britain and France for aid. 1. Appeasement h ...
Guided Notes – Holocaust and End of WWII
... Casualties were high, but _____________________________ was a huge victory for the Allies. ...
... Casualties were high, but _____________________________ was a huge victory for the Allies. ...
US Reaction
... War Production Board directed U.S. industry Office of Price Administration fixed priced & created ration books to save resources Office of War Information directed ...
... War Production Board directed U.S. industry Office of Price Administration fixed priced & created ration books to save resources Office of War Information directed ...
Chapter 31
... a. Austria divided, occupied then independent in 1956 b. Poland gain East Germany, but lose land to Russia c. USSR/USA sign separate treaties with Japan d. German peace treaty not even agreed upon until 1980s e. Korea divided between USSR and USA f. European colonies returned to Europeans a. But...i ...
... a. Austria divided, occupied then independent in 1956 b. Poland gain East Germany, but lose land to Russia c. USSR/USA sign separate treaties with Japan d. German peace treaty not even agreed upon until 1980s e. Korea divided between USSR and USA f. European colonies returned to Europeans a. But...i ...
Chapter 31 - Warren County Schools
... a. Austria divided, occupied then independent in 1956 b. Poland gain East Germany, but lose land to Russia c. USSR/USA sign separate treaties with Japan d. German peace treaty not even agreed upon until 1980s e. Korea divided between USSR and USA f. European colonies returned to Europeans a. But...i ...
... a. Austria divided, occupied then independent in 1956 b. Poland gain East Germany, but lose land to Russia c. USSR/USA sign separate treaties with Japan d. German peace treaty not even agreed upon until 1980s e. Korea divided between USSR and USA f. European colonies returned to Europeans a. But...i ...
chapter-35-america-in-wwii-35
... Landed at Normandy France Best kept secret of war Eisenhower was “Overlord” code name for invasion Germans believed attack (Overlord) would come at Calais to North Patton used as decoy 600 warships 4000 tanks 176000 men supported by 11000 planes 1 week allies had landed 326,000 men 50,000 vehicles 1 ...
... Landed at Normandy France Best kept secret of war Eisenhower was “Overlord” code name for invasion Germans believed attack (Overlord) would come at Calais to North Patton used as decoy 600 warships 4000 tanks 176000 men supported by 11000 planes 1 week allies had landed 326,000 men 50,000 vehicles 1 ...
Lesson 4 A War on Two Fronts - Pearson-Global
... 1943, Roosevelt and Churchill met in Casablanca, Morocco, to plan their next move. The conference resulted in two important decisions. First, the Allies decided to increase bombing of Germany and invade Italy. Second, Roosevelt announced that the Allies would accept only unconditional surrender, ...
... 1943, Roosevelt and Churchill met in Casablanca, Morocco, to plan their next move. The conference resulted in two important decisions. First, the Allies decided to increase bombing of Germany and invade Italy. Second, Roosevelt announced that the Allies would accept only unconditional surrender, ...
WWII European Front Notes Outline
... F. Yalta Conference (Feb. 1945) • 2nd mtg. of FDR, Churchill, Stalin • Soviets agree to join war v. Japan, in exchange… – Soviet sphere of influence in Manchuria; Sakhalin; and Kurile Islands • FDR and Churchill concede E. European nations bordering USSR should be “Soviet friendly,” in exchange… – S ...
... F. Yalta Conference (Feb. 1945) • 2nd mtg. of FDR, Churchill, Stalin • Soviets agree to join war v. Japan, in exchange… – Soviet sphere of influence in Manchuria; Sakhalin; and Kurile Islands • FDR and Churchill concede E. European nations bordering USSR should be “Soviet friendly,” in exchange… – S ...
The Allied Response World War II Section 2
... Why was the Battle of Stalingrad a turning point? Answer(s): The German army had seemed invincible, but after failing to take Stalingrad, it was now retreating to the west. ...
... Why was the Battle of Stalingrad a turning point? Answer(s): The German army had seemed invincible, but after failing to take Stalingrad, it was now retreating to the west. ...
Chapter 24 and 25 Notes
... • US Forces began their attack on Omaha beach at 6:30am, but before this time, things had gone awry… ...
... • US Forces began their attack on Omaha beach at 6:30am, but before this time, things had gone awry… ...
The Allied Response World War II Section 2
... Why was the Battle of Stalingrad a turning point? Answer(s): The German army had seemed invincible, but after failing to take Stalingrad, it was now retreating to the west. ...
... Why was the Battle of Stalingrad a turning point? Answer(s): The German army had seemed invincible, but after failing to take Stalingrad, it was now retreating to the west. ...
APUSH WWII notes
... 2. F.D.R. used the war as an excuse to pump lots of money into the stagnant South to revitalize it, helping to start the blossoming of the “Sunbelt.” i. Still, some 1.6 million blacks left the South for better places, and explosive tensions developed over black housing, employment, and segregation f ...
... 2. F.D.R. used the war as an excuse to pump lots of money into the stagnant South to revitalize it, helping to start the blossoming of the “Sunbelt.” i. Still, some 1.6 million blacks left the South for better places, and explosive tensions developed over black housing, employment, and segregation f ...
Chapter 38: America In World War II
... 2. F.D.R. used the war as an excuse to pump lots of money into the stagnant South to revitalize it, helping to start the blossoming of the “Sunbelt.” i. Still, some 1.6 million blacks left the South for better places, and explosive tensions developed over black housing, employment, and segregation f ...
... 2. F.D.R. used the war as an excuse to pump lots of money into the stagnant South to revitalize it, helping to start the blossoming of the “Sunbelt.” i. Still, some 1.6 million blacks left the South for better places, and explosive tensions developed over black housing, employment, and segregation f ...
File - Lindsay Social Studies
... The war in the Pacific essentially began on September 18, 1931, when Japan invaded Manchuria, which was known for its natural resources. The Japanese thought that from Manchuria, they could go on to control all of northern China. After Japan had established dominance in China, it could expand elsewh ...
... The war in the Pacific essentially began on September 18, 1931, when Japan invaded Manchuria, which was known for its natural resources. The Japanese thought that from Manchuria, they could go on to control all of northern China. After Japan had established dominance in China, it could expand elsewh ...
Culture - Warren County Schools
... would not continue to annex/take/invade lands March 1939 – Hitler annexed the rest of Map Czechoslovakia Britain and France warned him of war if he continued ...
... would not continue to annex/take/invade lands March 1939 – Hitler annexed the rest of Map Czechoslovakia Britain and France warned him of war if he continued ...
A Day That Will Live in Infamy
... • Examine the origins of American involvement in the war, with an emphasis on the events that precipitated the attack on Pearl Harbor. • Essential Question: Describe FDR’s approach to foreign policy. ...
... • Examine the origins of American involvement in the war, with an emphasis on the events that precipitated the attack on Pearl Harbor. • Essential Question: Describe FDR’s approach to foreign policy. ...
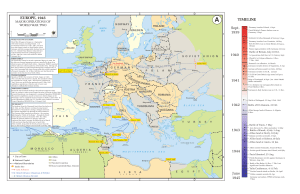
europe, 1945
... of three task forces which landed on 8 November 1942. Moving east, these forces linked up with General Montgomery’s Eighth Army in English Channel Apr. 1943, becoming 18th Army Group under the overall command Normandy Invasion, of General Alexander. By 12 May 1943 this unit had forced the D-Day, 6 J ...
... of three task forces which landed on 8 November 1942. Moving east, these forces linked up with General Montgomery’s Eighth Army in English Channel Apr. 1943, becoming 18th Army Group under the overall command Normandy Invasion, of General Alexander. By 12 May 1943 this unit had forced the D-Day, 6 J ...
Unit 8: World War II Erupts (1919
... 25 One of the reasons new democracies set up after WWI failed was because they were _____. 26 After Hitler was appointed Chancellor he established the __________________or Third German Empire that he believed would last for 1,000 years DOWN 2 The belief in the superiority of one's own nation over al ...
... 25 One of the reasons new democracies set up after WWI failed was because they were _____. 26 After Hitler was appointed Chancellor he established the __________________or Third German Empire that he believed would last for 1,000 years DOWN 2 The belief in the superiority of one's own nation over al ...
Chapter 7 Notes and Answers
... The Allies and Axis become a little more complicated as the war goes on but for now this is what you need to know: Allies France, Poland, Britain (The first Allies to join together against Hitler) The following countries joined in: Commonwealth (Australia, Canada, India, New Zealand, Nigeria and So ...
... The Allies and Axis become a little more complicated as the war goes on but for now this is what you need to know: Allies France, Poland, Britain (The first Allies to join together against Hitler) The following countries joined in: Commonwealth (Australia, Canada, India, New Zealand, Nigeria and So ...
Dictators and Warlords
... “right of all peoples to choose the form of government under which they will live.” The Atlantic Charter called for a “permanent system of general security,” such as an organization like the League of Nations. ...
... “right of all peoples to choose the form of government under which they will live.” The Atlantic Charter called for a “permanent system of general security,” such as an organization like the League of Nations. ...
The Allied War in Europe
... By midnight, many Germans had been pushed back and had begun retreating back into the countryside. ...
... By midnight, many Germans had been pushed back and had begun retreating back into the countryside. ...
Allies of World War II

The Allies of World War II, called the United Nations from the 1 January 1942 declaration, were the countries that opposed the Axis powers together during the Second World War (1939–1945). The Allies promoted the alliance as seeking to stop German, Japanese and Italian aggression.The anti-German coalition at the start of the war (1 September 1939) consisted of France, Poland and Great Britain, soon to be joined by the British Commonwealth (Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa). Poland was a minor factor after its defeat in 1939; France was a minor factor after its defeat in 1940. After first having cooperated with Germany in partitioning Poland whilst remaining neutral in the Allied-Axis conflict, the Soviet Union perforce joined the Allies in June 1941 after being invaded by Germany. The United States provided war material and money all along, and officially joined in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. As of 1942, the ""Big Three"" leaders of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States controlled Allied policy; relations between the UK and the U.S. were especially close. China had been already at war with Japan since 1937 but officially joined the Allies in 1941. The Big Three and China were referred as a ""trusteeship of the powerful"", then were recognized as the Allied ""Big Four"" in Declaration by United Nations and later the ""Four Policemen"" of ""United Nations"" for the Allies. Other key Allies included British India, the Netherlands, and Yugoslavia as well as Free France; there were numerous others. Together they called themselves the ""United Nations"" and in 1945 created the modern UN.