The War Begins
... 3. What is a Dictatorship? ___________________ ______________________________________ 4. What was the full name of Hitler’s political party, and what was the shorter name for it? ____________________ ________________________________________________________ 5. What are Concentration Camps? Where have ...
... 3. What is a Dictatorship? ___________________ ______________________________________ 4. What was the full name of Hitler’s political party, and what was the shorter name for it? ____________________ ________________________________________________________ 5. What are Concentration Camps? Where have ...
1943 – TEHRAN CONFERENCE: The `Big Three` met. Each leader
... at Westminster College used the term "iron curtain" in the context of Sovietdominated Eastern Europe. ...
... at Westminster College used the term "iron curtain" in the context of Sovietdominated Eastern Europe. ...
Warm Up # 60 -- Allied Response - British-Honors
... Afrika Corps. German general Erwin Rommel earned the nickname the Desert Fox for pushing British forces out of Libya. However, British troops weakened Axis power with their victory at the Battle of El Alamein (el-a-luh-MAYN) in Egypt. Meanwhile, Allied leaders planned for the American troops’ arriva ...
... Afrika Corps. German general Erwin Rommel earned the nickname the Desert Fox for pushing British forces out of Libya. However, British troops weakened Axis power with their victory at the Battle of El Alamein (el-a-luh-MAYN) in Egypt. Meanwhile, Allied leaders planned for the American troops’ arriva ...
World War II Exam—Honors A TEST NO.
... 1. Both Fascists and Nazis were anti-Communist. 2. Japan’s government ordered the military invasion of Manchuria in northern China to obtain needed resources for Japan. 3. Great Britain, France and Italy followed a policy of appeasement towards Hitler and Nazi Germany 4. In World War II, the U.S. su ...
... 1. Both Fascists and Nazis were anti-Communist. 2. Japan’s government ordered the military invasion of Manchuria in northern China to obtain needed resources for Japan. 3. Great Britain, France and Italy followed a policy of appeasement towards Hitler and Nazi Germany 4. In World War II, the U.S. su ...
Canada`s Role in Battles of WWII
... blasted their way through walls to get from building to building called “mouseholing” The battle continued over Christmas Day, 1943 but three days later the Germans withdrew. ...
... blasted their way through walls to get from building to building called “mouseholing” The battle continued over Christmas Day, 1943 but three days later the Germans withdrew. ...
Chapter16Assessment Events of World War II
... switched to the production of military goods. Many of these companies still exist. Working with a partner, use the Internet to research one such company. Find out what products the company made before and during the war, and how the company’s wartime role affected its reputation. Go to the Web Resea ...
... switched to the production of military goods. Many of these companies still exist. Working with a partner, use the Internet to research one such company. Find out what products the company made before and during the war, and how the company’s wartime role affected its reputation. Go to the Web Resea ...
Chapter 16- Pre-WWII Test Review
... arms if they paid cash and carried them away on their own ships Lend-Lease Act American law that allowed the U.S. to lend, lease, sell, or otherwise provide aid to other nations if doing so helped in the defense of the United States ...
... arms if they paid cash and carried them away on their own ships Lend-Lease Act American law that allowed the U.S. to lend, lease, sell, or otherwise provide aid to other nations if doing so helped in the defense of the United States ...
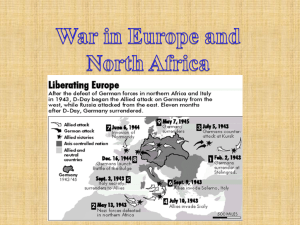
14_1 War in Europe and North Africa with Pair Share
... American Forces in North Africa and Italy Why was North Africa important? By controlling North Africa, the British could protect shipping on the Mediterranean Sea. They needed the ability to ship oil from the Middle East through the Suez Canal. What was the result of fighting in North Africa? Italy ...
... American Forces in North Africa and Italy Why was North Africa important? By controlling North Africa, the British could protect shipping on the Mediterranean Sea. They needed the ability to ship oil from the Middle East through the Suez Canal. What was the result of fighting in North Africa? Italy ...
Turning Point of Pacific War
... Desert Fox -Rommel’s forces eventually defeated at El Alamein After Operation Torch: -”Soft underbelly” campaign attack Germany through Italy -German troops make Italian campaign last many months—want to keep Allies away from Germany ...
... Desert Fox -Rommel’s forces eventually defeated at El Alamein After Operation Torch: -”Soft underbelly” campaign attack Germany through Italy -German troops make Italian campaign last many months—want to keep Allies away from Germany ...
AP- Ch. 31 WWII PP
... Soviet Foreign Minister Molotov signs the NaziSoviet Non-aggression Pact while German Foreign Minister Von Ribbentrop and Soviet leader Stalin look on under a portrait of Lenin ...
... Soviet Foreign Minister Molotov signs the NaziSoviet Non-aggression Pact while German Foreign Minister Von Ribbentrop and Soviet leader Stalin look on under a portrait of Lenin ...
Chapter 36: America in World War II
... U.S.-owned Pacific archipelago seized by Japan in the early months of World War II ...
... U.S.-owned Pacific archipelago seized by Japan in the early months of World War II ...
World War II - Lincoln Park High School
... German U-boats, which were submarines that traveled underwater that could sink ships that carried weapons and supplies to Great Britain. -The United States had Liberty Ships, which were cargo ships that would be used for transporting U.S. goods to Great Britain to support its war effort against the ...
... German U-boats, which were submarines that traveled underwater that could sink ships that carried weapons and supplies to Great Britain. -The United States had Liberty Ships, which were cargo ships that would be used for transporting U.S. goods to Great Britain to support its war effort against the ...
WWII L2 - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... Pearl Harbor on Dec. 7 (“a date that will live in infamy” - Roosevelt) because of the U.S. ban on scrap iron / oil shipments to Japan • U.S. declares war on Japan on Dec. 8 • U.S. forcibly houses Japanese Americans in internment camps until war is over • Battle of the Atlantic: with the Alliedsinkin ...
... Pearl Harbor on Dec. 7 (“a date that will live in infamy” - Roosevelt) because of the U.S. ban on scrap iron / oil shipments to Japan • U.S. declares war on Japan on Dec. 8 • U.S. forcibly houses Japanese Americans in internment camps until war is over • Battle of the Atlantic: with the Alliedsinkin ...
WARRING NATIONS - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... Pearl Harbor on Dec. 7 (“a date that will live in infamy” - Roosevelt) because of the U.S. ban on scrap iron / oil shipments to Japan • U.S. declares war on Japan on Dec. 8 • U.S. forcibly houses Japanese Americans in internment camps until war is over • Battle of the Atlantic: with the Alliedsinkin ...
... Pearl Harbor on Dec. 7 (“a date that will live in infamy” - Roosevelt) because of the U.S. ban on scrap iron / oil shipments to Japan • U.S. declares war on Japan on Dec. 8 • U.S. forcibly houses Japanese Americans in internment camps until war is over • Battle of the Atlantic: with the Alliedsinkin ...
World War II
... closer and closer to Japan and using them as bases for air attacks on Japan, and cutting off Japanese supplies through submarine warfare against Japanese shipping. ...
... closer and closer to Japan and using them as bases for air attacks on Japan, and cutting off Japanese supplies through submarine warfare against Japanese shipping. ...
SS8H9v2
... • Britain is alone • Britain RAF Royal Air Force protects Britain • U.S. sends them equipment ...
... • Britain is alone • Britain RAF Royal Air Force protects Britain • U.S. sends them equipment ...
16.4 The Allied Victory
... 2/3 were Nisei, native-born American citizens Many volunteered for military service ...
... 2/3 were Nisei, native-born American citizens Many volunteered for military service ...
The Failure of Appeasement
... • Germany used its new Blitzkrieg, or “lighting war” tactic and invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. • France and Britain declared War, but took no direct action. The “Phony War” began. • In August 1939 the Soviet Union signed a non-aggression pact with Germany (pledging not to attack each other in ...
... • Germany used its new Blitzkrieg, or “lighting war” tactic and invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. • France and Britain declared War, but took no direct action. The “Phony War” began. • In August 1939 the Soviet Union signed a non-aggression pact with Germany (pledging not to attack each other in ...
Allies of World War II

The Allies of World War II, called the United Nations from the 1 January 1942 declaration, were the countries that opposed the Axis powers together during the Second World War (1939–1945). The Allies promoted the alliance as seeking to stop German, Japanese and Italian aggression.The anti-German coalition at the start of the war (1 September 1939) consisted of France, Poland and Great Britain, soon to be joined by the British Commonwealth (Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa). Poland was a minor factor after its defeat in 1939; France was a minor factor after its defeat in 1940. After first having cooperated with Germany in partitioning Poland whilst remaining neutral in the Allied-Axis conflict, the Soviet Union perforce joined the Allies in June 1941 after being invaded by Germany. The United States provided war material and money all along, and officially joined in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. As of 1942, the ""Big Three"" leaders of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States controlled Allied policy; relations between the UK and the U.S. were especially close. China had been already at war with Japan since 1937 but officially joined the Allies in 1941. The Big Three and China were referred as a ""trusteeship of the powerful"", then were recognized as the Allied ""Big Four"" in Declaration by United Nations and later the ""Four Policemen"" of ""United Nations"" for the Allies. Other key Allies included British India, the Netherlands, and Yugoslavia as well as Free France; there were numerous others. Together they called themselves the ""United Nations"" and in 1945 created the modern UN.