The Allied Offensive in Europe
... Destroying these targets would cripple Germany’s military operations. The Allied Power achieved their goal of gaining air supremacy by the time the cross-Channel invasion was ready. This was crucial to victory. On D-Day, June 6, 1944, the operation started at 2 a.m. with the landing of parachute tr ...
... Destroying these targets would cripple Germany’s military operations. The Allied Power achieved their goal of gaining air supremacy by the time the cross-Channel invasion was ready. This was crucial to victory. On D-Day, June 6, 1944, the operation started at 2 a.m. with the landing of parachute tr ...
4 Focus Question: Should the U.S. have entered World War II before
... considered the cost of World War I too great and wanted the country to focus on recovering from the Great Depression and implementing President Roosevelt’s New Deal programs. Isolationists did not want to fight another long and costly war. As a result, Congress passed the Neutrality Act of 1935 whic ...
... considered the cost of World War I too great and wanted the country to focus on recovering from the Great Depression and implementing President Roosevelt’s New Deal programs. Isolationists did not want to fight another long and costly war. As a result, Congress passed the Neutrality Act of 1935 whic ...
WWII Part 3
... 3. Allied forces sailed from Italy, invaded Southern France 4. August 1944 – Allies entered Paris – Sept. – France liberated ...
... 3. Allied forces sailed from Italy, invaded Southern France 4. August 1944 – Allies entered Paris – Sept. – France liberated ...
File - Ms. halty`s class
... • Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin met in February, 1945 in Yalta, Ukraine • Discuss plans of dividing up Europe anticipating the defeat of Germany • Germany was divided and most of Eastern Europe was controlled by the Soviet Union ...
... • Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin met in February, 1945 in Yalta, Ukraine • Discuss plans of dividing up Europe anticipating the defeat of Germany • Germany was divided and most of Eastern Europe was controlled by the Soviet Union ...
World War II
... • SSWH18 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the global political, economic, and social impact of World War II. • a. Describe the major conflicts and outcomes; include Pearl Harbor, El-Alamein, Stalingrad, D-Day, Guadalcanal, the Philippines, and the end of the war in Europe and Asia. • ...
... • SSWH18 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the global political, economic, and social impact of World War II. • a. Describe the major conflicts and outcomes; include Pearl Harbor, El-Alamein, Stalingrad, D-Day, Guadalcanal, the Philippines, and the end of the war in Europe and Asia. • ...
AP U - Webs
... c) enact a new neutrality law enabling the Allies to buy American war materials on a cash-and-carry basis d) call for the quarantining of aggressor nations e) pass a conscription law 27. America’s neutrality effectively ended when a) Japan attacked Pearl Harbor b) Germany attacked Poland c) the cons ...
... c) enact a new neutrality law enabling the Allies to buy American war materials on a cash-and-carry basis d) call for the quarantining of aggressor nations e) pass a conscription law 27. America’s neutrality effectively ended when a) Japan attacked Pearl Harbor b) Germany attacked Poland c) the cons ...
Unit 3 Notes
... A. German forces invaded Poland - Blitzkrieg – “lightning war” B. Allied Powers – Britain & France – declared war on Germany - Poland fell in less than a month C. German forces occupied Denmark in 4/1940 - then invaded Normandy, France D. May 1940, Germans seized Belgium, Luxembourg, & Netherlands E ...
... A. German forces invaded Poland - Blitzkrieg – “lightning war” B. Allied Powers – Britain & France – declared war on Germany - Poland fell in less than a month C. German forces occupied Denmark in 4/1940 - then invaded Normandy, France D. May 1940, Germans seized Belgium, Luxembourg, & Netherlands E ...
World War II Review Sheet
... 1. How did each of the following help lead to World War II? Treaty of Versailles ...
... 1. How did each of the following help lead to World War II? Treaty of Versailles ...
Chapter 26 Notes
... The American people, in the eyes of the Japanese leaders, were _________ ‐‐once divided over participating in the war, America people now took up arms The U.S. joined _______________ nations and Nationalist China in a combined effort to defeat Japan ‐‐believing that the U.S. involvement in the ____ ...
... The American people, in the eyes of the Japanese leaders, were _________ ‐‐once divided over participating in the war, America people now took up arms The U.S. joined _______________ nations and Nationalist China in a combined effort to defeat Japan ‐‐believing that the U.S. involvement in the ____ ...
WWII notes - Montgomery County Schools
... -They did not complain -some even volunteered to serve in the U.S. military -Korematsu v. the United States – the process was constitutional; based not on race but “military urgency” - 1945 the camps finally closed -1988- President Reagan signed an act repaying all of the Japanese-Americans interne ...
... -They did not complain -some even volunteered to serve in the U.S. military -Korematsu v. the United States – the process was constitutional; based not on race but “military urgency” - 1945 the camps finally closed -1988- President Reagan signed an act repaying all of the Japanese-Americans interne ...
How did the Great Depression help cause WWII?
... December 8th, 1941 - America declared war on Japan In which Germany and Italy then declared war on the ...
... December 8th, 1941 - America declared war on Japan In which Germany and Italy then declared war on the ...
File
... By winter, the German advance had been stopped, and German troops were trapped in Russia with insufficient winter gear ...
... By winter, the German advance had been stopped, and German troops were trapped in Russia with insufficient winter gear ...
World War II - SJS AP World History
... Hot War to Cold War Problems still after Potsdam Conference, July 1945 Austria divided, occupied then independent in 1956 Poland gain East Germany, but lost land to Russia USSR/USA sign separate treaties with Japan German peace treaty not even agreed upon ‘til 80s Clement Attlee, Harry Ko ...
... Hot War to Cold War Problems still after Potsdam Conference, July 1945 Austria divided, occupied then independent in 1956 Poland gain East Germany, but lost land to Russia USSR/USA sign separate treaties with Japan German peace treaty not even agreed upon ‘til 80s Clement Attlee, Harry Ko ...
AP U.S. History Name________________________ Due
... ___________ 7. U.S.-owned Pacific archipelago seized by Japan in the early months of World War II _________ 8. Crucial naval battle of June 1942, in which U.S. Admiral Chester Nimitz blocked the Japanese attempt to conquer a strategic island near Hawaii __________ 9. Controversial U.S.-British deman ...
... ___________ 7. U.S.-owned Pacific archipelago seized by Japan in the early months of World War II _________ 8. Crucial naval battle of June 1942, in which U.S. Admiral Chester Nimitz blocked the Japanese attempt to conquer a strategic island near Hawaii __________ 9. Controversial U.S.-British deman ...
American Reactions to the Outbreak of WW2
... sell weapons to the Allies on a “cash and carry” basis Allied nations could buy U.S.-made war goods but had to pay in cash and had to transport goods on their own ships The cash-and-carry policy allowed the USA to aid the Allies while remaining neutral and avoid the causes of American entry into the ...
... sell weapons to the Allies on a “cash and carry” basis Allied nations could buy U.S.-made war goods but had to pay in cash and had to transport goods on their own ships The cash-and-carry policy allowed the USA to aid the Allies while remaining neutral and avoid the causes of American entry into the ...
World War II (1939-1945)
... FDR: “A date which will live in infamy” December 8, 1941- FDR receives war declaration from Congress against Japan Germany, Italy declare war on United States ...
... FDR: “A date which will live in infamy” December 8, 1941- FDR receives war declaration from Congress against Japan Germany, Italy declare war on United States ...
WORLD WAR II SUMMARY OF KEY INFORMATION
... from 2.5 million to less than 700,000. People were earning a paycheck. 2. There were large population shifts—people moved to find work in factories. 3. Major Organizations in the War economy: A. The War Production Board and Office of War Mobilization supervised the conversion of factories to war-tim ...
... from 2.5 million to less than 700,000. People were earning a paycheck. 2. There were large population shifts—people moved to find work in factories. 3. Major Organizations in the War economy: A. The War Production Board and Office of War Mobilization supervised the conversion of factories to war-tim ...
File
... counteroffensive to encircle the enemy. At this point the Germans probably could have fought their way out, but Hitler would not allow them to: they were ordered to hold their ground at all costs.. As winter set in a rescue mission was mounted, but it was halted short of its goal, and the freezing a ...
... counteroffensive to encircle the enemy. At this point the Germans probably could have fought their way out, but Hitler would not allow them to: they were ordered to hold their ground at all costs.. As winter set in a rescue mission was mounted, but it was halted short of its goal, and the freezing a ...
Document
... • Congress passes series of Neutrality Acts to keep United States out Where do you think FDR stands on becoming involved in the war? ...
... • Congress passes series of Neutrality Acts to keep United States out Where do you think FDR stands on becoming involved in the war? ...
WWII MILITARY LEADERS
... Created a United Nations to promote world peace. Germany and Berlin would be divided into 4 zones controlled by the US, British, France and Soviet Union Eastern European countries under Soviet control would have “free elections” Stalin agreed but kept Eastern Europe under Soviet control after WW ...
... Created a United Nations to promote world peace. Germany and Berlin would be divided into 4 zones controlled by the US, British, France and Soviet Union Eastern European countries under Soviet control would have “free elections” Stalin agreed but kept Eastern Europe under Soviet control after WW ...
World War II Section 2
... Traded blows for two years 1942—Battle of El Alamein British victory under Gen. Bernard Montgomery • Axis power lessened in North Africa ...
... Traded blows for two years 1942—Battle of El Alamein British victory under Gen. Bernard Montgomery • Axis power lessened in North Africa ...
Timeline
... include the day, month and year of the event if it appears in the textbook, or is one that is critical to the war, such as the bombing of Pearl Harbor and D-Day. Also, keep the spacing on your timeline consistent with the events. Finally, indicate in some way that the Holocaust is happening througho ...
... include the day, month and year of the event if it appears in the textbook, or is one that is critical to the war, such as the bombing of Pearl Harbor and D-Day. Also, keep the spacing on your timeline consistent with the events. Finally, indicate in some way that the Holocaust is happening througho ...
Allies of World War II

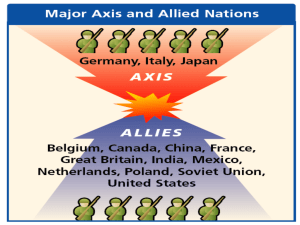
The Allies of World War II, called the United Nations from the 1 January 1942 declaration, were the countries that opposed the Axis powers together during the Second World War (1939–1945). The Allies promoted the alliance as seeking to stop German, Japanese and Italian aggression.The anti-German coalition at the start of the war (1 September 1939) consisted of France, Poland and Great Britain, soon to be joined by the British Commonwealth (Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa). Poland was a minor factor after its defeat in 1939; France was a minor factor after its defeat in 1940. After first having cooperated with Germany in partitioning Poland whilst remaining neutral in the Allied-Axis conflict, the Soviet Union perforce joined the Allies in June 1941 after being invaded by Germany. The United States provided war material and money all along, and officially joined in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. As of 1942, the ""Big Three"" leaders of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States controlled Allied policy; relations between the UK and the U.S. were especially close. China had been already at war with Japan since 1937 but officially joined the Allies in 1941. The Big Three and China were referred as a ""trusteeship of the powerful"", then were recognized as the Allied ""Big Four"" in Declaration by United Nations and later the ""Four Policemen"" of ""United Nations"" for the Allies. Other key Allies included British India, the Netherlands, and Yugoslavia as well as Free France; there were numerous others. Together they called themselves the ""United Nations"" and in 1945 created the modern UN.